
The Bridgewater Bridge is a road and rail bridge that carries the Midland Highway and South Railway Line across the Derwent River in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. The steel truss vertical lift bridge and specially-built causeway connect the Hobart suburbs of Bridgewater and Granton. The bridge was completed in 1946 and accommodates a two-lane highway, a single track railway and a grade-separated footpath.

The Melba Line is a 1,067 mm narrow-gauge railway on the West Coast of Tasmania. The line was originally constructed as a private railway line named the Emu Bay Railway and was one of the longest-lasting and most successful private railway companies in Australia. While at present the line travels from Burnie to Melba Flats, it previously ran through to Zeehan carrying minerals and passengers as an essential service for the West Coast community.

Pacific National is one of Australia's largest rail freight businesses.

The Australian National Railways Commission was an agency of the Government of Australia that was a railway operator between 1975 and 1998. It traded as Australian National Railways (ANR) in its early years, before being rebranded as Australian National. AN was widely used from 1980, the logotype being registered as a trade mark.

The Tasmanian Government Railways (TGR) was the former operator of the mainline railways in Tasmania, Australia. Formed in 1872, the railway company was managed by the Government of Tasmania, and existed until absorption into the Australian National Railways Commission in 1978.

Australian Transport Network (ATN) was a freight railway operator in Australia that commenced operating in November 1997. The company operated narrow gauge trains in Tasmania and standard gauge trains in New South Wales and Victoria. It was formed as a joint venture with Tranz Rail owning 67% and Wisconsin Central 33%. In February 2004, ATN was sold to Pacific National.

Rail transport in Tasmania consists of a network of narrow gauge track of 1,067 mm reaching virtually all cities and major towns in the island state of Tasmania, Australia. Today, rail services are focused primarily on bulk freight, with no commercial passenger services being operated. The mainline railways of Tasmania are currently operated by TasRail, a Government of Tasmania-owned Corporation, who owns and maintains both rolling stock, locomotives, and track infrastructure.

The Y class is a class of diesel locomotives built by the Tasmanian Government Railways between 1961 and 1971.

The Derwent Valley Railway is an inoperational heritage railway in Tasmania, Australia. Its base is in New Norfolk. It is 3' 6" narrow gauge.

The 1300 class were a class of diesel locomotive built by English Electric, Rocklea for Queensland Rail between 1967 and 1972. They were later sold to AN Tasrail.

The Brighton Transport Hub is an intermodal transport hub in the northern Hobart suburb of Brighton operated by TasRail.
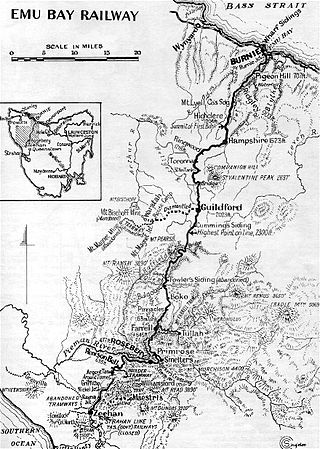
The Emu Bay Railway was a Tasmania, Australian railway company. The railway was significant during full operation, in that it linked the Tasmanian Government Railways system at Burnie with that at Zeehan that further linked to the Mount Lyell railway allowing connection through to Queenstown.

The West Coast Wilderness Railway is a reconstruction of the Mount Lyell Mining and Railway Company Mount Lyell railway in Western Tasmania between Queenstown and Regatta Point, Strahan. The railway is significant because of its Abt rack system to conquer the mountainous terrain through rainforest, with original locomotives still operating on the railway today. Now operating as a tourist experience with a focus on sharing the history of Tasmania's West Coast, the original railway began operations in 1897 as the only link between Queenstown and the port of Strahan.

The D/DA class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Clyde Engineering, Granville for the Western Australian Government Railways in 1971-1972.

AN Tasrail was an Australian railway operator that operated the Tasmanian rail network from March 1978 until November 2004. Originally a subsidiary of the Federal Government's Australian National, it was sold to Australian Transport Network (ATN) in November 1997. ATN was acquired by Pacific National in 2004 and the AN Tasrail subsidiary was later acquired by the Tasmanian Government in 2009 to become TasRail.

The 2350 class were a class of diesel locomotive built by English Electric, Rocklea for Queensland Railways in 1973–1974. All were later sold to AN Tasrail.
The Z class are a class of diesel locomotives built by English Electric Rocklea for the Tasmanian Government Railways in 1973. They were a development of the WAGR RA class and were the last of a line of very successful locomotives fitted with the English Electric 12CSVT Mk II engine.

The TR class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Progress Rail, Patterson, Georgia, United States for TasRail in 2013–2014. They are currently the main Tasmanian locomotive class handling the majority of mainline services across the state.

The DQ class were a class of diesel locomotives in New Zealand and Tasmania. Originally built by Clyde Engineering in the 1960s as Queensland Rails 1460 and 1502 class locomotives. They were purchased by Tranz Rail in 1995 to be rebuilt, as a cheaper alternative to buying new locomotives. Tranz Rail rebuilt 16 locos into the DQ class. Tranz Rail then sold the 12 DQs to AN Tasrail. Only eight out of the twelve DQs are still in service today.
























