Related Research Articles

Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows. The word comes from the Latin arcus, meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In modern times, it is mainly a competitive sport and recreational activity. A person who practices archery is typically called an archer, bowman, or toxophilite.
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; and the preservation of a nation's intangible cultural heritage.

Kalaripayattu is an Indian martial art that originated in Kerala, a state on the southwestern coast of India. Kalaripayattu is known for its long-standing history within Indian martial arts, and is one of the oldest surviving martial arts in world.

Korean martial arts are fighting practices and methods which have their place in the history of Korea but have been adapted for use by both military and non-military personnel as a method of personal growth or recreation. The history of Korean martial arts can be traced as far back as the prehistoric era.
Indian martial arts refers to the fighting systems of the Indian subcontinent. A variety of terms are used for the English phrases "Indian martial arts", deriving from ancient sources. While they may seem to imply specific disciplines, by Classical times they were used generically for all fighting systems.
The North Indian state of Himachal Pradesh is a state that has remained largely uninfluenced by Western culture. Himachal Pradesh is a multi-religion practising, multicultural and multilingual state. Some of the most commonly spoken languages are Hindi and the various Pahari languages. The Hindu communities residing in Himachal include the Brahmins, Rajputs, Kannets, Rathis and Kolis. There are also tribal population in the state which mainly comprise Gaddis, Kinnarms, Gujjars, Pangawals and Lahaulis.

Bokator is an ancient battlefield martial art used by the ancient Khmer military. It is one of the oldest existing fighting systems originating from Cambodia.

Archery, or the use of bow and arrows, was probably developed in Africa by the later Middle Stone Age. It is documented as part of warfare and hunting from the classical period until the end of the 19th century, when it was made obsolete by the invention and spread of repeating firearms.
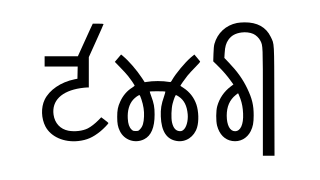
The Tākri script is an abugida writing system of the Brahmic family of scripts. It is derived from the Sharada script formerly employed for Kashmiri. It is the sister script of Laṇḍā scripts. It is another variant of Dogra Takri employed in Jammu region. Chamba Takri was considered by Grierson as the standard form of Takri, primarily because it was the first variety that was developed for print. In addition to Chamba and Dogra, there are numerous varieties, “with each Hill State or tract having its own style.” Until the late 1940s, the adapted version of the script was the official script for writing Dogri in the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir and for Kangri, Chambyali and Mandyali in Himachal Pradesh. However, the Takri script used in the Sirmour in Himachal Pradesh and Jaunsar-Bawar region has some distinction.

Although the earliest evidence of martial arts goes back millennia, the true roots are difficult to reconstruct. Inherent patterns of human aggression which inspire practice of mock combat and optimization of serious close combat as cultural universals are doubtlessly inherited from the pre-human stage and were made into an "art" from the earliest emergence of that concept. Indeed, many universals of martial art are fixed by the specifics of human physiology and not dependent on a specific tradition or era.
Dhanurveda (धनुर्वेद) is a Sanskrit treatise on warfare and archery, traditionally regarded as an upaveda attached to Yajurveda and attributed either to Bhrigu or Vishvamitra or Bharadwaja. It is one among the four upavedas to Vedas.

Mallakhamba or mallakhamb is a traditional sport, originating from the Indian subcontinent, in which a gymnast performs aerial yoga or gymnastic postures and wrestling grips in concert with a vertical stationary or hanging wooden pole, cane, or rope. The word "mallakhamb" also refers to the pole used in the sport. The pole is usually made from sheesham polished with castor oil. Three popular versions of Mallakhamb are practiced using a sheesham pole, cane, or rope. The origins of pole dancing can be traced back to the sport of Mallakhamb.

Huiyen Lallong is a traditional Meitei martial art form. It is one of the Indian martial arts, originating from Manipur. In the Meitei language, Huiyen means war while Lallong or Lanlong can mean net, knowledge or art. Huiyen Langlon consists of two main subforms: Thang-Ta and Sarit Sarak. The primary weapons of Huiyen Lallong are the Thang (sword) and Ta (spear). The spear can be used in its non-missile form while up close, or thrown from afar. Other weapons include the shield and the axe. Unarmed combat incorporates hand strikes, kicks, and grappling (Mukna). Because of Manipur's cultural similarity and geographical proximity with Myanmar, huyen langlon is closely related to Burmese bando and banshay.
A bow draw in archery is the method or technique of pulling back the bowstring to store energy for the bow to shoot an arrow. The most common method in modern target archery is the Mediterranean draw, which has long been the usual method in European archery. Other methods include the pinch draw and the Mongolian or "thumb" draw. In traditional archery practice outside Western Europe the variations of the thumb draw are by far the most dominant draw types, with the Mediterranean draw restricted to the Olympic style of target archery.

Sport is a significant part of life in India. The country has a sports history tracing back thousands of years, with sports being a part of tradition, culture, finance and entertainment. People in India closely follow various sports and enthusiastically participate in them. Cricket is the most popular spectator sport in the country, it generates the highest television viewership, and features full-capacity audiences in stadiums during international and Indian Premier League (IPL) matches. In recent decades, football has also become a popular sport in terms of broadcast viewership and stadium audience attendance. The Indian Super League (ISL), is the highest league of football in India. ISL and national team's matches attract considerable audience in stadium and on TV. The national football team has won two Gold medals at the Asian games, three Gold medals at the South Asian Games and one silver at the Asian Cup held in 1964 in Israel by virtue of their runner-up position, reached the semifinal of the 1960 Olympics, qualified for the 1950 FIFA World Cup and has won the SAFF Championship a record number of times.
Jignas Chittibomma is an Indian archer. He is noted for being instrumental in India's 2nd-place finish in the 2010 Commonwealth Games.
Modern competitive archery involves shooting arrows at a target for accuracy and precision from a set distance or distances. This is the most popular form of competitive archery worldwide and is called target archery. A form particularly popular in Europe, North America, and South America is field archery, shot at targets generally set at various distances in a wooded setting. There are also several other lesser-known and historical forms, as well as archery novelty games.
Many sports are played by the people of Tamil Nadu including both traditional sports and sports from other countries.

India has several traditional games and sports, some of which have been played for thousands of years. Many of these games do not require much equipment or playing space. Some traditional Indian games are only played in certain regions of India, or may be known by different names and played under different rules and regulations in different regions of the country. Many Indian games are also similar to other traditional South Asian games.
References
- ↑ While Kerala’s kalaripayattu and North India’s traditional kushti are a done and dusted deal, here are some unexplored gems to get you started on some uppercuts and roundabouts https://www.outlookindia.com/
- ↑ Himachal CM declares Thoda dance as rural game https://www.business-standard.com/
- 1 2 IANS (2019-11-28). "120-year-old traditional sport still played in Himachal". TheQuint. Retrieved 2023-08-20.
- ↑ The Six Prominent And Ancient Martial Art Forms Of India https://www.boldsky.com/ Pundreeka Valli
- ↑ PTI (2022-05-15). "Himachal Pradesh: 34 years on, martial art tournament makes comeback at state-level". ThePrint. Retrieved 2023-08-20.
- ↑ Kazi, Saad (2018-07-26). "7 Tempting Traditional Sports played in India". Voice of Indian Sports - KreedOn. Retrieved 2023-08-20.