
The bull shark, also known as the Zambezi shark in Africa and Lake Nicaragua shark in Nicaragua, is a species of requiem shark commonly found worldwide in warm, shallow waters along coasts and in rivers. It is known for its aggressive nature, and presence mainly in warm, shallow brackish and freshwater systems including estuaries and (usually) lower reaches of rivers. This aggressive nature is a reason for its population being listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Shark-culling occurs near beaches to protect beach goers, which is one of the causes of bull shark populations continuing to decrease.

The members of the family Percichthyidae are known as the temperate perches. They belong to the order Perciformes, the perch-like fishes.

The yellowspotted sawtail, or spotted sawtail, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This fish is found in the southwest Pacific Ocean.

Kuhl's maskray, also known as the blue-spotted stingray, blue-spotted maskray, or Kuhl's stingray, is a species of stingray of the family Dasyatidae. It was recently changed from Dasyatis kuhlii in 2008 after morphological and molecular analyses showed that it is part of a distinct genus, Neotrygon. The body is rhomboidal and colored green with blue spots. Maximum disk width is estimated 46.5 cm (18.3 in). It is popular in aquaria, but usually not distinguished from the blue-spotted ribbontail ray. The ribbontail has a rounded body, is a brighter green with brighter blue and more vivid spots, but Kuhl's maskray is larger. The stingray's lifespan is estimated at 13 years for females and 10 years for males. The blue-spotted stingray preys on many fish and small mollusks. It is also generally found from Indonesia to Japan, and most of Australia. Kuhl's maskray also is targeted by many parasites, such as tapeworms, flatworms, and flukes.

The western trumpeter whiting, Sillago burrus, is a species of marine fish of the smelt whiting family Sillaginidae that is commonly found along the northern coast of Australia and in southern Indonesia and New Guinea. As its name suggests, it is closely related to and resembles the trumpeter whiting which inhabits the east coast of Australia and is distinguishable by swim bladder morphology alone. The species inhabits a variety of sandy, silty and muddy substrates in depths from 0 to 15 m deep, with older fish inhabiting deeper waters. Western trumpeter whiting are benthic carnivores which take predominantly crustaceans and polychaetes as prey. The species reaches sexual maturity at the end of its first year of age, spawning in batches between December and February. The species is taken as bycatch with other species of whiting and shrimps in Australia.

The sand whiting, also known as the summer whiting, yellowfin whiting or blue-nose whiting, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the family Sillaginidae, the smelt-whitings. It is a slender, slightly compressed fish that is very similar to other species of Sillago, with detailed spine, ray and lateral line scale counts needed to distinguish the species between its nearest relative Sillago analis. The sand whiting is distributed along the east coast of Australia from Cape York south to Tasmania, as well as Lord Howe Island and New Caledonia in the Pacific Ocean.

The yellowtail trumpeter is a common species of coastal marine fish of the grunter family, Terapontidae. The yellowtail trumpeter is native to Australia and Papua New Guinea, ranging from Cape Leeuwin in Western Australia along the north coast to Bowen, Queensland, and along the southern coast of Papua New Guinea.

The Black bream, also commonly known as the southern black bream, southern bream and blue-nosed bream, is a species of anadromous ray-finned fish of the porgy family Sparidae. A deep-bodied fish, it is occasionally confused with other similar species that occur within its range, but is generally distinguished from these species by a lack of yellow ventral and anal fins. Southern black bream are endemic to the southern coasts of Australia from Shark Bay in Western Australia to Ulladulla, New South Wales, as well as Tasmania.

Acanthopagrus australis, the yellowfin bream, also known as sea bream, surf bream, silver bream or eastern black bream, is a species of marine and freshwater fish of the porgy family, Sparidae. It is a deep-bodied fish, occasionally confused with Acanthopagrus butcheri, but is generally distinguished by its yellowish ventral and anal fins. It is a popular target for recreational fishermen due to its capacity to fight well above its weight coupled with its table quality.
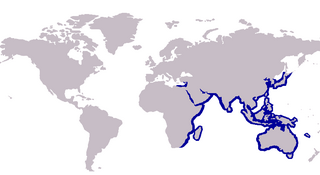
Smelt-whiting is the common name for various species of the family Sillaginidae. The Sillaginidae are distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific region, ranging from the west coast of Africa to Japan and Taiwan in the east, as well occupying as a number of small islands including New Caledonia in the Pacific Ocean. Well known members of this family include King George whiting, Japanese whiting, northern whiting, sand whiting and school whiting.

The squarenose unicornfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This species is found in the Indo-Pacific region.

Prionurus microlepidotus, the sixplate sawtail, Australian sawtail or sawtail surgeonfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This fish is found in the southwest Pacific Ocean.

The fringefin trevally, also called fringe-finned trevally, round-finned trevally or reef herring, is a species of inshore marine fish classified in the jack and horse mackerel family Carangidae. A relatively small fish, the fringefin trevally is known to reach 40 cm (16 in), but is mostly encountered at lengths less than 25 cm (9.8 in). The fringefin trevally has an ovate body, with distinctive orange-yellow fins and a black opercular spot. The dental patterns of the species distinguish it from the closely related scads of the genus Alepes. Males have characteristic elongated dorsal and anal fins which produce a series of trailing filaments. The fringefin trevally is restricted to the waters of the Indo-Pacific, ranging from northern Australia to Papua New Guinea and eastern Indonesia. An inshore species, it is found in coastal and estuarine environments and exhibits daily and seasonal movements. The fringefin trevally is predatory, taking crustaceans as prey. The species is often taken as bycatch in prawn trawls and occasionally taken by anglers.

Parapercis is a genus of sandperches belonging to the fish family Pinguipedidae.
Leptachirus is a genus of small soles native to brackish and fresh water in New Guinea and northern Australia.

Pardachirus is a genus of soles mainly native to coastal water in the Indo-Pacific. A single species, P. poropterus is restricted to estuaries and lower sections of freshwater streams. At least some species in the genus are toxic.
The rare velvetfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a velvetfish belonging to the family Aploactinidae. It is known only from the coasts of Queensland and New South Wales in Australia. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Matsubarichthys.
Gnatholepis is a genus of fish in the family Gobiidae, the gobies. It is the only marine genus in the subfamily Gobionellinae, which otherwise includes mostly estuary-dwelling and freshwater fish. Gnatholepis are tropical fish associated with sandy habitat around corals.

The congoli, also known as the freshwater flathead, marble fish, marbled flathead, sand trout, sanding, sandy, sandy whiting or tupong. is a species of marine ray-finned fish and it is the only species of fish in the monotypic family Pseudaphritidae and the genus Pseudaphritis. It was initially classified as a member of the family Bovichtidae.
The pinkeye mullet, also known simply as pinkeye, or freshwater mullet, Richmond mullet, or river mullet, is a species of ray-finned fish from the grey mullet family Mugilidae and the only species in the genus Trachystoma. It is endemic to northeastern Australia where it occurs from the Burnett River in Queensland to the Clyde River in New South Wales. It is a subtropical species which is found in deep, slow flowing sections of rivers as well as in estuaries although it moves into coastal seas to spawn. It feeds mainly on algae and plant material, as well as detritus and benthic invertebrates.















