
William I, usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle to establish his throne, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading an army of Normans to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose.

Harold Godwinson, also called Harold II, was the last crowned Anglo-Saxon English king. Harold reigned from 6 January 1066 until his death at the Battle of Hastings, fighting the Norman invaders led by William the Conqueror during the Norman conquest of England. His death marked the end of Anglo-Saxon rule over England.

The Battle of Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest of England. It took place approximately 7 mi (11 km) northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Norman victory.

Edgar Ætheling or Edgar II was the last male member of the royal house of Cerdic of Wessex. He was elected King of England by the Witenagemot in 1066, but never crowned.
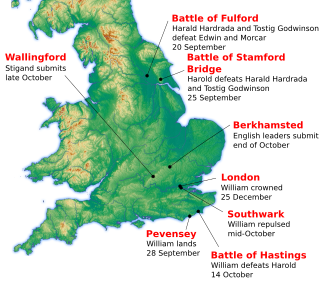
The Norman Conquest was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror.

Pope Nicholas II, otherwise known as Gerard of Burgundy, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 January 1059 until his death in 27 July 1061. At the time of his election, he was bishop of Florence. During his Papacy, Nicholas II successfully expanded the influence of the papacy in Milan and southern Italy. He was also responsible for passing papal election reforms.

The Anglo-Normans were the medieval ruling class in England, composed mainly of a combination of francized ethnic Anglo-Saxons, Normans, Northern French, Flemings, and Bretons, following the Norman conquest. A small number of Normans had earlier befriended future Anglo-Saxon king of England, Edward the Confessor, during his exile in his mother's homeland of Normandy in northern France. When he returned to England, some of them went with him; as such, there were Normans already settled in England prior to the conquest. Edward's successor, Harold Godwinson, was defeated by Duke William the Conqueror of Normandy at the Battle of Hastings, leading to William's accession to the English throne.
William Malet held senior positions within the Norman forces that occupied England from 1066. He was appointed the second High Sheriff of Yorkshire in 1068. Of the so-called companions of William of Normandy, Malet is one of about a dozen for whom there is evidence of their presence at the Battle of Hastings of 14 October 1066. For example, the contemporary chronicler William of Poitiers recorded that Malet was present at the battle.
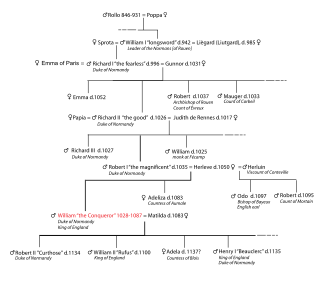
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles the Simple in 911. In 924 and again in 933, Normandy was expanded by royal grant. Rollo's male-line descendants continued to rule it until 1135. In 1202 the French king Philip II declared Normandy a forfeited fief and by 1204 his army had conquered it. It remained a French royal province thereafter, still called the Duchy of Normandy, but only occasionally granted to a duke of the royal house as an apanage.

Norman or Norman French is a Romance language which can be classified as one of the langues d'oïl, which also includes French, Picard and Walloon. The name "Norman French" is sometimes used to describe not only the Norman language, but also the administrative languages of Anglo-Norman and Law French used in England. For the most part, the written forms of Norman and modern French are mutually intelligible. This intelligibility was largely caused by the Norman language's planned adaptation to French orthography (writing).
Robert de Beaumont, 1st Earl of Leicester, Count of Meulan, also known as Robert of Meulan, was a powerful Norman nobleman, one of the very few proven Companions of William the Conqueror during the Norman Conquest of England in 1066, and was revered as one of the wisest men of his age. Chroniclers spoke highly of his eloquence and his learning, and three kings of England valued his counsel. He was granted immense land-holdings in England by William the Conqueror and by Henry I and was created Earl of Leicester.

The Harrying of the North was a series of military campaigns waged by William the Conqueror in the winter of 1069–1070 to subjugate Northern England, where the presence of the last Wessex claimant, Edgar Ætheling, had encouraged Anglo-Saxon Northumbrian, Anglo-Scandinavian and Danish rebellions. William paid the Danes to go home, but the remaining rebels refused to meet him in battle, and he decided to starve them out by laying waste to the Northern shires using scorched earth tactics, especially in the historic county of Yorkshire and the city of York, before relieving the English aristocracy of their positions, and installing Norman aristocrats throughout the region.

Gisa was Bishop of Wells from 1060 to 1088. A native of Lorraine, Gisa came to England as a chaplain to King Edward the Confessor. After his appointment to Wells, he travelled to Rome rather than be consecrated by Stigand, the Archbishop of Canterbury. As bishop, Gisa added buildings to his cathedral, introduced new saints to his diocese, and instituted the office of archdeacon in his diocese. After the Norman Conquest, Gisa took part in the consecration of Lanfranc, the new Archbishop of Canterbury, and attended Lanfranc's church councils. His tomb in Wells Cathedral was opened in the 20th century and a cross was discovered in his tomb.
The Carmen de Hastingae Proelio is a 20th-century name for the Carmen Widonis, the earliest history of the Norman invasion of England from September to December 1066, in Latin. It is attributed to Guy, Bishop of Amiens, a noble of Ponthieu and monastically-trained bishop and administrator close to the French court, who eventually served as a chaplain for Matilda of Flanders, William the Conqueror's queen. Bishop Guy was an uncle to Guy I, Count of Ponthieu, who figures rather prominently in the Bayeux Tapestry as the vassal of Duke William of Normandy who captured Harold Godwinson, later to become King Harold II of England, in 1064.

The Italo-Normans, or Siculo-Normans (Siculo-Normanni) when referring to Sicily and Southern Italy, are the Italian-born descendants of the first Norman conquerors to travel to southern Italy in the first half of the eleventh century. While maintaining much of their distinctly Norman piety and customs of war, they were shaped by the diversity of southern Italy, by the cultures and customs of the Greeks, Lombards, and Arabs in Sicily.
William I of England has been depicted in a number of modern works.

The term Norman–Arab–Byzantine culture, Norman–Sicilian culture or, less inclusively, Norman–Arab culture, refers to the interaction of the Norman, Byzantine Greek, Latin, and Arab cultures following the Norman conquest of the former Emirate of Sicily and North Africa from 1061 to around 1250. The civilization resulted from numerous exchanges in the cultural and scientific fields, based on the tolerance shown by the Normans towards the Latin- and Greek-speaking Christian populations and the former Arab Muslim settlers. As a result, Sicily under the Normans became a crossroad for the interaction between the Norman and Latin Catholic, Byzantine–Orthodox, and Arab–Islamic cultures.

The Normans were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. The term is also used to denote emigrants from the duchy who conquered other territories such as England and Sicily. The Norse settlements in West Francia followed a series of raids on the French northern coast mainly from Denmark, although some also sailed from Norway and Sweden. These settlements were finally legitimized when Rollo, a Scandinavian Viking leader, agreed to swear fealty to King Charles III of West Francia following the siege of Chartres in 911. The intermingling in Normandy produced an ethnic and cultural "Norman" identity in the first half of the 10th century, an identity which continued to evolve over the centuries.

The British is a 2012 British television series produced by Sky Atlantic. It comprises seven fifty-minute episodes. It covers several major events in the history of Britain throughout the years 43 AD to 1953. Including the Norman Conquest, Industrial Revolution and the Queen's Coronation. It stars Russell Brand, Jessie J, and Dame Helen Mirren, and is narrated by Jeremy Irons. It premiered 6 September 2012 on Sky Atlantic.
Robert, Count of Eu and Lord of Hastings, son of William I, Count of Eu, and his wife Lesceline. Count of Eu and Lord of Hastings.















