
A leucine zipper is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. They were first described by Landschulz and collaborators in 1988 when they found that an enhancer binding protein had a very characteristic 30-amino acid segment and the display of these amino acid sequences on an idealized alpha helix revealed a periodic repetition of leucine residues at every seventh position over a distance covering eight helical turns. The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues were proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains from one alpha helix interdigitate with those from the alpha helix of a second polypeptide, facilitating dimerization.

Jun dimerization protein 2 (JUNDM2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JDP2 gene. The Jun dimerization protein is a member of the AP-1 family of transcription factors.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF1 gene.

Activating transcription factor 4 , also known as ATF4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF4 gene.

Hepatic leukemia factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLF gene.
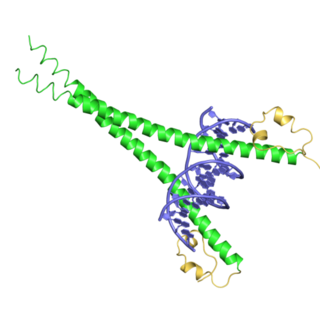
Transcription factor MafG is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFG gene.

Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREB3 gene.

D site of albumin promoter binding protein, also known as DBP, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DBP gene.

DNA-binding protein A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSDA gene.

TSC22 domain family protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSC22D1 gene.

CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein gamma (C/EBPγ) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPG gene. This gene has no introns.

Developmentally-regulated GTP-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRG1 gene.

Transcription factor MafK is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFK gene.

Basic leucine zipper transcription factor, ATF-like, also known as BATF, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BATF gene.

Transcription factor MafF is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFF gene.

Mitochondrial transcription termination factor 1, also known as MTERF1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MTERF gene.

Transcription factor EC is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFEC gene.

Spermatogenic leucine zipper protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPZ1 gene.

The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required to hold together (dimerize) two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic amino acids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containing this domain are transcription factors.
Small Maf proteins are basic region leucine zipper-type transcription factors that can bind to DNA and regulate gene regulation. There are three small Maf (sMaf) proteins, namely MafF, MafG, and MafK, in vertebrates. HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC)-approved gene names of MAFF, MAFG and MAFK are “v-maf avian musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog F, G, and K”, respectively.


















