
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related with, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services. Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities.
Investment is the dedication of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.

In finance, valuation is the process of determining the present value (PV) of an asset. In a business context, it is often the hypothetical price that a third party would pay for a given asset. Valuations can be done on assets or on liabilities. Valuations are needed for many reasons such as investment analysis, capital budgeting, merger and acquisition transactions, financial reporting, taxable events to determine the proper tax liability.

Fixed assets, also known as long-lived assets, tangible assets or property, plant and equipment (PP&E), are a term used in accounting for assets and property that cannot easily be converted into cash. Fixed assets are different from current assets, such as cash or bank accounts, because the latter are liquid assets. In most cases, only tangible assets are referred to as fixed.
A capital asset is defined to include property of any kind held by an assessee, whether connected with their business or profession or not connected with their business or profession. It includes all kinds of property, movable or immovable, tangible or intangible, fixed or circulating. Thus, land and building, plant and machinery, motorcar, furniture, jewellery, route permits, goodwill, tenancy rights, patents, trademarks, shares, debentures, securities, units, mutual funds, zero-coupon bonds etc. are capital assets.

Asset allocation is the implementation of an investment strategy that attempts to balance risk versus reward by adjusting the percentage of each asset in an investment portfolio according to the investor's risk tolerance, goals and investment time frame. The focus is on the characteristics of the overall portfolio. Such a strategy contrasts with an approach that focuses on individual assets.

Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financial loss and uncertainty about its extent.
In finance, an asset class is a group of financial instruments that have similar financial characteristics and behave similarly in the marketplace. We can often break these instruments into those having to do with real assets and those having to do with financial assets. Often, assets within the same asset class are subject to the same laws and regulations; however, this is not always true. For instance, futures on an asset are often considered part of the same asset class as the underlying instrument but are subject to different regulations than the underlying instrument.
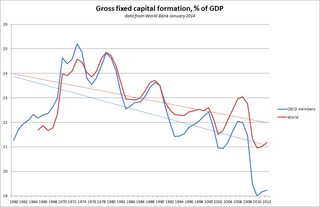
Capital formation is a concept used in macroeconomics, national accounts and financial economics. Occasionally it is also used in corporate accounts. It can be defined in three ways:
Real estate investing involves the purchase, management and sale or rental of real estate for profit. Improvement of realty property as part of a real estate investment strategy is generally considered to be a sub-specialty of real estate investing called real estate development. Someone who actively or passively invests in real estate is called a real estate entrepreneur or a real estate investor.
A self-directed individual retirement account is an individual retirement account (IRA) which allows alternative investments for retirement savings. Some examples of these alternative investments are real estate, private mortgages, private company stock, oil and gas limited partnerships, precious metals, digital assets, horses and livestock, and intellectual property. The increased investment options available in self-directed IRAs prompted the SEC to issue a public notice in 2011 due an increased risk of fraud in alternative assets.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:

An alternative investment is an investment in any asset class excluding stocks, bonds, and cash. The term is a relatively loose one and includes tangible assets such as precious metals, collectibles and some financial assets such as real estate, commodities, private equity, distressed securities, hedge funds, exchange funds, carbon credits, venture capital, film production, financial derivatives, cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens, and tax receivable agreements. Investments in real estate, forestry and shipping are also often termed "alternative" despite the ancient use of such real assets to enhance and preserve wealth. Alternative investments are to be contrasted with traditional investments.
A financial asset is a non-physical asset whose value is derived from a contractual claim, such as bank deposits, bonds, and participations in companies' share capital. Financial assets are usually more liquid than other tangible assets, such as commodities or real estate.
Private equity real estate is a term used in investment finance to refer to a specific subset of the real estate investment asset class. Private equity real estate refers to one of the four quadrants of the real estate capital markets, which include private equity, private debt, public equity and public debt.
A real estate derivative is a financial instrument whose value is based on the price of real estate. The core uses for real estate derivatives are: hedging positions, pre-investing assets and re-allocating a portfolio. The major products within real estate derivatives are: swaps, futures contracts, options and structured products. Each of these products can use a different real estate index. Further, each property type and region can be used as a reference point for any real estate derivative.

In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash . The balance sheet of a firm records the monetary value of the assets owned by that firm. It covers money and other valuables belonging to an individual or to a business.
Risk parity is an approach to investment management which focuses on allocation of risk, usually defined as volatility, rather than allocation of capital. The risk parity approach asserts that when asset allocations are adjusted to the same risk level, the risk parity portfolio can achieve a higher Sharpe ratio and can be more resistant to market downturns than the traditional portfolio. Risk parity is vulnerable to significant shifts in correlation regimes, such as observed in Q1 2020, which led to the significant underperformance of risk-parity funds in the Covid-19 sell-off.

A Delaware statutory trust (DST) is a legally recognized trust that is set up for the purpose of business, but not necessarily in the U.S. state of Delaware. It may also be referred to as an Unincorporated Business Trust or UBO.
Real Assets is an investment asset class that covers investments in physical assets such as real estate, energy, and infrastructure. Real assets have an inherent physical worth. Real assets differ from financial assets in that financial assets get their value from a contractual right and are typically intangible.






