
The necropolis of Draʻ Abu el-Naga' is located on the West Bank of the Nile at Thebes, Egypt, just by the entrance of the dry bay that leads up to Deir el-Bahari and north of the necropolis of el-Assasif. The necropolis is located near the Valley of the Kings.

Tomb ANB is a sepulchre located in the west of the necropolis of Dra' Abu el-Naga', near Thebes, Egypt. It may well have been intended as the burial place of the 18th Dynasty Pharaoh Amenhotep I and his mother Ahmose-Nefertari.

Sekhemre-Wepmaat Intef-Aa was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 17th Dynasty of Egypt, who lived late during the Second Intermediate Period, when Egypt was divided into two by Hyksos controlled Lower Egypt and Theban ruled Upper Egypt.

The Theban Tomb TT16 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Panehsy, who was Prophet of Amenhotep (I) of the Forecourt, during the reign of Ramesses II.
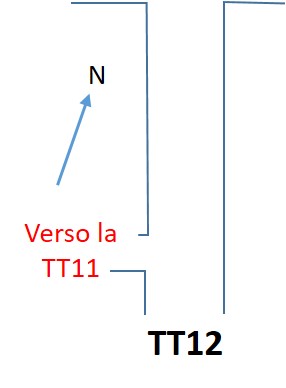
The Theban tomb TT12 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Hery, who was Overseer of the Granary of the King's Mother Ahhotep, during the reigns of Seqenenre Tao II to Amenhotep I.
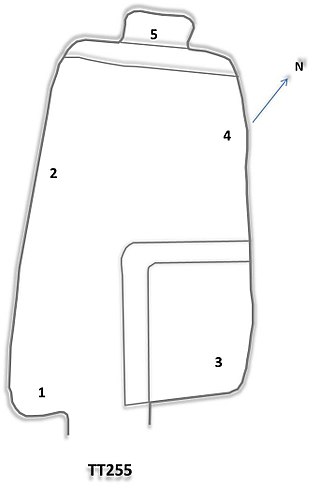
The Theban Tomb TT255 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga'. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The sepulchre is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Roy, who lived at the end of the 18th Dynasty, during the reign of Horemheb.
Ahmose called Turo was Viceroy of Kush under Amenhotep I and Thutmose I.
Anhotep was Viceroy of Kush, Governor of the South Lands, Scribe of the Tables of the Two Lands during the reign of Ramesses II. His wife was named Hunuro. Anhotep's tomb is TT300 in Dra' Abu el-Naga.
Maya or May was a High Priest of Amun of ancient Egypt, until at least year 4 of Akhenaten.

The Theban Tomb TT35 is located in Dra Abu el-Naga, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian noble named Bakenkhons I, who lived during the 19th Dynasty, during the reign of Ramesses II. Bakenkhons was a High Priest of Amun.

The Theban Tomb TT156 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Pennesuttawy, who was a troop commander and superintendent of the Southern Desert Lands during the reign of Ramesses II in the Nineteenth Dynasty.
The Theban Tomb TT169 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Senna, who was the head of the goldworkers of Amun during the reign of Amenhotep II in the Eighteenth Dynasty.
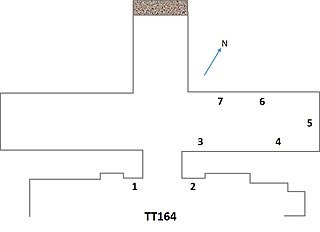
The Theban Tomb TT164 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.

Sekhemre Sementawy Djehuti was possibly the second king of the Theban 16th Dynasty reigning over parts of Upper Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period. Alternatively, he may be a king of the late 13th Dynasty or the fourth king of the 17th Dynasty. Djehuty is credited with a reign of 3 years in the first entry of the 11th column of the Turin canon. According to Egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker, he was succeeded by Sobekhotep VIII.
Nakhtmin was a Troop Commander of Kush and Royal Envoy to Every Foreign Land during the reign of Ramesses II.

Tomb A.6 is the modern number given to a now lost Theban tomb in Dra' Abu el-Naga'. The burial dates to the ancient Egyptian 18th Dynasty and belonged to the overseer of the marshland dwellers Dhjehutinefer, who is also called Seshu. The place was visited by the expedition of Karl Richard Lepsius, who copied the tomb owner's title overseer of the marshland dwellers of the lord of the two lands, but not the name. It seems that the tomb was then already heavily destroyed. Before 1906 the French Egyptologist Henri Gauthier visited A.6 and described the few remains of the decoration and published a short note. Gauthier recorded some further titles of Dhjehutinefer, such as scribe and counter of cattle and fowl of the temple of Amun. A fragment belonging to the tomb is a wall painting that is today in the Metropolitan Museum in New York. On the fragment in New York also mentioned the wife of Djehutinefer, a woman called Benbu. Several funerary cones belonging to the tomb are known. They provide the name of Djehutynefer's father who was the scribe Mesu.

Tomb A.5 is the modern number given to a now lost Theban tomb in Dra' Abu el-Naga'. The burial dates to the Ancient Egyptian 18th Dynasty and belonged to the overseer of the granary of the Lord of the Two Lands, Neferhotep. The tomb was visited by the French traveller Frédéric Cailliaud, who copied and published several scenes. Evidently, he saw the tomb in a fairly good condition and was described by others as superb. The location of the tomb got lost within the Nineteenth century. According to the old drawings published., there are several scenes depicted in the tomb. These include both hunting in the marshes and hunting in the desert, a banquet, and scenes showing vintage and agriculture.
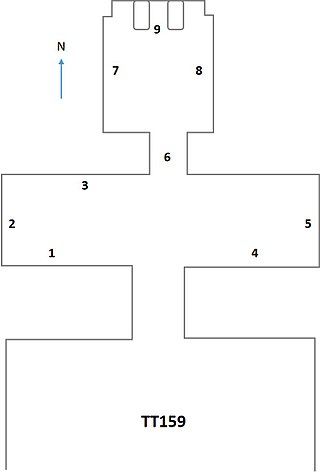
The Theban Tomb TT159 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.
The Theban Tomb TT286 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.














