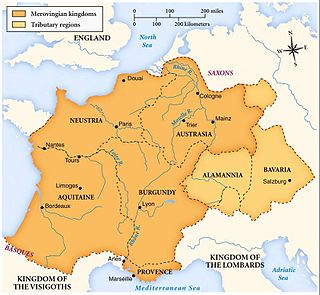
The Merovingian dynasty was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gallo-Romans under their rule. They conquered most of Gaul, defeating the Visigoths (507) and the Burgundians (534), and also extended their rule into Raetia (537). In Germania, the Alemanni, Bavarii and Saxons accepted their lordship. The Merovingian realm was the largest and most powerful of the states of western Europe following the breaking up of the empire of Theodoric the Great.

Clovis was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single king and ensuring that the kingship was passed down to his heirs. He is considered to have been the founder of the Merovingian dynasty, which ruled the Frankish kingdom for the next two centuries. Clovis is important in the historiography of France as "the first king of what would become France".

Childeric I was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a king, both on his Roman-style seal ring, which was buried with him, and in fragmentary later records of his life. He was father of Clovis I, who acquired effective control over all or most Frankish kingdoms, and a significant part of Roman Gaul.

Gregory of Tours was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours during the Merovingian period and is known as the "father of French history." He was a prelate in the Merovingian kingdom, encompassing Gaul's historic region.

Merovech was the ancestor of the Merovingian dynasty. He was reportedly a king of the Salian Franks, but records of his existence are mixed with legend and myth. The most important written source, Gregory of Tours, recorded that Merovech was said to be descended from Chlodio, a roughly contemporary Frankish warlord who pushed from the Silva Carbonaria in modern central Belgium as far south as the Somme, north of Paris in modern-day France. His supposed descendants, the kings Childeric I and Clovis I, are the first well-attested Merovingians.

Aetius was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433–454). He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian federates settled throughout the West. Notably, he mustered a large Roman and allied (foederati) army in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, ending a devastating invasion of Gaul by Attila in 451, though the Hun and his subjugated allies still managed to invade Italy the following year, an incursion best remembered for the ruthless Sack of Aquileia and the intercession of Pope Leo I.

Syagrius was a Roman general and the last ruler of a Roman rump state in northern Gaul, now called the Kingdom of Soissons. Gregory of Tours referred to him as King of the Romans. Syagrius's defeat by king Clovis I of the Franks is considered the end of Western Roman rule outside of Italy. He inherited his position from his father, Aegidius, the last Roman magister militum per Gallias. Syagrius preserved his father's territory between the Somme and the Loire around Soissons after the collapse of central rule in the Western Empire, a domain Gregory of Tours called the "Kingdom" of Soissons. Syagrius governed this Gallo-Roman enclave from the death of his father in 464 until 486, when he was defeated in battle by Clovis I.
Aegidius was the ruler of the short-lived Kingdom of Soissons from 461 to 464/465. Before his ascension, he became magister militum per Gallias "Master of the Soldiers for Gaul"m serving under the Western Roman emperor Majorian in 458. An ardent supporter of Majorian, Aegidius rebelled against General Ricimer when he assassinated Majorian and replaced him with Emperor Libius Severus. Aegidius may have pledged his allegiance to the Eastern Roman emperor Leo I.

The Kingdom of the Franks, also known as the Frankish Kingdom, the Frankish Empire or Francia, was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Frankish Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties during the Early Middle Ages. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era.

Pharamond, also spelled Faramund, is a legendary early king of the Franks, first referred to in the anonymous 8th-century Liber Historiae Francorum, which depicts him as the first king of the Franks.

Chlodio, also Clodio, Clodius, Clodion, Cloio or Chlogio, was a Frankish king who attacked and then apparently ruled Roman-inhabited lands around Cambrai and Tournai, near the modern border of Belgium and France. He is known from very few records.

Saint Hermenegild or Ermengild, was the son of king Liuvigild of the Visigothic Kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula and southern France. He fell out with his father in 579, then revolted the following year. During his rebellion, he converted from Arianism to Catholicism. Hermenegild was defeated in 584 and exiled. His death was later celebrated as a martyrdom due to the influence of Pope Gregory I's Dialogues, in which he portrayed Hermenegild as a "Catholic martyr rebelling against the tyranny of an Arian father."

The Salian Franks, also called the Salians, were a northwestern subgroup of the early Franks who appear in the historical record in the fourth and fifth centuries. They lived west of the Lower Rhine in what was then the Roman Empire and today the Netherlands and Belgium.

The Kingdom or Domain of Soissons was a rump state of the Western Roman Empire in northern Gaul, between the Somme and the Seine, that lasted for some 25 years during Late Antiquity. The rulers of the rump state, notably its final ruler Syagrius, were referred to as "kings of the Romans" by the Germanic peoples surrounding Soissons, with the polity itself being identified as the Regnum Romanorum, "Kingdom of the Romans", by the Gallo-Roman historian Gregory of Tours. Whether this title was used by Syagrius himself or was applied to him by the barbarians surrounding his realm in a similar way to how they referred to their own leaders as kings is unknown. "Kingdom of Soissons" is a later, historiographical term for the state.

The Battle of Soissons was fought in 486 between Frankish forces under Clovis I and the Gallo-Roman domain of Soissons under Syagrius. The battle was a victory for the Franks, and led to the conquest of the Roman rump state of Soissons, a milestone for the Franks in their attempt to establish themselves as a major regional power.

The Franks were originally a Germanic people who lived near the Lower Rhine, on the northern frontier of the late Roman Empire, but they successfully expanded their power and influence during the Middle Ages, until much of the population of western Europe, particularly in or near France, were commonly described as Franks, for example in the context of their joint efforts during the crusades starting in the 11th century. This expansion came about because the romanized Frankish dynasties based within the collapsing Western Roman Empire first became the rulers of the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine, and then subsequently imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire.

Theudis, was king of the Visigoths in Hispania from 531 to 548.
The pagan religion of the Germanic tribal confederation of the Franks has been traced from its roots in polytheistic Germanic paganism through to the incorporation of Greco-Roman components in the Early Middle Ages. This religion flourished among the Franks until the conversion of the Merovingian king Clovis I to Nicene Christianity, though there were many Frankish Christians before that. After Clovis I, Frankish paganism was gradually replaced by the process of Christianisation, but there were still pagans in the late 7th century.
Dispargum could refer to either the city of Duisburg on the Rhine, or the village of Duisburg near Brussels, or the city of Diest.
A Frankish campaign against the Thoringi is said to have taken place around 491 AD, and resulted in a defeat for the latter. These Thoringi are usually identified as the Thuringii.
















