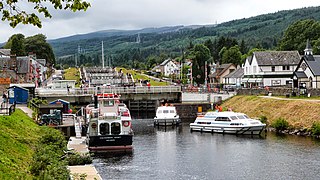Fort William formerly and, , formerly is a town in Lochaber in the Scottish Highlands, located on the eastern shore of Loch Linnhe. At the 2011 census, Fort William had a population of 10,459, making it the second largest settlement in both the Highland council area, and the whole of the Scottish Highlands; only the city of Inverness has a larger population.
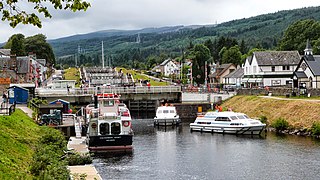
Fort Augustus is a settlement in the parish of Boleskine and Abertarff, at the south-west end of Loch Ness, Scottish Highlands. The village has a population of around 646 (2001). Its economy is heavily reliant on tourism.

Inverness is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Historically it served as the county town of the county of Inverness-shire. Inverness lies near two important battle sites: the 11th-century battle of Blàr nam Fèinne against Norway which took place on the Aird, and the 18th century Battle of Culloden which took place on Culloden Moor. It is the northernmost city in the United Kingdom and lies within the Great Glen at its northeastern extremity where the River Ness enters the Beauly Firth. At the latest, a settlement was established by the 6th century with the first royal charter being granted by Dabíd mac Maíl Choluim in the 12th century. Inverness and Inverness-shire are closely linked to various influential clans, including Clan Mackintosh, Clan Fraser and Clan MacKenzie.

Simon Fraser, 11th Lord Lovat, nicknamed 'the Fox', was a Scottish Jacobite and Chief of Clan Fraser of Lovat, known for his feuding and changes of allegiance. In 1715, he had been a supporter of the House of Hanover, but in 1745 he changed sides and supported the Stuart claim on the crown of Great Britain. Lovat was among the Highlanders defeated at the Battle of Culloden and convicted of treason against the Crown, following which he was sentenced to death and subsequently beheaded.

Mallaig is a port in Lochaber, on the west coast of the Highlands of Scotland. The local railway station, Mallaig, is the terminus of the West Highland railway line and the town is linked to Fort William by the A830 road – the "Road to the Isles".

Fort George is a large 18th-century fortress near Ardersier, to the north-east of Inverness in the Highland council area of Scotland. It was built to control the Scottish Highlands in the aftermath of the Jacobite rising of 1745, replacing a Fort George in Inverness constructed after the 1715 Jacobite rising to control the area. The current fortress has never been attacked and has remained in continuous use as a garrison.

The Great Glen, also known as Glen Albyn or Glen More, is a glen in Scotland running for 62 miles (100 km) from Inverness on the edge of Moray Firth, in an approximately straight line to Fort William at the head of Loch Linnhe. It follows a geological fault known as the Great Glen Fault, and bisects the Scottish Highlands into the Grampian Mountains to the southeast and the Northwest Highlands to the northwest.

Kilchurn Castle is a ruined structure on a rocky peninsula at the northeastern end of Loch Awe, in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It was first constructed in the mid-15th century as the base of the Campbells of Glenorchy, who extended both the castle and their territory in the area over the next 150 years. After the Campbells became Earls of Breadalbane and moved to Taymouth Castle, Kilchurn fell out of use and was in ruins by 1770. It is now in the care of Historic Environment Scotland and is open to the public in summer.

Beauly is a village in the Highland area, on the River Beauly, 5 miles (8 km) west of Inverness by the Far North railway line. The town is historically within Kilmorack Parish of the Scottish County of Inverness.

Clan Fraser of Lovat is a Highland Scottish clan and the principal branch of Clan Fraser. The Frasers of Lovat are strongly associated with Inverness and the surrounding area since the Clan's founder gained lands there in the 13th century. The Frasers were originally based in the Aberdeenshire area, and both the Clan Fraser and the Clan Fraser of Lovat have their own separate clan chiefs who are recognized by the Lord Lyon King of Arms under Scottish law.

Aberchalder is a small settlement and estate at the northern end of Loch Oich in the Scottish Highlands and is in the Highland council area of Scotland. It lies on the A82 road and is situated in two parishes, Boleskine and Kilmonivaig. Fort Augustus is within 5 mi (8.0 km).

The Invergarry and Fort Augustus Railway was a branch-line railway built in Scotland, connecting the named places with the main line at Spean Bridge. It opened in 1903.

Fort Augustus Abbey, properly St. Benedict's Abbey, at Fort Augustus, Inverness-shire, Scotland, was a Benedictine monastery, from late in the nineteenth century to 1998 that also housed a school for young boys until 1993.

The siege of Fort William took place in the Scottish Highlands during the 1745 Jacobite Rising, from 20 March to 3 April 1746.

Loch Ness is a large freshwater loch in the Scottish Highlands extending for approximately 37 kilometres southwest of Inverness. It takes its name from the River Ness, which flows from the northern end. Loch Ness is best known for claimed sightings of the cryptozoological Loch Ness Monster, also known affectionately as "Nessie". It is one of a series of interconnected, murky bodies of water in Scotland; its water visibility is exceptionally low due to a high peat content in the surrounding soil. The southern end connects to Loch Oich by the River Oich and a section of the Caledonian Canal. The northern end connects to Loch Dochfour via the River Ness, which then ultimately leads to the North Sea via the Moray Firth.

Bernera Barracks is in Glenelg in the West Highlands of Scotland. The barracks were constructed between 1717 and 1723 as part of a campaign by the British government to subdue the local population which had risen up in arms in the Jacobite Rising of 1715, and which would do so again in 1745. The barracks were designed by Andrews Jelfe and John Lambertus Romer of the Board of Ordnance, or possibly their predecessor James Smith, and built by Sir Patrick Strachan. Some of the stone used in the construction was taken from Dun Telve and Dun Troddan, nearby iron-age brochs. The Government troops who were garrisoned here during the Jacobite uprisings were also intended to control the crossing to Skye. Following the 1715 rising, Glenelg was chosen along with Fort George, Fort Augustus and Fort William as one of four sites in the Highlands for military barracks.

A network of military roads, sometimes called General Wade's Military Roads, was constructed in the Scottish Highlands during the middle part of the 18th century as part of an attempt by the British Government to bring order to a part of the country which had risen up in the Jacobite rebellion of 1715.

The siege of Fort Augustus took place from 22 February to 1 March 1746, during the Jacobite rising of 1745. After a short siege, the government garrison surrendered to a Jacobite force, which then moved on to besiege Fort William, using artillery captured at Fort Augustus.

The first siege of Fort Augustus, at the SW end of Loch Ness, Scotland, took place in December 1745 and was part of the Jacobite rising of 1745.

The Raids on Lochaber and Shiramore took place in the Scottish Highlands between 22 May and 31 August 1746 and were part of the closing operations of the British-Hanoverian Government to bring to an end the Jacobite rising of 1745. Sometimes referred to as the "mopping up" operations, many rebels surrendered themselves and their arms, while others were captured and punished. It also included the hunt for the Jacobite leader Bonnie Prince Charles Edward Stuart otherwise known as the Young Pretender. Most of the work was done on behalf of the Government by the Independent Highland Companies of militia, the Campbell of Argyll Militia and also Loudon's Highlanders regiment.