Related Research Articles
Hawaiian is a Polynesian language and critically endangered language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaiʻi, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the US state of Hawaii. King Kamehameha III established the first Hawaiian-language constitution in 1839 and 1840.

Italian is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent Romance language from Latin, together with Sardinian. Spoken by about 85 million people including 67 million native speakers (2024), Italian is an official language in Italy, San Marino, and Switzerland, and is the primary language of Vatican City. It has official minority status in Croatia and in some areas of Slovenian Istria.

The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form. The IPA is used by lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguists, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators.
Hanyu Pinyin, or simply pinyin, is the most common romanization system for Standard Chinese. In official documents, it is referred to as the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet. It is the official system used in China, Singapore, Taiwan, and by the United Nations. Its use has become common when transliterating Standard Chinese mostly regardless of region, though it is less ubiquitous in Taiwan. It is used to teach Standard Chinese, normally written with Chinese characters, to students already familiar with the Latin alphabet. The system makes use of diacritics to indicate the four tones found in Standard Chinese, though these are often omitted in various contexts, such as when spelling Chinese names in non-Chinese texts, or when writing non-Chinese words in Chinese-language texts. Pinyin is also used by various input methods on computers and to categorize entries in some Chinese dictionaries. Hànyǔ literally means 'Han language'—meaning, the Chinese language—while pinyin literally means 'spelled sounds'.

The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic branch of the Indo-European language family.
Slovak is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e., data incorporating relations among entities and variables.

Malayalam is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was designated a "Classical Language of India" in 2013. Malayalam has official language status in Kerala, Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé), and is also the primary spoken language of Lakshadweep and is spoken by 35 million people in India. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with a significant number of speakers in the Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka, and Kanyakumari, Coimbatore and Nilgiris district of Tamil Nadu. It is also spoken by the Malayali Diaspora worldwide, especially in the Persian Gulf countries, due to the large populations of Malayali expatriates there. They are a significant population in each city in India including Mumbai, Bengaluru, Delhi, Kolkata, Pune etc. Malayalam is closely related to the Tamil language.
Northeast Malakula, or Uripiv-Wala-Rano-Atchin, is a dialect chain spoken on the islands of Uripiv, Wala, Rano, and Atchin and on the mainland opposite to these islands. Uripiv-Wala-Rano-Atchin is spoken today by about 9,000 people. Literacy rate of its speakers in their own language is 10–30%.
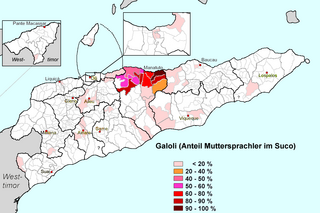
The Galoli, or Galolen, are a people of East Timor with a population of about 50,000, primarily along the northern coast of the district of Manatuto. To the west lies the Mambai people. There is an old colony on the southern coast of Wetar island, the Talo, who speak the Talur dialect.
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby island Liran.

Niuafoʻou, or Niuafoʻouan, is the language spoken on Tonga's northernmost island, Niuafoʻou.

English is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, whose speakers, called Anglophones, originated in early medieval England. The namesake of the language is the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain.
The Orang Laut language or Loncong, is one of the Malayic languages. It is one of several native languages of Orang Laut of the Bangka and Belitung islands in Indonesia, and may be two distinct languages.

Go is a statically typed, compiled high-level programming language designed at Google by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson. It is syntactically similar to C, but also has memory safety, garbage collection, structural typing, and CSP-style concurrency. It is often referred to as Golang because of its former domain name, golang.org, but its proper name is Go.
Zazao is an Oceanic language spoken in the Solomon Islands. Its speakers live on Santa Isabel Island. It is classified as “critically endangered” by the UNESCO Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger, because its speakers usually speak the Cheke Holo language or the Zabana language.
Dampelas (Dampal) is a Celebic language of Sulawesi in Indonesia. It is the main language of Dampelas District (kecamatan).
Gane is an Austronesian language of southern Halmahera, Indonesia, spoken by the Gane people. There are estimated to be roughly 5200 native speakers of the language. It is closely related to the Taba language.
Lauje is a Celebic language of Sulawesi in Indonesia. Ampibabo, spoken in Ampibabo District, may be a separate language.

A transformer is a deep learning architecture developed by Google and based on the multi-head attention mechanism, proposed in a 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need". Text is converted to numerical representations called tokens, and each token is converted into a vector via looking up from a word embedding table. At each layer, each token is then contextualized within the scope of the context window with other (unmasked) tokens via a parallel multi-head attention mechanism allowing the signal for key tokens to be amplified and less important tokens to be diminished. The transformer paper, published in 2017, is based on the softmax-based attention mechanism proposed by Bahdanau et. al. in 2014 for machine translation, and the Fast Weight Controller, similar to a transformer, proposed in 1992.
References
- 1 2 Ethnologue Languages of the World:Tagbu. Retrieved January 18, 2016.