
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial law from 1972 until 1981 and kept most of his martial law powers until he was deposed in 1986, branding his rule as "constitutional authoritarianism" under his Kilusang Bagong Lipunan. One of the most controversial leaders of the 20th century, Marcos's rule was infamous for its corruption, extravagance, and brutality.

The president of the Philippines is the head of state, head of government and chief executive of the Philippines. The president leads the executive branch of the Philippine government and is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of the Philippines.

The People Power Revolution, also known as the EDSA Revolution or the February Revolution, was a series of popular demonstrations in the Philippines, mostly in Metro Manila, from February 22 to 25, 1986. There was a sustained campaign of civil resistance against regime violence and electoral fraud. The nonviolent revolution led to the departure of Ferdinand Marcos, the end of his 20-year dictatorship and the restoration of democracy in the Philippines.

Imelda Romualdez Marcos is a Filipino politician who served as the First Lady of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986, wielding significant political power during the presidency of her husband, 10th president Ferdinand Marcos. She is the mother of current president Bongbong Marcos.

Cesar Enrique Aguinaldo Virata is a Filipino former statesman and businessman who was the fourth Prime Minister of the Philippines from 1981 to 1986. He is currently the corporate vice chairman of the Rizal Commercial Banking Corporation. He is the eponym of the Cesar Virata School of Business, the business school of the University of the Philippines Diliman.

The prime minister of the Philippines was the official designation of the head of the government of the Philippines from 1978 until the People Power Revolution in 1986. During martial law and the fourth republic, the prime minister served as the head the Armed Forces of the Philippines. A limited version of this office, officially known as the President of the Council of Government, existed temporarily in 1899 during the First Philippine Republic.
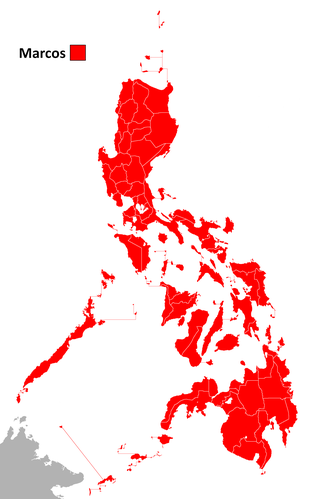
The 1981 Philippine presidential election and national referendum was held on June 16, 1981. President Ferdinand E. Marcos of the Kilusang Bagong Lipunan (KBL) defeated retired general and World War II veteran Alejo Santos of the Nacionalista Party in a landslide victory. Most opposition parties boycotted the election as a sign of protest over the 1978 election for the Interim Batasang Pambansa, which they condemned as fraudulent. At the same time, a national referendum was held on the question in holding elections for barangay elections in 1982.

The history of the Philippines, from 1965 to 1986, covers the presidency of Ferdinand Marcos. The Marcos era includes the final years of the Third Republic (1965–1972), the Philippines under martial law (1972–1981), and the majority of the Fourth Republic (1981–1986). By the end of the Marcos dictatorial era, the country was experiencing a debt crisis, extreme poverty, and severe underemployment.
The Interim Batasang Pambansa was the legislature of the Republic of the Philippines from its inauguration on June 12, 1978, to June 5, 1984. It served as a transitional legislative body mandated by the 1973 Constitution as the Philippines shifted from a presidential to a semi-presidential form of government.

The Fourth Philippine Republic, also known as the FourthRepublic of the Philippines was established after Ferdinand Marcos Sr won the June 16, 1981, Philippine Presidential Election. Marcos announced the beginning of the Fourth Republic on June 30, during his inauguration speech. On February 25, 1986, due to the 1986 EDSA Revolution, Marcos ended into exile in Hawaii and Corazon Aquino became the 11th president of the Philippines. The Fourth Republic would come to an end under Aquino's leadership, and the Fifth Republic would commence with the adoption of a new constitution.

Martial law in the Philippines refers to the various historical instances in which the Philippine head of state placed all or part of the country under military control—most prominently during the administration of Ferdinand Marcos, but also during the Philippines' colonial period, during the second world war, and more recently on the island of Mindanao during the administrations of Gloria Macapagal Arroyo and Rodrigo Duterte. The alternative term "martial law era" as applied to the Philippines is typically used to describe the Marcos martial law period specifically.

The inauguration of the president of the Republic of the Philippines is a ceremony marking the commencement of the six-year term of a president of the Philippines, who is both head of state and head of government. The inauguration is performed on June 30, as mandated by the 1987 Constitution. Under the older 1935 Constitution, the date was December 30, which is also Rizal Day; the last inauguration held on the older date was Ferdinand Marcos' second one on December 30, 1969. The most recent public presidential inauguration ceremony was that of President Bongbong Marcos, who began his six-year term in office on Thursday, June 30, 2022.

The first inauguration of Ferdinand E. Marcos as the tenth President of the Philippines took place on December 30, 1965 at the Quirino Grandstand in Manila. The inauguration marked the beginning of the first four-year term of Ferdinand Marcos as President and second four-year term of Fernando Lopez as Vice President. The oath of office was administered by Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines César Bengzon. Marcos swore his oath on two closed family Bibles, one owned by his father Mariano and another given by his wife Imelda. One of the Bibles would later be used in the inauguration of his son Ferdinand Jr. in 2022.

The inauguration of Ferdinand E. Marcos as the tenth president of the Philippines took place on December 30, 1969, at the Quirino Grandstand in Manila. The inauguration marked the commencement of the second four-year term of Ferdinand Marcos as president and the third term of Fernando Lopez as Vice President. The oath of office was administered by Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines Roberto Concepcion.
The Confirmation of Ferdinand E. Marcos as the third Prime Minister of the Philippines took place on June 12, 1978 at the Batasang Pambansa Complex in Quezon City. The confirmation by the Interim Batasang Pambansa marked the commencement of the first term of President Ferdinand Marcos as Prime Minister.
1981 in the Philippines details events of note that happened in the Philippines in the year 1981.

At 7:17 pm on September 23, 1972, President Ferdinand Marcos announced on television that he had placed the entirety of the Philippines under martial law. This marked the beginning of a 14-year period of one-man rule that would effectively last until Marcos was exiled from the country on February 25, 1986. Even though the formal document proclaiming martial law – Proclamation No. 1081, which was dated September 21, 1972 – was formally lifted on January 17, 1981, Marcos retained essentially all of his powers as dictator until he was ousted.

The Marcos family is a political family in the Philippines. They have established themselves in the country's politics, having established a political dynasty that traces its beginnings to the 1925 election of Mariano Marcos to the Philippine House of Representatives as congressman for the second district of Ilocos Norte; reached its peak during the 21-year rule of Ferdinand Marcos as president of the Philippines that included his 14-year dictatorship beginning with the declaration of Martial Law throughout the country; and continues today with the political careers of Imelda Marcos, Imee Marcos, Sandro Marcos and reached a fresh political apex with the presidency of Bongbong Marcos.

The inauguration of Bongbong Marcos as the 17th president of the Philippines took place around noon (PHT) on Thursday, June 30, 2022, at the National Museum of Fine Arts. The chief justice of the Supreme Court administered the oath of office.














