
Gospel originally meant the Christian message, but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words and deeds of Jesus, culminating in his trial and death and concluding with various reports of his post-resurrection appearances. Modern scholars are cautious of relying on the gospels uncritically, but nevertheless, they provide a good idea of the public career of Jesus, and critical study can attempt to distinguish the original ideas of Jesus from those of the later authors.

Papias was a Greek Apostolic Father, Bishop of Hierapolis, and author who lived c. 60 – c. 130 AD. He wrote the Exposition of the Sayings of the Lord in five books. This work, which is lost apart from brief excerpts in the works of Irenaeus of Lyons and Eusebius of Caesarea, is an important early source on Christian oral tradition and especially on the origins of the canonical Gospels.

The Gospel of Thomas is an extra-canonical sayings gospel. It was discovered near Nag Hammadi, Egypt, in December 1945 among a group of books known as the Nag Hammadi library. Scholars speculate that the works were buried in response to a letter from Bishop Athanasius declaring a strict canon of Christian scripture. Scholars have proposed dates of composition as early as AD 200 and as late as AD 250. Since its discovery, many scholars have seen it as evidence in support of the existence of a "Q source," which might have been very similar in its form as a collection of sayings of Jesus without any accounts of his deeds or his life and death, referred to as a sayings gospel.

The Jesus Seminar was a group of about 50 critical biblical scholars and 100 laymen founded in 1985 by Robert Funk that originated under the auspices of the Westar Institute. The seminar was very active through the 1980s and 1990s, and into the early 21st century.

The gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical wording. They stand in contrast to John, whose content is largely distinct. The term synoptic comes via Latin from the Greek σύνοψις, synopsis, i.e. "(a) seeing all together, synopsis"; the sense of the word in English, the one specifically applied to these three gospels, of "giving an account of the events from the same point of view or under the same general aspect" is a modern one.

The Gospel of the Hebrews, or Gospel according to the Hebrews, is a lost Jewish–Christian gospel. The text of the gospel is lost, with only fragments of it surviving as brief quotations by the early Church Fathers and in apocryphal writings. The fragments contain traditions of Jesus' pre-existence, incarnation, baptism, and probable temptation, along with some of his sayings. Distinctive features include a Christology characterized by the belief that the Holy Spirit is Jesus' Divine Mother and a first resurrection appearance to James, the brother of Jesus, showing a high regard for James as the leader of the Jewish Christian church in Jerusalem. It was probably composed in Greek in the first decades of the 2nd century, and is believed to have been used by Greek-speaking Jewish Christians in Egypt during that century.

The Gospel of Philip is a non-canonical Gnostic Gospel dated to around the 3rd century but lost in medieval times until rediscovered by accident, buried with other texts near Nag Hammadi in Egypt, in 1945.
Agrapha are sayings of Jesus that are not found in the canonical Gospels. The term was used for the first time by J.G. Körner, a German Bible scholar, in 1776.

Guy Mattison Davenport was an American writer, translator, illustrator, painter, intellectual, and teacher.
Benjamin Urrutia is an author and scholar. With Guy Davenport, Urrutia edited The Logia of Yeshua, which collected what Urrutia and Davenport consider to be Jesus' authentic sayings from a variety of canonical and non-canonical sources. Urrutia interprets Jesus' mission as a leadership role in the "Israelite nonviolent resistance to Roman oppression".
The term logia, plural of logion, is used variously in ancient writings and modern scholarship in reference to communications of divine origin. In pagan contexts, the principal meaning was "oracles", while Jewish and Christian writings used logia in reference especially to "the divinely inspired Scriptures". A famous and much-debated occurrence of the term is in the account by Papias of Hierapolis on the origins of the canonical Gospels. Since the 19th century, New Testament scholarship has tended to reserve the term logion for a divine saying, especially one spoken by Jesus, in contrast to narrative, and to call a collection of such sayings, as exemplified by the Gospel of Thomas, logia.

M source, which is sometimes referred to as M document, or simply M, comes from the M in "Matthean material". It is a hypothetical textual source for the Gospel of Matthew. M Source is defined as that 'special material' of the Gospel of Matthew that is neither Q source nor Mark.

The Apocryphon of James, also known by the translation of its title – the Secret Book of James, is a pseudonymous text amongst the New Testament apocrypha. It describes the secret teachings of Jesus to Peter and James, given after the Resurrection but before the Ascension.

The baptism of Jesus by John the Baptist is a major event in the life of Jesus which is described in three of the gospels: Matthew, Mark and Luke. It is considered to have taken place at Al-Maghtas, also called Bethany Beyond the Jordan, today located in Jordan.

The criterion of embarrassment is a type of critical analysis in which an account is likely to be true as the author would have no reason to invent an account which might embarrass them. Certain Biblical scholars have used this as a metric for assessing whether the New Testament's accounts of Jesus' actions and words are historically probable.
The term Bible fiction refers to works of fiction which use characters, settings and events taken from the Bible. The degree of fictionalization in these works varies and, although they are often written by Christians or Jews, this is not always the case.

The Q source is a hypothetical written collection of primarily Jesus' sayings. Q is part of the common material found in the Gospels of Matthew and Luke but not in the Gospel of Mark. According to this hypothesis, this material was drawn from the early Church's oral gospel traditions.

Oral gospel traditions is the hypothetical first stage in the formation of the written gospels as information was passed by word of mouth. These oral traditions included different types of stories about Jesus. For example, people told anecdotes about Jesus healing the sick and debating with his opponents. The traditions also included sayings attributed to Jesus, such as parables and teachings on various subjects which, along with other sayings, formed the oral gospel tradition. The supposition of such traditions have been the focus of scholars such as Bart Ehrman, James Dunn, and Richard Bauckham, although each scholars vary widely on their conclusions, with Ehrman and Bauckham publicly debating on the subject.
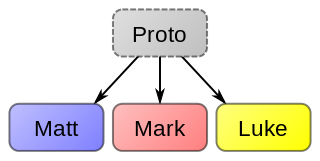
The Hebrew Gospel hypothesis is that a lost gospel, written in Hebrew or Aramaic, predated the four canonical gospels. Some have suggested a complete unknown proto-gospel as the source of the canonical gospels. This hypothesis is usually based upon an early Christian tradition from the 2nd-century bishop Papias of Hierapolis. According to Papias, Matthew the Apostle was the first to compose a gospel, and he did so in Hebrew. Papias appeared to imply that this Hebrew or Aramaic gospel was subsequently translated into the canonical Gospel of Matthew. Jerome took this information one step further and claimed that all known Jewish-Christian gospels really were one and the same, and that this gospel was the authentic Matthew. As a consequence he assigned all known quotations from Jewish-Christian gospels to the "gospels of the Hebrews", but modern studies have shown this to be untenable. Modern variants of the hypothesis survive, but have not found favor with scholars as a whole.
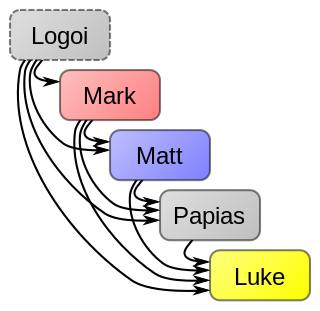
Advanced by Dennis R. MacDonald, the Q+/Papias hypothesis (Q+/PapH) offers an alternative solution to the synoptic problem. MacDonald prefers to call this expanded version of Q Logoi of Jesus, which is supposed to have been its original title.















