Related Research Articles
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established in 1787 by the Congress of the Confederation through the Northwest Ordinance, it was the nation's first post-colonial organized incorporated territory.

John Sevier was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennessee's pre-statehood period, both militarily and politically, and he was elected the state's first governor in 1796. He served as a colonel of the Washington District Regiment in the Battle of Kings Mountain in 1780, and he commanded the frontier militia in dozens of battles against the Cherokee in the 1780s and 1790s.
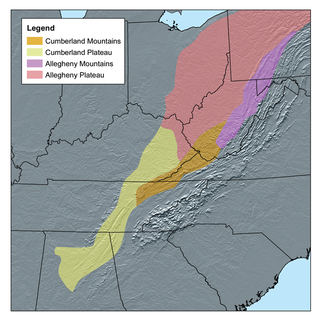
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the dissected plateau lands lying west of the main Appalachian Mountains. The terms stem from historical usage rather than geological difference, so there is no strict dividing line between the two. Two major rivers share the names of the plateaus, with the Allegheny River rising in the Allegheny Plateau and the Cumberland River rising in the Cumberland Plateau in Harlan County, Kentucky.

The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands division. The physiographic province is divided into three sections: the Hudson Valley, the Central, and the Tennessee.

The Overmountain Men were American frontiersmen from west of the Blue Ridge Mountains which are the leading edge of the Appalachian Mountains, who took part in the American Revolutionary War. While they were present at multiple engagements in the war's southern campaign, they are best known for their role in the American victory at the Battle of Kings Mountain in 1780. The term "overmountain" arose because their settlements were west of, or "over", the Blue Ridge, which was the primary geographical boundary dividing several of the 13 American states from the Native American lands to the west. The Overmountain Men hailed from parts of Virginia, North Carolina, and what is now Tennessee and Kentucky.

The Watauga Association was a semi-autonomous government created in 1772 by frontier settlers living along the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. Although it lasted only a few years, the Watauga Association provided a basis for what later developed into the state of Tennessee and likely influenced other western frontier governments in the trans-Appalachian region. North Carolina annexed the Watauga settlement area, by then known as the Washington District, in November 1776. Within a year, the area was placed under a county government, becoming Washington County, North Carolina, in November 1777. This area covers the present day Washington County, Carter County, and other areas now located in the northeast part of the state of Tennessee.

Tennessee is one of the 50 states of the United States. What is now Tennessee was initially part of North Carolina, and later part of the Southwest Territory. It was admitted to the Union on June 1, 1796, as the 16th state. Tennessee earned the nickname "The Volunteer State" during the War of 1812, when many Tennesseans helped with the war effort, especially during the Americans victory at the Battle of New Orleans in 1815. The nickname became even more applicable during the Mexican–American War in 1846, after the Secretary of War asked the state for 2,800 soldiers, and Tennessee sent over 30,000 volunteers.

The prehistory and history of Kentucky span thousands of years, and have been influenced by the state's diverse geography and central location. Archaeological evidence of human occupation in Kentucky begins approximately 9,500 BCE. A gradual transition began from a hunter-gatherer economy to agriculture c. 1800 BCE. Around 900 CE, the Mississippian culture took root in western and central Kentucky; the Fort Ancient culture appeared in eastern Kentucky. Although they had many similarities, the Fort Ancient culture lacked the Mississippian's distinctive, ceremonial earthen mounds.

The Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, usually shortened to Sycamore Shoals, is a rocky stretch of river rapids along the Watauga River in Elizabethton, Tennessee. Archeological excavations have found Native Americans lived near the shoals since prehistoric times, and Cherokees gathered there. As Europeans began settling the Trans-Appalachian frontier, the shoals proved strategic militarily, as well as shaped the economies of Tennessee and Kentucky. Today, the shoals are protected as a National Historic Landmark and are maintained as part of Sycamore Shoals State Historic Park.

Fort Watauga, also known as Fort Caswell, was a fortification located in the Watauga River's Sycamore Shoals near modern-day Elizabethton, Tennessee. It was constructed from 1775 to 1776 by the Watauga Association, a semi-autonomous government founded by American settlers living near the river, to defend the settlers against attacks from British-allied Indians. The fort was originally named Fort Caswell after the governor of North Carolina, Richard Caswell.

Sycamore Shoals State Historic Area is a state park located in Elizabethton, in the U.S. state of Tennessee. The park consists of 70 acres (28.3 ha) situated along the Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, a National Historic Landmark where a series of events critical to the establishment of the states of Tennessee and Kentucky, and the settlement of the Trans-Appalachian frontier in general, took place. Along with the historic shoals, the park includes a visitor center and museum, the reconstructed Fort Watauga, the Carter House and Sabine Hill . For over a thousand years before the arrival of European explorers, Sycamore Shoals and adjacent lands had been inhabited by Native Americans. The first permanent European settlers arrived in 1770, and established the Watauga Association—one of the first written constitutional governments west of the Appalachian Mountains—in 1772. Richard Henderson and Daniel Boone negotiated the Treaty of Sycamore Shoals in 1775, which saw the sale of millions of acres of Cherokee lands in Kentucky and Tennessee and led to the building of the Wilderness Road. During the American Revolution, Sycamore Shoals was both the site of Fort Watauga, where part of a Cherokee invasion was thwarted in 1776, and the mustering ground for the Overmountain Men in 1780.
The Washington District of North Carolina was in a remote area west of the Appalachian Mountains, officially existing for only a short period, although it had been self-proclaimed and functioning as an independent governing entity since the spring of 1775. The district was the bureaucratic successor to the Watauga Association, a group of Virginian settlers that colonized the area in 1769, originally believing themselves to be in trans-Appalachian Virginia territory. When the settlement's application to be united with Virginia was denied, they asked North Carolina to annex the settlement, which occurred in November, 1776.

The 1822–23 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1822 and 1823, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.
John Tipton was an American frontiersman and statesman who was active in the early development of the state of Tennessee. He is best remembered for leading the opposition to the State of Franklin movement in the 1780s, as well as for his rivalry with Franklinite leader John Sevier. He served in the legislatures of Virginia, North Carolina, the Southwest Territory, and Tennessee, and was a delegate to Tennessee's 1796 constitutional convention. Tipton's homestead still stands and is managed as the Tipton-Haynes State Historic Site.
The Indian barrier state was a British proposal to establish a Native American buffer state in the portion of the Great Lakes region of North America. It was never created. The idea was to create it west of the Appalachian Mountains, bounded by the Ohio and Mississippi rivers and the Great Lakes. The concept of establishing such a state, first conceived in the late 1750s, was part of a long-term plan to reconcile the Indian tribes to British presence and diminish hostilities between the tribes and the British Army following its victory in the French and Indian War in 1763.

The Washington District Regiment was authorized on December 23, 1776 by the Province of North Carolina Congress. It was subordinate to the Salisbury District Brigade of militia. The regiment was renamed the Washington County Regiment. The regiment was engaged in battles and skirmishes against the British and Cherokee during the American Revolution in Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia between 1776 and 1782. It was active until the end of the war.
John Richard Alden was an American historian and author of a number of books on the era of the American Revolutionary War.

Cross Mountain is a mountain in the Cumberland Mountains in the U.S. state of Tennessee. At an elevation of 3,534 feet (1,077 m), it is the highest mountain in Tennessee that is not part of the Blue Ridge Mountains. It contains rich deposits of coal, and in 1911 was the site of one of the deadliest mining disasters in state history.
The Trans-Appalachian Frontier: People, Societies, and Institutions, 1775–1850 is a book written by Malcolm J. Rohrbough and published by Oxford University Press in 1978 and Indiana University Press in 2008. The work covers the history of European and American migration, settlement, and community development in the Trans-Appalachian Frontier from before United States independence in 1775 until the Compromise of 1850.
Kentucke's Frontiers is a book by Craig Thompson Friend published in 2010 by Indiana University Press. Starting from the 1720s to the conclusion of the War of 1812, Kentucke's Frontiers explores the political, military, and social history of the Kentucky frontier and how these came together to shape the public memory of frontier Kentucky.
References
- ↑ O'Brien, Greg (2003). "Reviewed work: Tennessee Frontiers: Three Regions in Transition, John R. Finger". Indiana Magazine of History. 99 (1): 63–64. JSTOR 27792447.
- 1 2 3 Hofstra, Warren R. (2002). "Reviewed work: Tennessee Frontiers: Three Regions in Transition, John R. Finger". The Georgia Historical Quarterly. 86 (3): 457–460. JSTOR 40584575.
- ↑ Waller, Altina L. (2003). "Reviews of Books:Tennessee Frontiers: Three Regions in Transition John R. Finger". The American Historical Review. 108: 185–186. doi:10.1086/533090.
- ↑ "Tennessee Frontiers", Indiana University Press, retrieved 28 August 2023