
Perception is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the sensory system. Vision involves light striking the retina of the eye; smell is mediated by odor molecules; and hearing involves pressure waves.

In visual perception, an optical illusion is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that arguably appears to differ from reality. Illusions come in a wide variety; their categorization is difficult because the underlying cause is often not clear but a classification proposed by Richard Gregory is useful as an orientation. According to that, there are three main classes: physical, physiological, and cognitive illusions, and in each class there are four kinds: Ambiguities, distortions, paradoxes, and fictions. A classical example for a physical distortion would be the apparent bending of a stick half immersed in water; an example for a physiological paradox is the motion aftereffect. An example for a physiological fiction is an afterimage. Three typical cognitive distortions are the Ponzo, Poggendorff, and Müller-Lyer illusion. Physical illusions are caused by the physical environment, e.g. by the optical properties of water. Physiological illusions arise in the eye or the visual pathway, e.g. from the effects of excessive stimulation of a specific receptor type. Cognitive visual illusions are the result of unconscious inferences and are perhaps those most widely known.

An impossible object is a type of optical illusion that consists of a two-dimensional figure which is instantly and naturally understood as representing a projection of a three-dimensional object but cannot exist as a solid object. Impossible objects are of interest to psychologists, mathematicians and artists without falling entirely into any one discipline.
Gestalt psychology, gestaltism, or configurationism is a school of psychology and a theory of perception that emphasises the processing of entire patterns and configurations, and not merely individual components. It emerged in the early twentieth century in Austria and Germany as a rejection of basic principles of Wilhelm Wundt's and Edward Titchener's elementalist and structuralist psychology.

Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions
In photography and cinematography, perspective distortion is a warping or transformation of an object and its surrounding area that differs significantly from what the object would look like with a normal focal length, due to the relative scale of nearby and distant features. Perspective distortion is determined by the relative distances at which the image is captured and viewed, and is due to the angle of view of the image being either wider or narrower than the angle of view at which the image is viewed, hence the apparent relative distances differing from what is expected. Related to this concept is axial magnification – the perceived depth of objects at a given magnification.

An autostereogram is a two-dimensional (2D) image that can create the optical illusion of a three-dimensional (3D) scene. Autostereograms use only one image to accomplish the effect while normal stereograms require two. The 3D scene in an autostereogram is often unrecognizable until it is viewed properly, unlike typical stereograms. Viewing any kind of stereogram properly may cause the viewer to experience vergence-accommodation conflict.

Ambiguous images or reversible figures are visual forms that create ambiguity by exploiting graphical similarities and other properties of visual system interpretation between two or more distinct image forms. These are famous for inducing the phenomenon of multistable perception. Multistable perception is the occurrence of an image being able to provide multiple, although stable, perceptions.

An Ames room is a distorted room that creates an optical illusion. Likely influenced by the writings of Hermann Helmholtz, it was invented by American scientist Adelbert Ames Jr. in 1946, and constructed in the following year.

Roger Newland Shepard was an American cognitive scientist and author of the "universal law of generalization" (1987). He was considered a father of research on spatial relations. He studied mental rotation, and was an inventor of non-metric multidimensional scaling, a method for representing certain kinds of statistical data in a graphical form that can be comprehended by humans. The optical illusion called Shepard tables and the auditory illusion called Shepard tones are named for him.
Geons are the simple 2D or 3D forms such as cylinders, bricks, wedges, cones, circles and rectangles corresponding to the simple parts of an object in Biederman's recognition-by-components theory. The theory proposes that the visual input is matched against structural representations of objects in the brain. These structural representations consist of geons and their relations. Only a modest number of geons are assumed. When combined in different relations to each other and coarse metric variation such as aspect ratio and 2D orientation, billions of possible 2- and 3-geon objects can be generated. Two classes of shape-based visual identification that are not done through geon representations, are those involved in: a) distinguishing between similar faces, and b) classifications that don’t have definite boundaries, such as that of bushes or a crumpled garment. Typically, such identifications are not viewpoint-invariant.
Monocular vision is vision using only one eye. It is seen in two distinct categories: either a species moves its eyes independently, or a species typically uses two eyes for vision, but is unable to use one due to circumstances such as injury.

Miniature faking, also known as diorama effect or diorama illusion, is a process in which a photograph of a life-size location or object is made to look like a photograph of a miniature scale model. Blurring parts of the photo simulates the shallow depth of field normally encountered in close-up photography, making the scene seem much smaller than it actually is; the blurring can be done either optically when the photograph is taken, or by digital postprocessing. Many diorama effect photographs are taken from a high angle to simulate the effect of looking down on a miniature. Tilt–shift photography is also associated with miniature faking.

In visual perception, the kinetic depth effect refers to the phenomenon whereby the three-dimensional structural form of an object can be perceived when the object is moving. In the absence of other visual depth cues, this might be the only perception mechanism available to infer the object's shape. Being able to identify a structure from a motion stimulus through the human visual system was shown by Hans Wallach and O'Connell in the 1950s through their experiments.
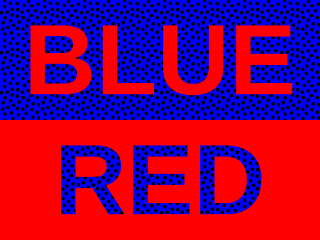
Chromostereopsis is a visual illusion whereby the impression of depth is conveyed in two-dimensional color images, usually of red–blue or red–green colors, but can also be perceived with red–grey or blue–grey images. Such illusions have been reported for over a century and have generally been attributed to some form of chromatic aberration.
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision, color vision, scotopic vision, and mesopic vision, using light in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment. This is different from visual acuity, which refers to how clearly a person sees. A person can have problems with visual perceptual processing even if they have 20/20 vision.
Haptic memory is the form of sensory memory specific to touch stimuli. Haptic memory is used regularly when assessing the necessary forces for gripping and interacting with familiar objects. It may also influence one's interactions with novel objects of an apparently similar size and density. Similar to visual iconic memory, traces of haptically acquired information are short lived and prone to decay after approximately two seconds. Haptic memory is best for stimuli applied to areas of the skin that are more sensitive to touch. Haptics involves at least two subsystems; cutaneous, or everything skin related, and kinesthetic, or joint angle and the relative location of body. Haptics generally involves active, manual examination and is quite capable of processing physical traits of objects and surfaces.
Representational momentum is a small, but reliable, error in our visual perception of moving objects. Representational moment was discovered and named by Jennifer Freyd and Ronald Finke. Instead of knowing the exact location of a moving object, viewers actually think it is a bit further along its trajectory as time goes forward. For example, people viewing an object moving from left to right that suddenly disappears will report they saw it a bit further to the right than where it actually vanished. While not a big error, it has been found in a variety of different events ranging from simple rotations to camera movement through a scene. The name "representational momentum" initially reflected the idea that the forward displacement was the result of the perceptual system having internalized, or evolved to include, basic principles of Newtonian physics, but it has come to mean forward displacements that continue a presented pattern along a variety of dimensions, not just position or orientation. As with many areas of cognitive psychology, theories can focus on bottom-up or top-down aspects of the task. Bottom-up theories of representational momentum highlight the role of eye movements and stimulus presentation, while top-down theories highlight the role of the observer's experience and expectations regarding the presented event.

Hans Wallach was a German-American experimental psychologist whose research focused on perception and learning. Although he was trained in the Gestalt psychology tradition, much of his later work explored the adaptability of perceptual systems based on the perceiver's experience, whereas most Gestalt theorists emphasized inherent qualities of stimuli and downplayed the role of experience. Wallach's studies of achromatic surface color laid the groundwork for subsequent theories of lightness constancy, and his work on sound localization elucidated the perceptual processing that underlies stereophonic sound. He was a member of the National Academy of Sciences, a Guggenheim Fellow, and recipient of the Howard Crosby Warren Medal of the Society of Experimental Psychologists.

An accidental viewpoint is a singular position from which an image can be perceived, creating either an ambiguous image or an illusion. The image perceived at this angle is viewpoint-specific, meaning it cannot be perceived at any other position, known as generic or non-accidental viewpoints. These view-specific angles are involved in object recognition. In its uses in art and other visual illusions, the accidental viewpoint creates the perception of depth often on a two-dimensional surface with the assistance of monocular cues.














