
Eurostar is an international high-speed rail service in Western Europe, connecting Belgium, France, Germany, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom.

The sleeping car or sleeper is a railway passenger car that can accommodate all passengers in beds of one kind or another, for the purpose of sleeping. George Pullman was the American innovator of the sleeper car.
The Rail Delivery Group Limited (RDG), previously the Association of Train Operating Companies, is the British rail industry membership body that brings together passenger and freight rail companies, Network Rail and High Speed 2. The RDG is approximately half-funded by Network Rail, the remainder of its funding being provided by the various transport groups it represents.

Heathrow Express is a high-frequency airport rail link operating between London Heathrow Airport and London Paddington. Opened in 1998, trains run non-stop, with a journey time of 15 minutes. The service is operated jointly by Great Western Railway and Heathrow Express Operating Company, a wholly owned subsidiary of Heathrow Airport Holdings. Around 16,000 passengers use the service each day.
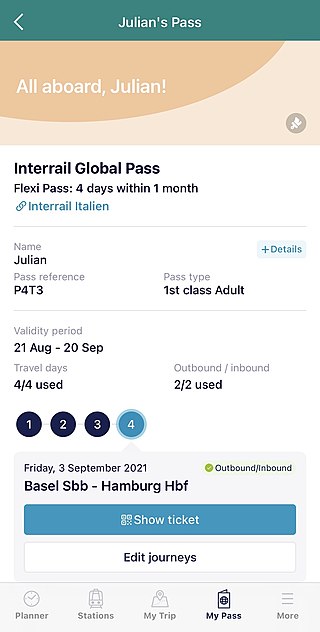
The Interrail Pass is a rail pass available to European citizens and residents. Citizens of other countries residing outside Europe may purchase the Eurail Pass instead. Types of Interrail Pass include the Interrail Global Pass and the Interrail One Country Pass.

Sirkeci railway station, listed on maps as Istanbul railway station, is a railway terminal in Istanbul, Turkey. The terminal is located in Sirkeci, on the tip of Istanbul's historic peninsula, right next to the Golden Horn and just northwest of Gülhane Park and the Topkapı Palace. Sirkeci Terminal on the European side of the Bosporus strait, along with Haydarpaşa Terminal on the Asian side, are Istanbul's two intercity and commuter railway terminals. Built in 1890 by the Oriental Railway as the eastern terminus of the world-famous Orient Express that once operated between Paris and Istanbul in the period between 1883 and 2009, Sirkeci Terminal has become a symbol of the city. As of 19 March 2013, service to the station was indefinitely suspended due to the rehabilitation of the existing line between Kazlıçeşme and Halkalı for the new Marmaray commuter rail line. On 29 October 2013, a new underground station was opened to the public and is serviced by Marmaray trains travelling across the Bosphorus. Station reopened on 26 February 2024 as part of T6 Sirkeci–Kazlıçeşme Tramway Line / U3 Sirkeci–Kazlıçeşme Rail Line. Sirkeci Terminal has a total of 4 platforms with 7 tracks. Formerly, commuter trains to Halkalı would depart from tracks 2, 3 and 4; while regional trains to Kapıkule, Edirne and Uzunköprü, along with international trains to Bucharest, Sofia and Belgrade would depart from tracks 1 and 5.
The Eurail Pass, introduced in 1959 and formerly known as Europass or Eurorail Pass, is a rail pass which permits travel through 33 European countries on nearly all railroads and several shipping lines. The Eurail Group, based in Utrecht, is responsible for the marketing and management of the Eurail and Interrail passes. The company is owned by over 35 European railway and shipping companies. The Eurail Pass is available to non-European residents, and the Interrail Pass is available to European residents. The passes, which provide access to 250,000 kilometres (160,000 mi) of European railway, are used by over 33,000 travellers annually.

Caledonian Sleeper is the collective name for overnight sleeper train services between London and Scotland, in the United Kingdom. It is one of only two currently operating sleeper services on the railway in the United Kingdom, the other being the Night Riviera which runs between London and Penzance.

ScotRail was a train operating company in Scotland owned by National Express that operated the ScotRail franchise from March 1997 until October 2004. Prior to March 1997 ScotRail ran the trains and after October 2004 First ScotRail ran them.

The Beijing–Kowloon through train was an intercity railway service between Hung Hom station in Hong Kong and the Beijing West railway station in China, jointly operated by the MTRC of Hong Kong and China Railway, China's national rail service. The train ran to Beijing and Hong Kong every other day. Services used the East Rail line in Hong Kong, crossed the boundary between Hong Kong and mainland China at Lo Wu and then continued along China's railway network via the Guangshen railway and the Jingguang railway to Beijing. Total journey time was approximately 23 hours, and the train uses 25T class train carriages.

Railteam B.V. is a closed company with limited liability (B.V.) based in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. It operates as an alliance of European railway companies in the field of international high-speed rail in Europe, modelled on the airline alliances and was founded in Brussels on 2 July 2007.
CIV or International Convention for the transportation of Passengers in rail transport refers to a set of uniform rules shared by European railway operators, to cover international journeys.
SNCF Connect, formerly OUI.sncf until January 25, 2022, is a subsidiary of SNCF selling passes and point-to-point tickets for rail travel around Europe. It has commercial links to major European rail operators including SNCF, Eurostar, Deutsche Bahn, and Thalys, and is made up of four independent companies in distinct geographical areas. As at 2003, It was the largest French electronic commerce website in volume. One quarter of French SNCF tickets are sold by this website.

The European Rail Timetable, more commonly known by its former names, the Thomas Cook European Timetable, the Thomas Cook Continental Timetable or simply Cook's Timetable, is an international timetable of selected passenger rail schedules for every country in Europe, along with a small amount of such content from areas outside Europe. It also includes regularly scheduled passenger shipping services and a few coach services on routes where rail services are not operated. Except during World War II and a six-month period in 2013–14, it has been in continuous publication since 1873. Until 2013 it was published by Thomas Cook Publishing, in the United Kingdom, and since 1883 has been issued monthly. The longstanding inclusion of "Continental" in the title reflected the fact that coverage was, for many years, mostly limited to continental Europe. Information on rail services in Great Britain was limited to only about 30 pages until 1954 and then omitted entirely until 1970. June 2011 marked the 1500th edition.
Ouigo is a French low-cost service range of both conventional and high-speed trains. The literal translation of Ouigo from French to English is "yes go"; the name is also a play on words with the English homonym "we go." It is composed of two different services: Ouigo Grande Vitesse, which is a brand of SNCF operating high-speed trains; and Ouigo Vitesse Classique, a brand under which Oslo, a subsidiary of SNCF, operates conventional speed trains.
Raileurope.co.uk is an online booking service for train travel in the United Kingdom and Europe. It sells tickets through its website and via its smartphone app which is available on iOS and Android platforms.
Monisha Rajesh is a British journalist and travel writer.
Midnight Trains is a French start-up railway company.
The Agreement on Journey Continuation (AJC) is a commercial agreement between 17 major European rail operators, to allow international train passengers on the next possible train without additional costs, in case of a missed train connection.

In Britain and Ireland, a SailRail ticket allows travel with a combination of train and ferry. The brand, which was in existence by 2005, is principally associated with rail tickets between National Rail stations in Great Britain and stations in Ireland, including ferry travel on one of three routes across the Irish Sea.











