Related Research Articles
Fahd Mohammed Ahmed al-Quso, also known as Abu Huthaifah, Abu Huthaifah Al-Yemeni, Abu Al-Bara', Abu Hathayfah Al-Adani, Abu Huthaifah Al-Adani, Fahd Mohammed Ahmed Al-Awlaqi, Huthaifah Al-Yemeni, or Abu Huthaifah Al-Abu Al-Bara, was alleged to be a terrorist by American and Yemeni officials, and on the FBI Most Wanted Terrorists list. He was wanted by the FBI, Interpol, and the United States Department of State, which had offered 5 million dollars to anyone with information about him. He was killed by a US drone strike in Yemen on 6 May 2012.

Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, abbreviated as AQAP, also known as Ansar al-Sharia in Yemen, is a Sunni Islamist insurgent extremist group, which is part of the al-Qaeda network and primarily active in Yemen and Saudi Arabia. It is considered the most active of al-Qaeda's branches that emerged after the weakening of central leadership.

Nasir Abdel Karim al-Wuhayshi alias Abu Basir, was a Yemeni Islamist, who served as the leader of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP). Both Saudi Arabia and Yemen considered al-Wuhayshi to be among their most wanted fugitives. In October 2014, the US State Department increased the reward for any information leading to the capture or killing of al-Wuhayshi to US$10 million, the same as ISIS leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi. Wuhayshi was killed in a US drone strike in Hadhramaut Governorate of Yemen on 12 June 2015.

Qasim Yahya Mahdi al-Raymi was a Yemeni militant who was the emir of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP). Al-Raymi was one of 23 men who escaped in the 3 February 2006 prison-break in Yemen, along with other notable al-Qaeda members. Al-Raymi was connected to a July 2007 suicide bombing that killed eight Spanish tourists. In 2009, the Yemeni government accused him of being responsible for the running of an al-Qaeda training camp in Abyan province. After serving as AQAP's military commander, al-Raymi was promoted to leader after the death of Nasir al-Wuhayshi on 12 June 2015.

Ibrahim Hassan Tali al-Asiri was a citizen of Saudi Arabia suspected of being chief bomb-maker of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula. He was reported to have been responsible for making the bombs used by his brother Abdullah al-Asiri in his suicide bombing, the 2009 Christmas Day bomb plot, the 2010 cargo plane bomb plot, and the May 8th 2012 Terror Plot.

The Al-Qaeda insurgency in Yemen is an ongoing armed conflict between the Yemeni government, the United States and their allies, and al-Qaeda-affiliated cells in Yemen. It is a part of the Global War on Terror.
The Battle of Zinjibar was a battle between forces loyal to Yemeni leader Ali Abdullah Saleh and Islamist militant forces, possibly including elements of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP), for control of the town of Zinjibar and its surroundings as part of the wider insurgency in the self-declared Al-Qaeda Emirate in Yemen. Many of the Islamist forces operating in Abyan province refer to themselves as Ansar al-Sharia.
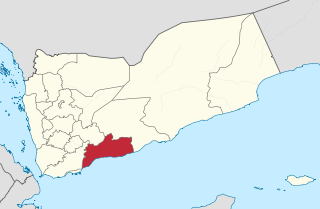
The 2012 Abyan offensive was an offensive by the Yemeni military against Islamist militant forces, possibly including elements of Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP), in the province of Abyan with the purpose of re-capturing the militant-held towns of Zinjibar and Jaʿār.
The following lists events that happened during 2012 in Yemen.

United States drone strikes in Yemen started after the September 11, 2001 attacks in the United States, when the US military attacked the Islamist militant presence in Yemen, in particular Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula using drone warfare.
"Yemeni Crisis (2011–present)" refers to events of the Houthi insurgency in Yemen, the Yemeni Revolution, the Al-Qaeda insurgency in Yemen and the South Yemen insurgency.
In early December 2015, two Yemeni towns, Zinjibar and Ja'ar, were captured by the jihadist group Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP). This was the second capture and occupation of Zinjibar during unrest in Yemen. The town was earlier taken by AQAP's in May 2011 and held until the summer of 2012.
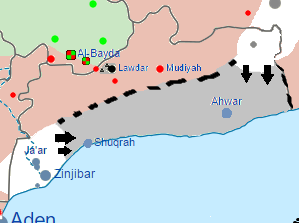
The Southern Abyan Offensive refers to a 2016 offensive that AQAP launched in late February, which ended with a victory for AQAP as Yemeni tribal fighters loyal to president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi were driven out of the Abyan Governorate.

The Shabwah Governorate offensive is an insurgent campaign by Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) forces to take control of Shabwah Governorate during the Yemeni Civil War.
The Second Battle of Mukalla refers to an armed conflict between al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and the Saudi-led Coalition. The aim of the coalition offensive was to disable the newly resurgent al-Qaeda Emirate in Yemen by recapturing its capital, Mukalla. The battle led to a coalition victory, in which the coalition forces gained control of Mukalla and the surrounding coastal areas.
The following is a timeline of the Yemeni civil war, which began in September 2014.
Usayd al-Adani was a senior leader of Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula.
The Hadramaut insurgency was an insurgency in Yemen launched by AQAP and ISIL-YP against forces loyal to president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.
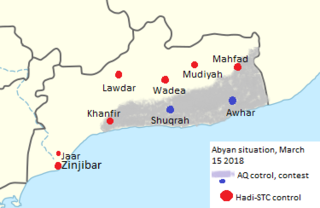
The Abyan conflict was a series of clashes between forces of AQAP loyal to Yemeni president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, and forces loyal to Southern Movement for the control of Abyan between 2016 and 2018.
References
- ↑ Background Note: Yemen Archived June 4, 2019, at the Wayback Machine US Department of State, January 2006
- ↑ Herbert-Burns, Rupert; Bateman, Sam; Lehr, Peter (September 2008). Lloyd's MIU handbook of maritime security. Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 60. ISBN 9781420054804. Archived from the original on February 17, 2023. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ↑ Blau, Justine (April 5, 2003). "Al Qaeda Suspect Arrested In Yemen". CBS News. Archived from the original on October 1, 2016. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ↑ "Yemen raises al-Qaeda sentences". BBC News. BBC. February 5, 2005. Archived from the original on February 17, 2023. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ↑ Hull, Edmund J (2011). High-Value Target: Countering al Qaeda in Yemen (illustrated ed.). Washington DC: Potomac Books, Inc. p. 34. ISBN 9781597976794. Archived from the original on February 17, 2023. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ↑ "Three Baptist Hospital Staff Killed in Yemen". Domini.org. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ↑ "Firing squad executes Yemeni for killings of Baptist workers". The Christian Index. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved September 28, 2016.
- ↑ "News Brief". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. January 23, 2007. Archived from the original on October 2, 2016. Retrieved September 28, 2016.
- ↑ "Yemenite Jews under pressure from Muslim extremists". World Jewish Congress. January 23, 2007. Archived from the original on October 3, 2016. Retrieved September 28, 2016.
- ↑ "Ex-inmates: Torture rife in prisons run by Yemen rebels". The Associated Press. December 7, 2018. Archived from the original on January 9, 2019. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ↑ "Inside Yemen's secret prisons: 'We could hear the screams'". The Associated Press. Archived from the original on January 9, 2019. Retrieved June 22, 2017.
- ↑ "Detainees held without charges decry Emiratis' sexual abuses". The Associated Press. Archived from the original on January 6, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2018.
- ↑ Al Qaeda Arrests Worldwide Archived October 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine FOX News
- ↑ Associated Press December 21, 2001 (December 21, 2001). "Al Qaeda men sought in Yemen". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Scud affair draws US apology". BBC News. December 12, 2002. Archived from the original on July 2, 2018. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ↑ "U.S. lets Scud ship sail to Yemen". CNN. December 12, 2002. Archived from the original on January 2, 2007. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ↑ "Breaking News, UAE, GCC, Middle East, World News and Headlines - Emirates 24/7". Emirates 24/7. Archived from the original on August 1, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2014.
- ↑ "Wikileaks cable corroborates evidence of US airstrikes in Yemen". Amnesty International. December 1, 2010. Archived from the original on February 15, 2015. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- ↑ "The civilian massacre the US neither confirms nor denies". thebureauinvestigates.com. Archived from the original on April 8, 2015. Retrieved September 30, 2015.
- 1 2 "34 suspected Al-Qaeda'killed in Yemen air strike'". The Raw Story. December 24, 2009. Retrieved April 4, 2010.[ dead link ]
- 1 2 3 4 Gary D. Solis (2010). The Law of Armed Conflict: International Humanitarian Law in War. Cambridge University Press. pp. 538–47. ISBN 978-0-521-87088-7. Archived from the original on February 17, 2023. Retrieved May 19, 2010.
- 1 2 Walter Pincus (November 26, 2002). "U.S. Says Yemen Aided Missile Strike". The Daily Gazette. Archived from the original on September 4, 2015. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ↑ "Foreign Correspondent – 02/03/2004: The Yemen Option". Abc.net.au. Archived from the original on September 6, 2013. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill; Barry, Bob. "Charting the data for US air strikes in Yemen, 2002 - 2014". The Long War Journal. Archived from the original on July 6, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ↑ US Broadens Terror Fight, Readying Troops for Yemen, New York Times , March 2, 2002 Archived November 14, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "U.S. Citizen Among Those Killed In Yemen Predator Missile Strike – The Tech". Tech.mit.edu. November 8, 2002. Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- ↑ Nyier Abdou (November 20, 2002). "Death by Predator". Al-Ahram Weekly. Archived from the original on January 23, 2011. Retrieved May 19, 2010.
- ↑ "Q&A: Targeted Killings" Archived November 8, 2021, at the Wayback Machine , Eben Kaplan, The New York Times , January 25, 2006. Retrieved October 8, 2010.
- ↑ "Profile: Kamal Derwish". History Commons . Archived from the original on December 25, 2016. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- ↑ "Drones spur Yemenis' distrust of government and U.S." Reuters. October 27, 2010. Archived from the original on December 15, 2021. Retrieved November 3, 2010.
- ↑ "Suspected U.S. drone missile strike leaves 2 militants dead in Yemen". The Daily Star Newspaper - Lebanon. Archived from the original on October 7, 2012. Retrieved October 26, 2014.
- ↑ Archived March 21, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Mazzetti, Mark, "Drone Strike In Yemen Was Aimed At Awlaki", New York Times , 7 May 2011, p. 11; Coker, Margaret, "Drone Targets Yemeni Cleric", Wall Street Journal , 7 May 2011, p. 1.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill, "AQAP confirms deaths of 2 commanders in US airstrike Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 21 July 2011.
- ↑ Mazzetti, Mark, "U.S. Is Intensifying A Secret Campaign Of Yemen Airstrikes", New York Times , 9 June 2011.
- ↑ Associated Press, "Secret CIA drone base being built to target Yemen militants", Japan Times , 16 June 2011, p. 1.
- ↑ DeYoung, Karen, "U.S. Air Attacks In Yemen Intensify", Washington Post , 17 September 2011, p. 1.
- ↑ Whitlock, Craig, and Greg Miller, "U.S. assembling secret drone bases in Africa, Arabian Peninsula, officials say Archived October 3, 2017, at the Wayback Machine ", Washington Post , 21 September 2011.
- ↑ Barnes, Julian E., "U.S. Expands Drone Flights To Take Aim At East Africa", Wall Street Journal , 21 September 2011, p. 1.
- ↑ Arrabyee, Nasser, and Mark Mazzetti, "U.S. Strikes In Yemen Said To Kill 8 Militants", New York Times , 15 July 2011, p. 9.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill, "US airstrike kills 6 al Qaeda fighters in Yemen: report Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Archived July 18, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Arrabyee, Nasser; Mazzetti, Mark (July 14, 2011). "U.S. Strikes in Yemen Said to Kill 8 Militants". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 15, 2021. Retrieved February 20, 2017.
- ↑ Whitlock, Craig, and Mohammed al-Qadhi, "Al-Qaeda Fugitive In Yemen Eludes Attack", Washington Post , 16 July 2011, p. 9.
- ↑ Al-Qadhi, Mohammed, "Airstrikes Kill Militants In S. Yemen", Washington Post , 2 August 2011, p. 9.
- ↑ Wan, William (August 2, 2011). "Militants killed in air attacks in south Yemen". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on July 31, 2018. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
- ↑ "US Drones Kill 15 in Yemen's Abyan Province- Yemen Post English Newspaper Online". yemenpost.net. Archived from the original on August 2, 2011. Retrieved September 30, 2015.
- ↑ Al-Haj, Ahmed, Associated Press, "Yemen strikes kill 30 al-Qaida-linked fighters", Military Times , 24 August 2011.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill, "US airstrikes in southern Yemen kill 30 AQAP fighters: report Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 1 September 2011.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill, "US airstrikes kill AQAP fighters in southern Yemen Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 22 September 2011.
- ↑ Almasmari, Hakim, Margaret Coker, and Siobhan Gorman, "Drone Kills Top Al Qaeda Figure", Wall Street Journal , 1 October 2011, p. 1.
- ↑ New York Times , "Drone Strike In Yemen", 6 October 2011.
- ↑ Associated Press, "Yemen Says Local Al-Qaida Chief, 6 Others Killed", Arizona Daily Star , 15 October 2011.
- ↑ Reuters, "U.S. Drone Kills Yemen Al Qaeda Leader's Relative: Source", 23 December 2011.
- ↑ DeYoung, Karen, "U.S. Airstrike Targets Al-Qaeda In Yemen", Washington Post , 1 February 2012, p. 10; Roggio, Bill, "US drone strike kills 11 AQAP leaders, fighters: report Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 31 January 2012.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill, "US drone strike kills 3 AQAP fighters in Yemen Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 12 March 2012.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill, "US drone strike kills 4 AQAP fighters Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 15 March 2012.
- ↑ "U.S. drone kills 14 al-Qaida militants in Yemen's south". Archived from the original on October 26, 2014. Retrieved October 26, 2014.
- ↑ Roggio, Bill, "AQAP confirms commander linked to Osama bin Laden killed in drone strike Archived December 20, 2021, at the Wayback Machine ", Long War Journal , 30 April 2012.
- ↑ Al-Haj, Ahmed (Associated Press), "Airstrike kills senior al-Qaida leader in Yemen Archived September 23, 2014, at the Wayback Machine ", Yahoo! News , 7 May 2012.
- ↑ "Yemen wedding convoy strike highlights civilian drone war toll". Yahoo News UK. December 13, 2013. Archived from the original on September 28, 2017. Retrieved October 26, 2014.
- ↑ "Drone strike in Yemen killed 17, mostly civilians". Your Middle East. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved October 26, 2014.
- ↑ "US drone strike kills civilians in central Yemen". December 12, 2013. Archived from the original on December 19, 2021. Retrieved October 26, 2014.
- ↑ "Yemen says U.S. drone struck a wedding convoy, killing 14 - CNN.com". CNN. December 13, 2013. Archived from the original on December 15, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2013.
- ↑ Ali, Zaid; King, Laura (December 13, 2013). "U.S. drone strike on Yemen wedding party kills 17". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved February 21, 2020.
- ↑ Bill Roggio: US kills 3 AQAP operatives in Yemen drone strike Archived December 19, 2021, at the Wayback Machine , March 3, 2014
- ↑ Schmitt, Eric (April 21, 2014). "U.S. Drones and Yemeni Forces Kill Qaeda-Linked Fighters, Officials Say". The New York Times. The New York Times. Archived from the original on September 9, 2021. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ↑ "Five killed in Yemen drone strike". Al Jazeera. June 14, 2014. Archived from the original on August 1, 2018. Retrieved June 16, 2014.