Related Research Articles

Thebes, known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile about 800 kilometers (500 mi) south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Thebes was the main city of the fourth Upper Egyptian nome and was the capital of Egypt for long periods during the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom eras. It was close to Nubia and the Eastern Desert, with its valuable mineral resources and trade routes. It was a cult center and the most venerated city during many periods of ancient Egyptian history. The site of Thebes includes areas on both the eastern bank of the Nile, where the temples of Karnak and Luxor stand and where the city was situated; and the western bank, where a necropolis of large private and royal cemeteries and funerary complexes can be found. In 1979, the ruins of ancient Thebes were classified by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
The First Intermediate Period, described as a 'dark period' in ancient Egyptian history, spanned approximately 125 years, c. 2181–2055 BC, after the end of the Old Kingdom. It comprises the Seventh, Eighth, Ninth, Tenth, and part of the Eleventh Dynasties. The concept of a "First Intermediate Period" was coined in 1926 by Egyptologists Georg Steindorff and Henri Frankfort.

The Valley of the Queens is a site in Egypt, where the wives of pharaohs were buried in ancient times. It was known then as Ta-Set-Neferu, meaning "the place of beauty". It was most famous for being the burial site of many wives of Pharaohs. Pharaohs themselves were buried in the Valley of the Kings.

Sehertawy Intef I was a local nomarch at Thebes during the early First Intermediate Period and the first member of the 11th Dynasty to lay claim to a Horus name. Intef reigned from 4 to 16 years c. 2120 BC or c. 2070 BC during which time he probably waged war with his northern neighbor, the Coptite nomarch Tjauti. Intef was buried in a saff tomb at El-Tarif, known today as Saff el-Dawaba.
Peter FitzGerald Dorman is an epigrapher, philologist, and Egyptologist. Recently a professor of history and archaeology at the American University of Beirut (AUB), he served as the 15th President of the university from 2008 to 2015. He spent most of his career as a professor and chair in the department of Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations (NELC) of the University of Chicago, and was director of Chicago House in Luxor, the Epigraphic Survey field project of the Oriental Institute. He is presently a professor emeritus of the University of Chicago.

Dendera Temple complex is located about 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) south-east of Dendera, Egypt. It is one of the best-preserved temple complexes of ancient Egypt. The area was used as the sixth nome of Upper Egypt, south of Abydos.

Tuna el-Gebel was the necropolis of Khmun. It is the largest known Greco-Roman necropolis in Egypt, dating from the New Kingdom to the Roman Period, and seeing heavy use in the Ptolemaic Period. Tuna el-Gebel is located in Al Minya Governorate in Middle Egypt.

Tomb KV9 in Egypt's Valley of the Kings was originally constructed by Pharaoh Ramesses V. He was interred here, but his uncle, Ramesses VI, later reused the tomb as his own. The layout is typical of the 20th Dynasty – the Ramesside period – and is much simpler than that of Ramesses III's tomb (KV11). The workmen accidentally broke into KV12 as they dug one of the corridors. In 2020, the Egyptian Tourism Authority released a full 3D model of the tomb with detailed photography, available online.
In ancient Egypt, a rope stretcher was a surveyor who measured real property demarcations and foundations using knotted cords, stretched so the rope did not sag. The practice is depicted in tomb paintings of the Theban Necropolis. Rope stretchers used 3-4-5 triangles and the plummet, which are still in use by modern surveyors.

The Valley of the Kings, also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings, is a valley in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the 16th to 11th century BC, rock-cut tombs were excavated for the pharaohs and powerful nobles of the New Kingdom.

Minya is the capital of the Minya Governorate in Upper Egypt. It is located approximately 245 km (152 mi) south of Cairo on the western bank of the Nile River, which flows north through the city.
The Theban Tomb TT36 is located in El-Assasif, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Ibi, who was "Chief Steward of the Adorer of the God", during the reign of Psamtik I during the 26th dynasty.

Nebiriau II was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the Theban-based 16th Dynasty, during the Second Intermediate Period.
Sewadjenre Nebiryraw was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the Theban-based 16th Dynasty, during the Second Intermediate Period.

A necropolis is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek νεκρόπολις nekropolis, literally meaning "city of the dead".
Amenemipet called Pairy was a Vizier of ancient Egypt. He served during the reign of Amenhotep II and Tuthmosis IV.
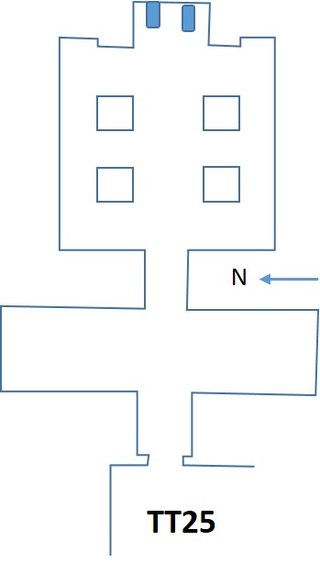
The Theban Tomb TT25 is located in El-Assasif. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The tomb is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official, Amenemhab.
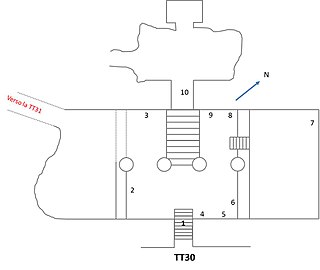
The Theban Tomb TT30 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official, Khonsumose.

QV80 is the tomb of (Mut-)Tuya, the Great Royal Wife of Seti I, and the mother of Ramses II, in Egypt's Valley of the Queens.
The Theban Tomb TT414 is located in El-Assasif, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb was originally constructed in the El-Assasif necropolis for the use of Ankh-hor and his family. Ankhor was the Chief Steward to the God's Wife Nitocris during the 26th Dynasty. Ankh-hor is dated to the reigns of Pharaohs Psamtik II and Apries. The tomb was later usurped during the 30th Dynasty and the Ptolemaic Period.
References
- ↑ Maria Cannata, Three Hundred Years of Death: The Egyptian Funerary Industry in the Ptolemaic Period, 2020, p. 346 [ ISBN missing ]
- ↑ Catharine H. Roehrig, Renée Dreyfus, Cathleen A. Keller, Hatshepsut, from Queen to Pharaoh, Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2005, p. 289 [ ISBN missing ]