Related Research Articles
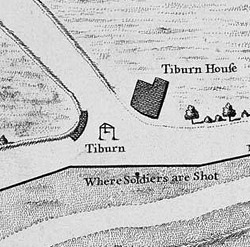
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in the county of Middlesex, England, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne, means 'boundary stream'.

Baucis and Philemon are two characters from Greek mythology, only known to us from Ovid's Metamorphoses. Baucis and Philemon were an old married couple in the region of Tyana, which Ovid places in Phrygia, and the only ones in their town to welcome disguised gods Zeus and Hermes, thus embodying the pious exercise of hospitality, the ritualized guest-friendship termed xenia, or theoxenia when a god was involved.

Hanging is killing a person by suspending them from the neck with a noose or ligature. Hanging has been a common method of capital punishment since the Middle Ages, and is the primary execution method in numerous countries and regions. The first known account of execution by hanging is in Homer's Odyssey. Hanging is also a method of suicide.

Gibbeting is the use of a gallows-type structure from which the dead or dying bodies of criminals were hanged on public display to deter other existing or potential criminals. Occasionally, the gibbet was also used as a method of public execution, with the criminal being left to die of exposure, thirst and/or starvation. The practice of placing a criminal on display within a gibbet is also called "hanging in chains".

"Ode on a Grecian Urn" is a poem written by the English Romantic poet John Keats in May 1819, first published anonymously in Annals of the Fine Arts for 1819.

"Journey of the Magi" is a 43-line poem written in 1927 by T. S. Eliot (1888–1965). It is one of five poems that Eliot contributed for a series of 38 pamphlets by several authors collectively titled the Ariel Poems and released by the British publishing house Faber and Gwyer. Published in August 1927, "Journey of the Magi" was the eighth in the series and was accompanied by illustrations drawn by American-born avant garde artist Edward McKnight Kauffer (1890–1954). The poems, including "Journey of the Magi", were later published in both editions of Eliot's collected poems in 1936 and 1963.

Hangmen Also Die! is a 1943 war film directed by the Austrian director Fritz Lang and written by John Wexley from a story by Bertolt Brecht and Lang. The film stars Brian Donlevy, with Walter Brennan, Anna Lee, and Gene Lockhart, and Dennis O'Keefe in support. Alexander Granach has a showy role as a Gestapo detective, and Hans Heinrich von Twardowski has a cameo as Reinhard Heydrich. Hanns Eisler composed the Academy Award nominated score, and James Wong Howe was cinematographer.
James Berry was an English executioner from 1884 until 1891. Berry was born in Heckmondwike in the West Riding of Yorkshire, where his father worked as a wool-stapler. His most important contribution to the science of hanging was his refinement of the long drop method developed by William Marwood, whom Berry knew quite well. His improvements were intended to diminish mental and physical suffering and some of them remained standard practice until the abolition of capital punishment for murder.

Horace Raymond Huntley was an English actor who appeared in dozens of British films from the 1930s to the 1970s. He also appeared in the ITV period drama Upstairs, Downstairs as the pragmatic family solicitor Sir Geoffrey Dillon.
Hangman may refer to:
"The Maid Freed from the Gallows" is one of many titles of a centuries-old folk song about a condemned maiden pleading for someone to buy her freedom from the executioner. Other variants and/or titles include "The Gallows Pole", "The Gallis Pole", "Hangman", "The Prickle-Holly Bush", "The Golden Ball", and "Hold Up Your Hand, Old Joshua She Cried." In the collection of ballads compiled by Francis James Child in the late 19th century, it is indexed as Child Ballad number 95; 11 variants, some fragmentary, are indexed as 95A to 95K. The Roud Folk Song Index identifies it as number 144.

Dule trees, or dool trees, in Britain were used as gallows for public hangings. They were also used as gibbets for the display of the corpse for a considerable period after such hangings. These "trees of lamentation or grief" were usually growing in prominent positions or at busy thoroughfares, particularly at crossroads, so that justice could be seen to have been done and as a salutary warning to others. Place names such as Gallows-Hill, Gallows-See, Gallows-Fey and Hill of the Gallows record the site of such places of execution.

William Calcraft was a 19th-century English hangman, one of the most prolific of British executioners. It is estimated in his 45-year career he carried out 450 executions. A cobbler by trade, Calcraft was initially recruited to flog juvenile offenders held in Newgate Prison. While selling meat pies on streets around the prison, Calcraft met the City of London's hangman, John Foxton.

Dov Béla Gruner was a Hungarian-born Zionist activist in Mandatory Palestine and a member of the pre-state Jewish underground Irgun. On April 16, 1947, Gruner was executed by the British Mandatory authorities in Palestine on charges of "firing on policemen and setting explosive charges with the intent of killing personnel on His Majesty's service." He is honored as one of the Olei Hagardom, the twelve Jewish pre-independence fighters who were executed by British and Egyptian authorities.

Claude Dauphin was a French actor. He appeared in more than 130 films between 1930 and 1978, including Barbarella, The Quiet American, and a voice role in The Tale of the Fox, considered to be one of the earliest stop-motion animated films.
"We are Seven" is a poem written by William Wordsworth and published in his Lyrical Ballads. It describes a discussion between an adult poetic speaker and a "little cottage girl" about the number of brothers and sisters who dwell with her. The poem turns on the question of whether to account two dead siblings as part of the family.

John Glyn-Jones was a British stage, radio, television and film actor.
Black Francis McHugh, also known as "Proinsías Dubh", was a notorious highwayman, or Rapparee, who 'robbed the rich to give to the poor' at the end of the 18th century. His origins lay in Meencloghore.
The history of vigilante justice and the Montana Vigilantes began in 1863 in what was at the time a remote part of eastern Idaho Territory. Vigilante activities continued, although somewhat sporadically, through the Montana Territorial period until the territory became the state of Montana on November 8, 1889. Vigilantism arose because territorial law enforcement and the courts had very little power in the remote mining camps during the territorial period.
References
- 1 2 "Full text of "Copyright Renewals 1923–1964"". Internet Archive. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ↑ Mainstream, Volume 7, Issue 1. 1954.