Related Research Articles

The Sudanese Armed Forces are the military forces of the Republic of the Sudan. In 2011, IISS estimated the regular forces' numbers at 109,300 personnel, while in 2016–2017, the Rapid Support Forces had 40,000 members participating in the Yemeni Civil War.

The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War of 1955 to 1972. Although it originated in southern Sudan, the civil war spread to the Nuba mountains and the Blue Nile. It lasted for 22 years and is one of the longest civil wars on record. The war resulted in the independence of South Sudan six years after the war ended.

John Garang de Mabior was a Sudanese politician and revolutionary leader. From 1983 to 2005, he led the Sudan People's Liberation Army during the Second Sudanese Civil War, and following a peace agreement he briefly served as First Vice President of Sudan for 3 weeks until his death in a helicopter crash on 30 July 2005. A developmental economist by profession, Garang was a major influence on the movement that led to the foundation of South Sudan.

The start of the period 1994 to 2002 of the Lord's Resistance Army insurgency in northern Uganda saw the conflict intensifying due to Sudanese support to the rebels. There was a peak of bloodshed in the mid-1990s and then a gradual subsiding of the conflict. Violence was renewed beginning with the offensive by the Uganda People's Defence Force in 2002.

Sudan–United States relations are the bilateral relations between Sudan and the United States. The United States government has been critical of Sudan's human rights record and has dispatched a strong UN Peacekeeping force to Darfur. Relations between both countries in recent years have greatly improved, with Sudan's post-revolutionary government compensating American victims of al-Qaeda terror attacks, the removal of Sudan from the State Department's blacklist of state sponsors of terrorism and the United States Congress having reinstated Sudan's sovereign immunity in December 2020.
Sudan has a conflict in the Darfur area of western Sudan. The Khartoum government had, in the past, given sanctuary to trans-national Islamic terrorists, but, according to the 9/11 Commission Report, ousted al-Qaeda and cooperated with the US against such groups while simultaneously involving itself in human rights abuses in Darfur. There are also transborder issues between Chad and Darfur, and, to a lesser extent, with the Central African Republic.

China–Sudan relations are the bilateral relations between the People's Republic of China and the Republic of Sudan. China is currently one of Sudan's largest trade partners, importing oil and exporting low cost manufactured items as well as armaments into the country. Both states enjoy a very robust and productive relationship in the fields of diplomacy, economic trade, and political strategy. They formally established diplomatic relations on January 4, 1959, when Sudan formally recognized the sovereignty of the People's Republic of China and have since become close global allies, supporting each other in times of internal crises and international controversy such as during the Second Sudanese Civil War, the Darfur Crisis, and the Xinjiang Conflict. China continues to provide massive support to Sudan by developing its oil resources and supplying millions of dollars in loans, aid, foreign direct investments, and humanitarian assistance. In return, Sudan has become a reliable political and economic ally in the international arena, allowing China to maintain a significant stake in its oil sector.
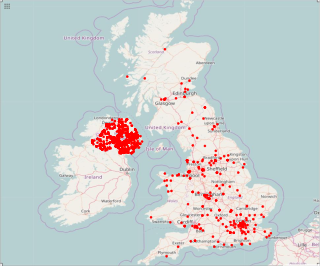
Terrorism in the United Kingdom, according to the Home Office, poses a significant threat to the state. There have been various causes of terrorism in the UK. Before the 2000s, most attacks were linked to the Northern Ireland conflict. In the late 20th century there were also attacks by Islamic terrorist groups.
Sudan is a source country for men, women and children trafficked internally for the purposes of forced labor and sexual exploitation. Sudan is also a transit and destination country for Ethiopian women trafficked abroad for domestic servitude. Sudanese women and girls are trafficked within the country, as well as possibly to Middle Eastern countries such as Qatar, for domestic servitude. U.S. State Department's Office to Monitor and Combat Trafficking in Persons placed the country in "Tier 3" in 2017. In 2020, Sudan was once again placed in the "Tier 3" category, since the latest Trafficking in Persons report showed that South Sudan had not made any prosecutions of human traffickers or convicted any individuals in connection with forced conscription of children into the armed forces in the last 5 years.

The South Sudan People's Defence Forces (SSPDF), formerly the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), is the army of the Republic of South Sudan. The SPLA was founded as a guerrilla movement against the government of Sudan in 1983 and was a key participant of the Second Sudanese Civil War, led by John Garang. After Garang's death in 2005, Salva Kiir was named the SPLA's new Commander-in-Chief. As of 2010, the SPLA was divided into divisions of 10,000–14,000 soldiers.

Iran–Sudan relations refers to diplomatic, economic and military relations between Sudan and Iran. For nearly three decades, Iran and Sudan enjoyed a close relationship. However, Sudan decided to expel all Iranian groups just hours before joining a Saudi military operation in Yemen in March 2015 as the Sudanese President is said to be calculating in favour of his fragile economy in addition to the trauma and horror which struck the Sudanese society when seeing its best and brightest joining the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIS) this March, generating a huge public alarm about regional security. The emotional component of protecting Saudi Arabia and walking back to the unfolded dramatically in Arab media. On January 4, 2016 Sudan cut off all diplomatic relations with Iran due to tensions between Saudi Arabia and Iran. As a result, the bond between both countries has severely soured.

Germany has experienced significant terrorism in its history, particularly during the Weimar Republic and during the Cold War, carried out by far-left and far-right German groups as well as by foreign terrorist organisations.
Terrorism in Mexico is the phenomenon of organized violence against civilians. It appeared in the 1960s, committed by communist guerrillas. Later attacks were by other political movements.

Terrorism in France refers to the terrorist attacks that have targeted the country and its population during the 20th and 21st centuries. Terrorism, in this case is much related to the country's history, international affairs and political approach. Legislation has been set up by lawmakers to fight terrorism in France.
This is a list of the number of incidents labelled as terrorism and not believed to have been carried out by a government or its forces. The following tables show the number of incidents, deaths, injuries based on data from the Global Terrorism Database (GTD) which is collected and collated by the National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (START) at the University of Maryland. The GTD defines a terrorist attack as "the threatened or actual use of illegal force and violence by a non‐state actor to attain a political, economic, religious, or social goal through fear, coercion, or intimidation."
References
- ↑ "The War on Terrorism: the United States and the SPLA in Sudan". www.espac.org. September 2001. Retrieved 2017-02-15.
- ↑ National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism. (2016). Global Terrorism Database (globalterrorismdb_0616dist.xlsx Archived July 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine ). Retrieved from "Global Terrorism Database". Archived from the original on July 6, 2016. Retrieved 2016-07-09. University of Maryland
- ↑ National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism. (2016). Global Terrorism Database (gtd1993_0616dist.xlsx Archived July 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine ). Retrieved from "Global Terrorism Database". Archived from the original on July 6, 2016. Retrieved 2016-07-09. University of Maryland