
Renewable energy, green energy, or low-carbon energy is energy from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. Renewable resources include sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. Renewable energy is often used for electricity generation, heating and cooling. Renewable energy projects are typically large-scale, but they are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development.

Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy, and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the Sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air.

A non-renewable resource is a natural resource that cannot be readily replaced by natural means at a pace quick enough to keep up with consumption. An example is carbon-based fossil fuels. The original organic matter, with the aid of heat and pressure, becomes a fuel such as oil or gas. Earth minerals and metal ores, fossil fuels and groundwater in certain aquifers are all considered non-renewable resources, though individual elements are always conserved.

Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include the production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse of energy that would otherwise be wasted. Energy conservation and efficiency measures reduce the demand for energy development, and can have benefits to society with improvements to environmental issues.

Energy is sustainable if it "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Most definitions of sustainable energy include considerations of environmental aspects such as greenhouse gas emissions and social and economic aspects such as energy poverty. Renewable energy sources such as wind, hydroelectric power, solar, and geothermal energy are generally far more sustainable than fossil fuel sources. However, some renewable energy projects, such as the clearing of forests to produce biofuels, can cause severe environmental damage.

Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change. This action either reduces emissions of greenhouse gases or removes those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global temperature is mostly due to emissions from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. There are various ways that mitigation can reduce emissions. These are transitioning to sustainable energy sources, conserving energy, and increasing efficiency. It is possible to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This can be done by enlarging forests, restoring wetlands and using other natural and technical processes. The name for these processes is carbon sequestration. Governments and companies have pledged to reduce emissions to prevent dangerous climate change. These pledges are in line with international negotiations to limit warming.

Energy recovery includes any technique or method of minimizing the input of energy to an overall system by the exchange of energy from one sub-system of the overall system with another. The energy can be in any form in either subsystem, but most energy recovery systems exchange thermal energy in either sensible or latent form.

Hell and High Water: Global Warming – the Solution and the Politics – and What We Should Do is a book by author, scientist, and former U.S. Department of Energy official Joseph J. Romm, published December 26, 2006. The author is "one of the world's leading experts on clean energy, advanced vehicles, energy security, and greenhouse gas mitigation."

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. In 2019, nearly 75% of new installed electricity generation capacity used renewable energy and the International Energy Agency (IEA) has predicted that by 2025, renewable capacity will meet 35% of global power generation.
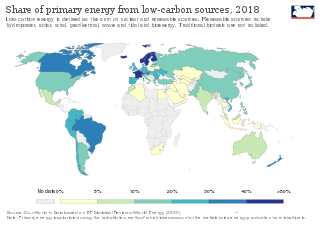
Low-carbon electricity or low-carbon power is electricity produced with substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions over the entire lifecycle than power generation using fossil fuels. The energy transition to low-carbon power is one of the most important actions required to limit climate change.

100% renewable energy is the goal of the use renewable resources for all energy. 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating, cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issues, as well as economic and energy security concerns. Shifting the total global primary energy supply to renewable sources requires a transition of the energy system, since most of today's energy is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels.
New Energy for America was a plan led by Barack Obama and Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on foreign oil, address global warming issues, and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump, and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to: invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy, invest in training for workers of clean technologies, strengthen the middle class, and help the economy.
Surviving the Century: Facing Climate Chaos and Other Global Challenges, edited by Herbert Girardet, is the first major book from the World Future Council, published by Earthscan in 2007. Eight main issues relating to the politics of climate change are covered in the book: countering climate chaos, renewable energy policy, creating sustainable cities, local farming systems, rainforests and climate change, cradle to cradle production systems, an alternative vision for trade and creating a living democracy.

Christopher Frank William Goodall is an English businessman, author and expert on new energy technologies. He is an alumnus of St Dunstan's College, University of Cambridge, and Harvard Business School (MBA).

Straight Up: America's Fiercest Climate Blogger Takes on the Status Quo Media, Politicians, and Clean Energy Solutions is a book by author, blogger, physicist and climate expert Joseph J. Romm. A Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and former Acting Assistant Secretary of the U.S. Department of Energy, Romm writes about methods of reducing global warming and increasing energy security through energy efficiency, green energy technologies and green transportation technologies.

An energy transition is a significant structural change in an energy system regarding supply and consumption. Currently, a transition to sustainable energy is underway to limit climate change. It is also called renewable energy transition. The current transition is driven by a recognition that global greenhouse-gas emissions must be drastically reduced. This process involves phasing-down fossil fuels and re-developing whole systems to operate on low carbon electricity. A previous energy transition took place during the industrial revolution and involved an energy transition from wood and other biomass to coal, followed by oil and most recently natural gas.
Atmospheric mining is the process of extracting valuable materials or other non-renewable resources from the atmosphere. Due to the abundance of molecular hydrogen and helium in the outer planets of the Solar System, advances in technology may eventually make mining their atmospheres a favorable alternative to mining terrestrial surfaces.

Renewable energy in Bangladesh refers to the use of renewable energy to generate electricity in Bangladesh. The current renewable energy comes from biogas that is originated from biomass, hydro power, solar and wind.

How to Avoid a Climate Disaster: The Solutions We Have and the Breakthroughs We Need is a 2021 book by Bill Gates. In it, Gates presents what he learned in over a decade of studying climate change and investing in innovations to address global warming and recommends technological strategies to tackle it.















