
Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 20 regions of Italy. It is one of the five Italian autonomous regions and is officially referred to as Regione Siciliana. The region has 5 million inhabitants. Its capital city is Palermo.

Apulia is a region of Italy, located in the southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Otranto and Gulf of Taranto to the south. The region comprises 19,345 square kilometers (7,469 sq mi), and its population is about four million.

Bari is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, in southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy after Naples, a port and university city, as well as the city of Saint Nicholas. The city itself has a population of 320,257 inhabitants, over 116 square kilometres (45 sq mi), while the urban area has 750,000 inhabitants. The metropolitan area has 1.3 million inhabitants.

Benevento is a city and comune of Campania, Italy, capital of the province of Benevento, 50 kilometres (31 mi) northeast of Naples. It is situated on a hill 130 metres above sea level at the confluence of the Calore Irpino and the Sabato. In 2020, Benevento has 58,418 inhabitants. It is also the seat of a Catholic archbishop.

Southern Italy, also known as Meridione or Mezzogiorno, is a macroregion of Italy consisting of the southern half of the Italian state.

Salento is a geographic and historical region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apulia in Southern Italy. It is a sub-peninsula of the Italian Peninsula, sometimes described as the "heel" of the Italian "boot". It encompasses the entire administrative area of the province of Lecce, a large part of the province of Brindisi and part of that of Taranto.

The Province of Caltanissetta is a province in the southern part of Sicily, Italy. Following the suppression of the Sicilian provinces, it was replaced in 2015 by the Free municipal consortium of Caltanissetta. It contains 22 comuni, which are listed at Comuni of the Province of Caltanissetta. Its coat of arms is a red crest and two green leaf stems on top with a laurel leaf on the right and a crown in the middle. The River Salso is the main river of the province; it is 122 kilometres (76 mi) long and originates in the province of Palermo, and it flows into the Mediterranean in this province at the end of the Gulf of Gela.

The Province of Caserta is a province in the Campania region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Caserta, situated about 36 kilometres (22 mi) by road north of Naples. The province has an area of 2,651.35 square kilometres (1,023.69 sq mi), and a total population of 924,414 as of 2016. The Palace of Caserta is located near to the city, a former royal residence which was constructed for the Bourbon kings of Naples. It was the largest palace and one of the largest buildings erected in Europe during the 18th century. In 1997, the palace was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Catepanateof Italy was a province of the Byzantine Empire, comprising mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of Salerno. Amalfi and Naples, although north of that line, maintained allegiance to Constantinople through the catepan. The Italian region of Capitanata derives its name from the Catepanate.

Ariano Irpino is an Italian town and municipality in the province of Avellino, in the Campania region. With a population of 22,535 (2017), it is the second-largest town of the Irpinia district and the province, with Avellino itself being the largest. Located 270 kilometres (170 mi) east-southeast of Rome, the comune was granted the official status of Città ("City") by a presidential decree of 1952, October 26.
Terra di Lavoro is the name of a historical region of Southern Italy. It corresponds roughly to the modern southern Lazio and northern Campania and upper north west and west border area of Molise regions of Italy.

Adelfia is a town and comune in the Metropolitan City of Bari, Apulia, southern Italy. The town is a combination of two smaller towns, being Montrone and Canneto.

The history of Islam in Sicily and Southern Italy began with the first Arab settlement in Sicily, at Mazara, which was captured in 827. The subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta started in the 10th century. The Emirate of Sicily lasted from 831 until 1061, and controlled the whole island by 902. Though Sicily was the primary Muslim stronghold in Italy, some temporary footholds, the most substantial of which was the port city of Bari, were established on the mainland peninsula, especially in mainland Southern Italy, though Muslim raids, mainly those of Muhammad I ibn al-Aghlab, reached as far north as Naples, Rome and the northern region of Piedmont. The Muslim raids were part of a larger struggle for power in Italy and Europe, with Christian Byzantine, Frankish, Norman and local Italian forces also competing for control. Muslims were sometimes sought as allies by various Christian factions against other factions.

The Peucetians were an Iapygian tribe which inhabited western and central Apulia in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Daunians and the Messapians, inhabited northern and southern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapian language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC; however, in Peucetian territory ancient Greek and Oscan language were spoken as well, as the legends of the currencies from Rubi and Azetium were trilingual. Peucetians lived in the eponymous region Peucetia, which was bordered by the Ofanto river and the Murge in the north, the Bradano river in the west and the territories of the Greek colony of Taras and the Messapians in the south. This region is mostly coincident with the Metropolitan City of Bari and parts of the provinces of Taranto and Barletta-Andria-Trani today.
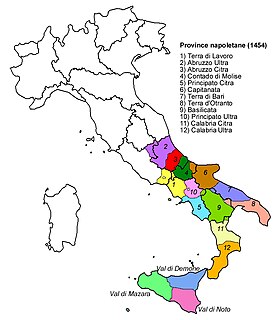
A justiciarate or justiciarship was a type of administrative subdivision that was used by several Italian states in the medieval period.

Apulian vase painting was a regional style of South Italian vase painting from ancient Apulia. It comprises geometric pottery and red-figure pottery.

The term Norman-Arab-Byzantine culture, Norman-Sicilian culture or, less inclusively, Norman-Arab culture, refers to the interaction of the Norman, Latin, Arab and Byzantine Greek cultures following the Norman conquest of Sicily and of Norman Africa from 1061 to around 1250. The civilization resulted from numerous exchanges in the cultural and scientific fields, based on the tolerance showed by the Normans towards the Greek-speaking populations and the Muslim settlers. As a result, Sicily under the Normans became a crossroad for the interaction between the Norman and Latin Catholic, Byzantine-Orthodox and Arab-Islamic cultures.

The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was a kingdom located in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy prior to Italian unification, comprising Sicily and all of the peninsula of Italy south of the Papal States, covering most of the area of today's Mezzogiorno.
Robert of Lauro was the Count of Caserta, a powerful nobleman and administrator in the Kingdom of Sicily, "effectively the king's viceroy on the mainland" between 1171 and his death. He was a close colleague of Count Tancred of Lecce, the future king. His influence helped his cousin Roger become Archbishop of Benevento (1179–1225).

The Terra di Otranto, or Terra d’Otranto, is an historical and geographical region of Apulia, largely corresponding to the Salento peninsula, anciently part of the Kingdom of Sicily and later of the Kingdom of Naples, which became a province of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.


















