Related Research Articles

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 6, 1956. Incumbent Republican President Dwight D. Eisenhower and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Richard Nixon, were reelected, defeating for a second time Democrat Adlai Stevenson II, former Illinois governor. This election was the sixth and most recent rematch in American presidential history. It was the second time in which the winner was the same both times, the first being William McKinley's victories over William Jennings Bryan in 1896 and 1900. This was the last election before term limits established by the Twenty-second Amendment to the United States Constitution, which first applied to Eisenhower, became effective.
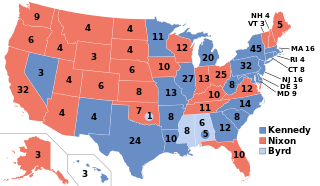
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1960. The Democratic ticket of Senator John F. Kennedy and his running mate, Senate Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, narrowly defeated the Republican ticket of incumbent Vice President Richard Nixon and his running mate, U.N. Ambassador Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. This was the first election in which 50 states participated, marking the first participation of Alaska and Hawaii, and the last in which the District of Columbia did not. This made it the only presidential election in which the threshold for victory was 269 electoral votes. It was also the first election in which an incumbent president—in this case, Dwight D. Eisenhower—was ineligible to run for a third term because of the term limits established by the 22nd Amendment.

On November 22, 1963, John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States, was assassinated while riding in a presidential motorcade through Dealey Plaza in Dallas, Texas. Kennedy was in the vehicle with his wife Jacqueline, Texas governor John Connally, and Connally's wife Nellie, when he was fatally shot from the nearby Texas School Book Depository by Lee Harvey Oswald, a former U.S. Marine. The motorcade rushed to Parkland Memorial Hospital, where Kennedy was pronounced dead about 30 minutes after the shooting; Connally was also wounded in the attack but recovered. Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson was hastily sworn in as president two hours and eight minutes later aboard Air Force One at Dallas Love Field.

Ethel Kennedy was an American human rights advocate. She was the wife of U.S. senator Robert F. Kennedy, a sister-in-law of U.S. president John F. Kennedy, and a daughter of businessman George Skakel.

Rory Elizabeth Katherine Kennedy is an American documentary filmmaker. Kennedy has made documentary films that center on social issues such as addiction, her opposition to nuclear power, the treatment of prisoners-of-war, and the politics of the Mexican border fence.

Michael Richard Beschloss is an American historian specializing in the United States presidency. He is the author of nine books on the presidency.

Arthur Meier Schlesinger Jr. was an American historian, social critic, and public intellectual. The son of the influential historian Arthur M. Schlesinger Sr. and a specialist in American history, much of Schlesinger's work explored the history of 20th-century American liberalism. In particular, his work focused on leaders such as Harry S. Truman, Franklin D. Roosevelt, John F. Kennedy, and Robert F. Kennedy. In the 1952 and 1956 presidential campaigns, he was a primary speechwriter and adviser to the Democratic presidential nominee, Adlai Stevenson II. Schlesinger served as special assistant and "court historian" to President Kennedy from 1961 to 1963. He wrote a detailed account of the Kennedy administration, from the 1960 presidential campaign to the president's state funeral, titled A Thousand Days: John F. Kennedy in the White House, which won the 1966 Pulitzer Prize for Biography or Autobiography.
Charles Eli Guggenheim was an American documentary film director, producer, and screenwriter. He was the most honored documentary filmmaker in the academy history, winning four Oscars from twelve nominations.

John Fitzgerald Kennedy, also known as JFK, was the 35th president of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the youngest person elected president. Kennedy served at the height of the Cold War, and the majority of his foreign policy concerned relations with the Soviet Union and Cuba. A Democrat, Kennedy represented Massachusetts in both houses of the United States Congress prior to his presidency.
Robert Lincoln Drew was an American documentary filmmaker known as one of the pioneers—and sometimes called father—of cinéma vérité, or direct cinema, in the United States. Two of his films, Primary and Crisis: Behind a Presidential Commitment, have been named to the National Film Registry of the Library of Congress. The moving image collection of Robert Drew is housed at the Academy Film Archive. The Academy Film Archive has preserved a number of his films, including Faces of November, Herself: Indira Gandhi, and Bravo!/Kathy's Dance. His many awards include an International Documentary Association Career Achievement Award.

John F. Kennedy's tenure as the 35th president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 1961, and ended with his assassination on November 22, 1963. Kennedy, a Democrat from Massachusetts, took office following his narrow victory over Republican incumbent vice president Richard Nixon in the 1960 presidential election. He was succeeded by Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson.

Stanley Bruce Herschensohn was an American conservative political commentator, author, film director, and senior fellow at the Pepperdine University School of Public Policy in Malibu, California.
Robert Kennedy Remembered is a 1968 American short documentary film produced and directed by Charles Guggenheim. In 1969, it won an Oscar for Best Short Subject at the 41st Academy Awards.

Robert Francis Kennedy, also known as RFK, was an American politician and lawyer. He served as the 64th United States attorney general from January 1961 to September 1964, and as a U.S. senator from New York from January 1965 until his assassination in June 1968, when he was running for the Democratic presidential nomination. Like his brothers John F. Kennedy and Ted Kennedy, he was a prominent member of the Democratic Party and is considered an icon of modern American liberalism.

The Stand in the Schoolhouse Door took place at Foster Auditorium at the University of Alabama on June 11, 1963. In a symbolic attempt to keep his inaugural promise of "segregation now, segregation tomorrow, segregation forever" and stop the desegregation of schools, George Wallace, the Democratic Governor of Alabama, stood at the door of the auditorium as if to block the way of the two African American students attempting to enter: Vivian Malone and James Hood.
Crisis: Behind a Presidential Commitment is a 1963 direct cinema documentary film directed by Robert Drew. The film centers on the University of Alabama's "Stand in the Schoolhouse Door" integration crisis of June 1963. Drew and the other filmmakers, including D. A. Pennebaker and Richard Leacock, were given expanded access to key areas, including United States President John F. Kennedy's Oval Office and the homes of United States Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy and Governor George Wallace of Alabama. The film first aired on the American Broadcasting Company (ABC) as an installment of Close-Up! four months after the incident, on October 28, 1963. It was added to the National Film Registry of the Library of Congress on December 28, 2011.

Pushinka, a dog, was given by the Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev to the President of the United States, John F. Kennedy, in 1961. Pushinka was the daughter of Strelka, who had travelled into space aboard Korabl-Sputnik 2.

A Tour of the White House with Mrs. John F. Kennedy was a television special featuring the first lady of the United States, Jacqueline Kennedy, on a tour of the recently renovated White House. It was broadcast on Valentine's Day, February 14, 1962, on both CBS and NBC, and broadcast four days later on ABC. The program was the first televised tour of the White House by a first lady and is considered the first prime-time documentary specifically designed to appeal to a female audience.

The 1960 presidential campaign of John F. Kennedy, then junior United States senator from Massachusetts, was formally launched on January 2, 1960, as Senator Kennedy announced his intention to seek the Democratic Party nomination for the presidency of the United States in the 1960 presidential election.
Robert F. Kennedy, the 64th United States Attorney General, a U.S. senator from New York, and the brother of United States president John F. Kennedy, has frequently been depicted or referenced in works of popular culture.
References
- ↑ "The Five Cities of June (1963)". Movies & TV Dept. The New York Times . 2012. Archived from the original on October 15, 2012. Retrieved November 29, 2008.
- ↑ "The 36th Academy Awards (1964) Nominees and Winners". oscars.org. Retrieved June 1, 2019.
- ↑ The Five Cities of June, 1963, JFK Presidential Library