In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.
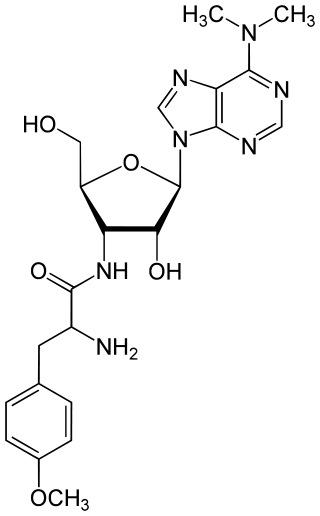
Puromycin is an antibiotic protein synthesis inhibitor which causes premature chain termination during translation.
A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis.

Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 are a class of oral hypoglycemics that block the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). They can be used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2.
Microbial collagenase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Thermolysin is a thermostable neutral metalloproteinase enzyme produced by the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus thermoproteolyticus. It requires one zinc ion for enzyme activity and four calcium ions for structural stability. Thermolysin specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds containing hydrophobic amino acids. However thermolysin is also widely used for peptide bond formation through the reverse reaction of hydrolysis. Thermolysin is the most stable member of a family of metalloproteinases produced by various Bacillus species. These enzymes are also termed 'neutral' proteinases or thermolysin -like proteinases (TLPs).
Blasticidin S is an antibiotic that is used in biology research for selecting cells in cell culture. Cells of interest can express the blasticidin resistance genes BSD or bsr, and can then survive treatment with the antibiotic. Blasticidin S is a nucleoside analogue antibiotic, resembling the nucleoside cytidine. Blasticidin works against human cells, fungi, and bacteria, all by disrupting protein translation. It was originally described by Japanese researchers in the 1950s seeking antibiotics for rice blast fungus.
Ubenimex (INN), also known more commonly as bestatin, is a competitive, reversible protease inhibitor. It is an inhibitor of arginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B), leukotriene A4 hydrolase (a zinc metalloprotease that displays both epoxide hydrolase and aminopeptidase activities), alanyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase M/N), leucyl/cystinyl aminopeptidase (oxytocinase/vasopressinase), and membrane dipeptidase (leukotriene D4 hydrolase). It is being studied for use in the treatment of acute myelocytic leukemia and lymphedema. It is derived from Streptomyces olivoreticuli. Ubenimex has been found to inhibit the enzymatic degradation of oxytocin, vasopressin, enkephalins, and various other peptides and compounds.

Phosphoramidon is a chemical compound derived from cultures of Streptomyces tanashiensis. It is an inhibitor of the enzyme thermolysin, of the membrane metallo-endopeptidase, and of the endothelin converting enzyme. Chemically, phosphoramidon differs from its closely related peptidase inhibitor talopeptin by a single stereocenter.

Ilomastat (INN), is a broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor.

Ecadotril is a neutral endopeptidase inhibitor ((NEP) EC 3.4.24.11) and determined by the presence of peptidase family M13 as a neutral endopeptidase inhibited by phosphoramidon. Ecadotril is the (S)-enantiomer of racecadotril. NEP-like enzymes include the endothelin-converting enzymes. The peptidase M13 family believed to activate or inactivate oligopeptide (pro)-hormones such as opioid peptides, neprilysin is another member of this group, in the case of the metallopeptidases and aspartic, the nucleophiles clan or family for example MA, is an activated water molecule. The peptidase domain for members of this family also contains a bacterial member and resembles that of thermolysin the predicted active site residues for members of this family and thermolysin occur in the motif HEXXH. Thermolysin complexed with the inhibitor (S)-thiorphan are isomeric thiol-containing inhibitors of endopeptidase EC 24-11 (also called "enkephalinase").

Candoxatril is the orally active prodrug of candoxatrilat (UK-73967).

Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease.
Pseudolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Glutamic proteases are a group of proteolytic enzymes containing a glutamic acid residue within the active site. This type of protease was first described in 2004 and became the sixth catalytic type of protease. Members of this group of protease had been previously assumed to be an aspartate protease, but structural determination showed it to belong to a novel protease family. The first structure of this group of protease was scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the active site of which contains a catalytic dyad, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), which give rise to the name eqolisin. This group of proteases are found primarily in pathogenic fungi affecting plant and human.
Streptomyces corchorusii is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces corchorusii produces butalactin.
Streptomyces griseoloalbus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces griseoloalbus produces grisein.
Streptomyces griseosporeus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces griseosporeus produces taitomycin, 2-amino-4-hydroxypentanonic acid and liposidomycins.
Streptomyces violaceochromogenes is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces violaceochromogenes produces cinerubin x, cinerubin y, arugomycin and viriplanin D.

The arylomycins are a class of antibiotics initially isolated from a soil sample obtained in Cape Coast, Ghana. In this initial isolation, two families of closely related arylomycins, A and B, were identified. The family of glycosylated arylomycin C lipopeptides were subsequently isolated from a Streptomyces culture in a screen for inhibitors of bacterial signal peptidase. The initially isolated arylomycins have a limited spectrum of activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. The only activity against Gram-negative bacteria was seen in strains with a compromised outer membrane.










