Related Research Articles

A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodity market for centuries for price risk management.

In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
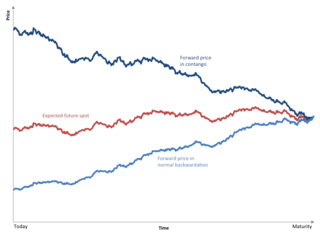
Normal backwardation, also sometimes called backwardation, is the market condition where the price of a commodity's forward or futures contract is trading below the expected spot price at contract maturity. The resulting futures or forward curve would typically be downward sloping, since contracts for further dates would typically trade at even lower prices. In practice, the expected future spot price is unknown, and the term "backwardation" may refer to "positive basis", which occurs when the current spot price exceeds the price of the future.

Contango is a situation where the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market, or carrying-cost market.

In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.
In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the forward price or delivery price. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the delivery date. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative.
In finance, a forward contract or simply a forward is a non-standardized contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future time at a price agreed on at the time of conclusion of the contract, making it a type of derivative instrument. The party agreeing to buy the underlying asset in the future assumes a long position, and the party agreeing to sell the asset in the future assumes a short position. The price agreed upon is called the delivery price, which is equal to the forward price at the time the contract is entered into.
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.

West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is a grade or mix of crude oil; the term is also used to refer to the spot price, the futures price, or assessed price for that oil. In colloquial usage, WTI usually refers to the WTI Crude Oil futures contract traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). The WTI oil grade is also known as Texas light sweet. Oil produced from any location can be considered WTI if the oil meets the required qualifications. Spot and futures prices of WTI are used as a benchmark in oil pricing. This grade is described as light crude oil because of its low density and sweet because of its low sulfur content.
The cost of carry or carrying charge is the cost of holding a security or a physical commodity over a period of time. The carrying charge includes insurance, storage and interest on the invested funds as well as other incidental costs. In interest rate futures markets, it refers to the differential between the yield on a cash instrument and the cost of the funds necessary to buy the instrument.
In finance, an asset class is a group of financial instruments that have similar financial characteristics and behave similarly in the marketplace. We can often break these instruments into those having to do with real assets and those having to do with financial assets. Often, assets within the same asset class are subject to the same laws and regulations; however, this is not always true. For instance, futures on an asset are often considered part of the same asset class as the underlying instrument but are subject to different regulations than the underlying instrument.
A convenience yield is an implied return on holding inventories. It is an adjustment to the cost of carry in the non-arbitrage pricing formula for forward prices in markets with trading constraints.
Holbrook Working was an American professor of economics and statistics at Stanford University's Food Research Institute known for his contributions on hedging, on the theory of futures prices, on an early theory of market maker behavior, and on the theory of storage.
The S&P GSCI serves as a benchmark for investment in the commodity markets and as a measure of commodity performance over time. It is a tradable index that is readily available to market participants of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange. The index was originally developed in 1991, by Goldman Sachs. In 2007, ownership transferred to Standard & Poor's, who currently own and publish it. Futures of the S&P GSCI use a multiple of 250. The index contains a much higher exposure to energy than other commodity price indices such as the Bloomberg Commodity Index.
In finance, a spread trade is the simultaneous purchase of one security and sale of a related security, called legs, as a unit. Spread trades are usually executed with options or futures contracts as the legs, but other securities are sometimes used. They are executed to yield an overall net position whose value, called the spread, depends on the difference between the prices of the legs. Common spreads are priced and traded as a unit on futures exchanges rather than as individual legs, thus ensuring simultaneous execution and eliminating the execution risk of one leg executing but the other failing.

The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution is a government ministry of India. The ministry is headed by a Cabinet rank minister.
The roll yield is the difference between the profit or loss of a futures contract and the change in the spot price of the underlying asset of that futures contract. Unlike fixed income or dividend yields, a roll yield does not provide a cash payment, and may not be counted as a profit in certain cases if it accounts for the underlying asset's cost-of-carry. Nonetheless, the roll yield is often characterized as a return that a futures investor capture in addition to the price change of the underlying asset of a futures contract.
The DBLCI Mean Reversion Index is a commodity index published by the Deutsche Bank. Launched at the same time as the Deutsche Bank Liquid Commodity Index (DBLCI) in February 2003, the DBLCI-Mean Reversion has the same underlying assets. The listed instruments are also rolled using the same mechanism as the DBLCI, namely energy contracts are rolled monthly and the metal and grain contracts are rolled annually. This occurs between the second and sixth business day of the month. The DBLCI-MR is also quoted in both total returns and excess returns terms in US dollars as well as EUR, JPY and GBP.

The Onion Futures Act is a United States law banning the trading of futures contracts on onions as well as "motion picture box office receipts".
A commodity index fund is a fund whose assets are invested in financial instruments based on or linked to a commodity price index. In just about every case the index is in fact a commodity futures index.
References
- ↑ Working, H. 1933, "Price Relations between July and September Wheat Futures at Chicago Since 1885", Wheat Studies of the Food Research Institute.