Related Research Articles
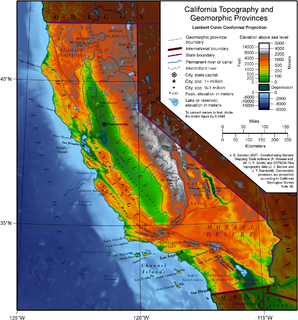
California is a U.S. state on the western coast of North America. Covering an area of 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2), California is among the most geographically diverse states. The Sierra Nevada, the fertile farmlands of the Central Valley, and the arid Mojave Desert of the south are some of the major geographic features of this U.S. state. It is home to some of the world's most exceptional trees: the tallest, most massive, and oldest. It is also home to both the highest and lowest points in the 48 contiguous states. The state is generally divided into Northern and Southern California, although the boundary between the two is not well defined. San Francisco is decidedly a Northern California city and Los Angeles likewise a Southern California one, but areas in between do not often share their confidence in geographic identity. The US Geological Survey defines the geographic center of the state at a point near North Fork, California.

Banning is a city in Riverside County, California, United States. The population was 29,603 at the 2010 census. It is situated in the San Gorgonio Pass, also known as Banning Pass. It is named for Phineas Banning, stagecoach line owner and the "Father of the Port of Los Angeles."

The San Jacinto Mountains are a mountain range in Riverside County, located east of Los Angeles in southern California in the United States. The mountains are named for one of the first Black Friars, Saint Hyacinth, who is popular patron in Latin America.

Francisco Hermenegildo Tomás Garcés, O.F.M., was a Spanish Franciscan friar who served as a missionary and explorer in the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. He explored much of the southwestern region of North America, including present day Sonora and Baja California in Mexico, and the U.S. states of Arizona and California. He was killed along with his companion friars during an uprising by the Native American population, and they have been declared martyrs for the faith by the Catholic Church. The cause for his canonization was opened by the Church.

The Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail is a 1,210-mile (1,950 km) National Park Service unit in the United States National Historic Trail and National Millennium Trail programs. The trail route extends from Nogales on the U.S.-Mexico border in Arizona, through the California desert and coastal areas in Southern California and the Central Coast region to San Francisco.

The San Gorgonio Pass, or Banning Pass, is a 2,600 ft (790 m) elevation gap on the rim of the Great Basin between the San Bernardino Mountains to the north and the San Jacinto Mountains to the south. The pass was formed by the San Andreas Fault, a major transform fault between the Pacific plate and the North American plate. The tall mountain ranges on either side of the pass result in the pass being a transitional zone from a Mediterranean climate west of the pass, to a Desert climate east of the pass. This also makes the pass area one of the windiest places in the United States, and why it is home to the San Gorgonio Pass wind farm.

The Tinajas Altas Mountains are an extremely arid northwest-southeast trending mountain range in southern Yuma County, Arizona, approximately 35 mi southeast of Yuma, Arizona. The southern end of the range extends approximately one mile into the northwestern Mexican state of Sonora on the northern perimeter of the Gran Desierto de Altar. The range is about 22 mi in length and about 4 mi wide at its widest point. The highpoint of the range is unnamed and is 2,766 feet above sea level and is located at 32°16'26"N, 114°02'48"W. Aside from the portion of the range in Mexico, the entirety of the range lies within the Barry M. Goldwater Air Force Range. They lie at the heart of the traditional homeland of the Hia C-eḍ O'odham people.

San Timoteo Canyon is a river valley canyon southeast of Redlands, in the far northwestern foothills of the San Jacinto Mountains in the Inland Empire region of Southern California.

Warner Springs is a small unincorporated community in northern San Diego County, California.

El Camino del Diablo is a historic 250-mile (400 km) road that currently extends through some of the most remote and arid terrain of the Sonoran Desert in Pima County and Yuma County, Arizona. In use for at least 1,000 years, El Camino del Diablo is believed to have started as a series of footpaths used by desert-dwelling Native Americans. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, the road was used extensively by conquistadores, explorers, missionaries, settlers, miners, and cartographers. Use of the trail declined sharply after the railroad reached Yuma in 1870. In recognition of its historic significance, El Camino del Diablo was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978. It has also been designated a Bureau of Land Management Back Country Byway.
Rancho Valle de San Felipe was a 9,972-acre (40.36 km2) Mexican land grant in present-day San Diego County, California given in 1846 by Governor Pío Pico to Felipe Castillo. The grant was located in the San Felipe Valley in the Laguna Mountains east of present-day Julian.
The Butterfield Overland Mail in California was created by the United States Congress on March 3, 1857, and operated until June 30, 1861. Subsequently, other stage lines operated along the route until the Southern Pacific Railroad arrived in Yuma, Arizona in 1877.

The geography of southern California refers to the geography of southern California in the United States.

Southern Emigrant Trail, also known as the Gila Trail, the Kearny Trail, Southern Trail and the Butterfield Stage Trail, was a major land route for immigration into California from the eastern United States that followed the Santa Fe Trail to New Mexico during the California Gold Rush. Unlike the more northern routes, pioneer wagons could travel year round, mountain passes not being blocked by snows, however it had the disadvantage of summer heat and lack of water in the desert regions through which it passed in New Mexico Territory and the Colorado Desert of California. Subsequently, it was a route of travel and commerce between the eastern United States and California. Many herds of cattle and sheep were driven along this route and it was followed by the San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line in 1857-1858 and then the Butterfield Overland Mail from 1858 - 1861.
Earthquake Valley is a desert valley east of Julian, California, which contains parts of the Anza-Borrego Desert State Park. It is the location of the Shelter Valley Ranchos subdivision, which is also known as the unincorporated community of Shelter Valley. The official USGS place name for the geologic feature in which Shelter Valley is situated is "Earthquake Valley", and the 1959 USGS Topographic map makes no reference to Shelter Valley. The name of the unincorporated community Shelter Valley is typically used both locally and by the media to refer generally to the geological feature of Earthquake Valley, and it is common for both names to be referenced in publications after the 1962 establishment of the subdivision. Author, poet, artist and primitivist Marshal South lived in and wrote about the general area, in a series of articles for Desert Magazine between 1941 and 1948. A number of notable trails pass through the valley, including the Pacific Crest Trail, the California Riding and Hiking Trail, and the Southern Emigrant Trail.

San Felipe Valley is an inland valley of the Peninsular Ranges, located in eastern San Diego County, California. Most of the valley is protected within the San Felipe Valley Wildlife Area.
The Butterfield Overland Mail route in Baja California was created as a result of an act by the United States Congress on March 3, 1857, and operated until June 30, 1861 as part of the Second Division of the route. Subsequently other stage lines operated along the route until the Southern Pacific Railroad arrived in Yuma, Arizona.

Vallecito, in San Diego County, California is an oasis of cienegas and salt grass along Vallecito Creek and a former settlement on the edge of the Colorado Desert in the Vallecito Valley. Its Spanish name is translated as "little valley". Vallecito was located at the apex of the gap in the Carrizo Badlands created by Carrizo Creek and its wash in its lower reach, to which Vallecito Creek is a tributary. The springs of Vallecito, like many in the vicinity, are a product of the faults that run along the base of the Peninsular Ranges to the west.

Scissors Crossing is a place name in San Diego County, California, in the United States. It is a wrong-way concurrency junction where State Route 78 intersects with County Route S2, and is a notable point on the Pacific Crest Trail. The unincorporated community of Shelter Valley lies 2 mi (3.2 km) to the south of Scissors Crossing along County Road S2.
Cooke's Wagon Road or Cooke's Road was the first wagon road between the Rio Grande and the Colorado River to San Diego, through the Mexican provinces of Nuevo México, Chihuahua, Sonora and Alta California, established by Philip St. George Cooke and the Mormon Battalion, from October 19, 1846 to January 29, 1847 during the Mexican–American War. It became the first of the wagon routes between New Mexico and California that with subsequent modifications before and during the California Gold Rush eventually became known as the Southern Trail or Southern Emigrant Trail.
References
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Teofulio Summit
- ↑ Exploring the Anza-Borrego Desert, Warner Ranch Junction to Earthquake Valley Published: 29 Apr 2002, last Updated: 8 Nov 2010. Details mentioned in this article were accurate at the time of publication. Read more: