In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.
Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula FeCl3(H2O)x. Also called ferric chloride, these compounds are available both in anhydrous and hydrated forms which are both hygroscopic. They are common sources of iron in its +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous derivative is a Lewis acid, while the hydrate is a mild oxidizing agent. It is used as a water cleaner and as an etchant for metals.
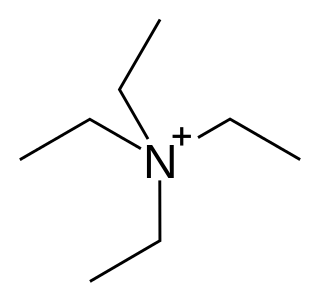
Tetraethylammonium (TEA) is a quaternary ammonium cation with the chemical formula [Et4N]+, consisting of four ethyl groups attached to a central nitrogen atom. It is a counterion used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salts of inorganic anions. It is used similarly to tetrabutylammonium, the difference being that its salts are less lipophilic, more easily crystallized and more toxic.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms a hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour.
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the dihydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations.

Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) describes any of several chemical compounds with the formula CrCl3 · xH2O, where x can be 0, 5, and 6. The anhydrous compound with the formula CrCl3 is a violet solid. The most common form of the trichloride is the dark green hexahydrate, CrCl3 · 6 H2O. Chromium chlorides find use as catalysts and as precursors to dyes for wool.

In chemistry, the term phosphonium describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.
A salt metathesis reaction, sometimes called a double displacement reaction, is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding affiliations. This reaction is represented by the general scheme:

18-Crown-6 is an organic compound with the formula [C2H4O]6 and the IUPAC name of 1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane. It is a white, hygroscopic crystalline solid with a low melting point. Like other crown ethers, 18-crown-6 functions as a ligand for some metal cations with a particular affinity for potassium cations (binding constant in methanol: 106 M−1). The point group of 18-crown-6 is S6. The dipole moment of 18-crown-6 varies in different solvent and under different temperature. Under 25 °C, the dipole moment of 18-crown-6 is 2.76 ± 0.06 D in cyclohexane and 2.73 ± 0.02 in benzene. The synthesis of the crown ethers led to the awarding of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Charles J. Pedersen.
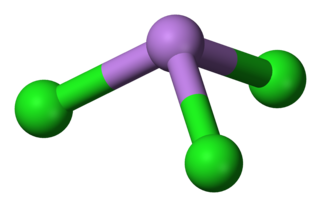
Arsenic trichloride is an inorganic compound with the formula AsCl3, also known as arsenous chloride or butter of arsenic. This poisonous oil is colourless, although impure samples may appear yellow. It is an intermediate in the manufacture of organoarsenic compounds.

Hexafluorophosphate is an anion with chemical formula of [PF6]−. It is an octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. [PF6]− is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, [SiF6]2−, and hexafluoroantimonate [SbF6]−. In this anion, phosphorus has a valence of 5. Being poorly nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion.
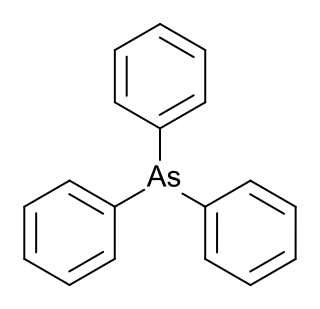
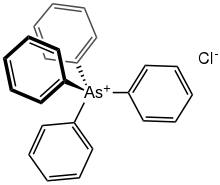
Triphenylarsine is the chemical compound with the formula As(C6H5)3. This organoarsenic compound, often abbreviated AsPh3, is a colorless crystalline solid that is used as a ligand and a reagent in coordination chemistry and organic synthesis. The molecule is pyramidal with As-C distances of 1.942–1.956 Å and C-As-C angles of 99.6–100.5°.

Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [( 3P)2N]Cl, often abbreviated [(Ph3P)2N]Cl, where Ph is phenyl C6H5, or even abbreviated [PPN]Cl or [PNP]Cl or PPNCl or PNPCl, where PPN or PNP stands for (Ph3P)2N. This colorless salt is a source of the [(Ph3P)2N]+ cation, which is used as an unreactive and weakly coordinating cation to isolate reactive anions. [(Ph3P)2N]+ is a phosphazene.
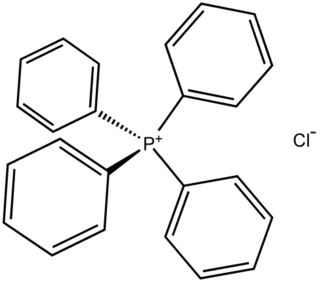
Tetraphenylphosphonium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula (C6H5)4PCl, abbreviated Ph4PCl or PPh4Cl. Tetraphenylphosphonium and especially tetraphenylarsonium salts were formerly of interest in gravimetric analysis of perchlorate and related oxyanions. This colourless salt is used to generate lipophilic salts from inorganic and organometallic anions. Thus, Ph4P+ is useful as a phase-transfer catalyst, again because it allows inorganic anions to dissolve in organic solvents.
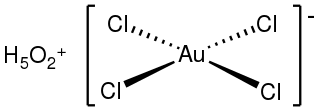
Chloroauric acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H[AuCl4]. It forms hydrates H[AuCl4]·nH2O. Both the trihydrate and tetrahydrate are known. Both are orange-yellow solids consisting of the planar [AuCl4]− anion. Often chloroauric acid is handled as a solution, such as those obtained by dissolution of gold in aqua regia. These solutions can be converted to other gold complexes or reduced to metallic gold or gold nanoparticles.
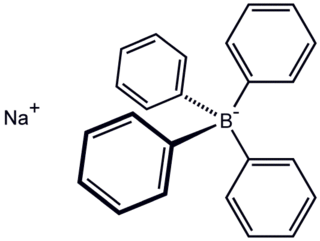
Sodium tetraphenylborate is the organic compound with the formula NaB(C6H5)4. It is a salt, wherein the anion consists of four phenyl rings bonded to boron. This white crystalline solid is used to prepare other tetraphenylborate salts, which are often highly soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry as a precipitating agent for potassium, ammonium, rubidium, and cesium ions, and some organic nitrogen compounds.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.

Tetraethylammonium cyanide is the organic compound with the formula (C2H5)4NCN. It is a "quat salt" of cyanide. It is a colorless, deliquescent solid that is soluble in polar organic media. It is used in the synthesis of cyanometallates.