Related Research Articles

The Yangtze or Yangzi is the longest river in Eurasia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows 6,300 km (3,915 mi) in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the seventh-largest river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population.

Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti. Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals and belugas than to the true dolphins. There are eight extant species of porpoise, all among the smallest of the toothed whales. Porpoises are distinguished from dolphins by their flattened, spade-shaped teeth distinct from the conical teeth of dolphins, and lack of a pronounced beak, although some dolphins also lack a pronounced beak. Porpoises, and other cetaceans, belong to the clade Cetartiodactyla with even-toed ungulates.
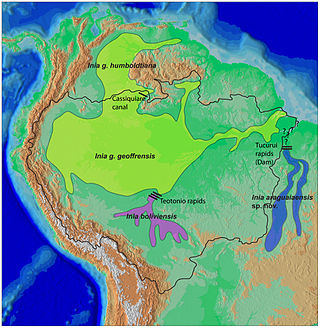
River dolphins are a polyphyletic group of fully aquatic mammals that reside exclusively in freshwater or brackish water. They are an informal grouping of dolphins, which itself is a paraphyletic group within the infraorder Cetacea. Extant river dolphins are placed in two superfamilies, Platanistoidea and Inioidea. They comprise the families Platanistidae, the recently extinct Lipotidae, Iniidae and Pontoporiidae. There are five extant species of river dolphins. River dolphins, alongside other cetaceans, belong to the clade Artiodactyla, with even-toed ungulates, and their closest living relatives the hippopotamuses, from which they diverged about 40 million years ago. Specific types of Dolphins can be pink.

Lipotidae is a family of river dolphins containing the possibly extinct baiji of China and the fossil genus Parapontoporia from the Late Miocene and Pliocene of the Pacific coast of North America. The genus Prolipotes, which is based on a mandible fragment from Neogene coastal deposits in Guangxi, China, has been classified as an extinct relative of the baiji, but is dubious.

Dongting Lake is a large, shallow lake in northeastern Hunan Province, China. It is a flood basin of the Yangtze River, so its volume depends on the season. The provinces of Hubei and Hunan are named after their location relative to the lake: Hubei means "North of the Lake" and Hunan, "South of the Lake".

The Indo-Pacific finless porpoise is one of eight porpoise species. The species ranges throughout most of the Indian Ocean, as well as the tropical and subtropical Pacific from Indonesia north to the Taiwan Strait. Overlapping with this species in the Taiwan Strait and replacing it northwards is the East Asian finless porpoise.

Neophocaena is a genus of porpoise native to the Indian and Pacific oceans, as well as the freshwater habitats of the Yangtze River basin in China. They are commonly known as finless porpoises. Genetic studies indicate that Neophocaena is the most basal living member of the porpoise family.
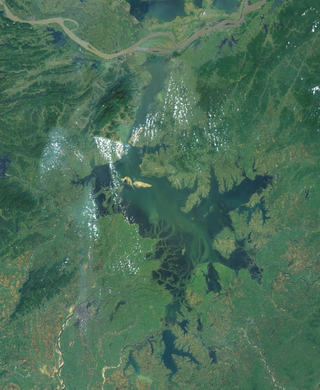
Poyang Lake, located in Jiujiang, is the largest freshwater lake in China.

Cetacean bycatch is the accidental capture of non-target cetacean species such as dolphins, porpoises, and whales by fisheries. Bycatch can be caused by entanglement in fishing nets and lines, or direct capture by hooks or in trawl nets.

The Ocean Park Conservation Foundation, Hong Kong, often referred to by its initialism OPCFHK is the conglomerate of the former Ocean Park Conservation Foundation (OPCF) and The Hong Kong Society for Panda Conservation (HKSPC) established under the Ocean Park Corporation, with effect from 1 July 2005. It is a registered charitable non-governmental organisation.
The Yangtze Freshwater Dolphin Expedition 2006 was a six-week search expedition undertaken in November and December 2006 in central China in an attempt to locate continued proof of the existence of the endangered baiji Yangtze dolphin. It was carried out under the direction of the Wuhan Institute of Hydrobiology and the Swiss-based baiji.org Foundation and was notable for drawing to an end without any positive results. Thus it was announced that the species was functionally extinct.

Functional extinction is the extinction of a species or other taxon such that:
- It disappears from the fossil record, or historic reports of its existence cease;
- The reduced population no longer plays a significant role in ecosystem function; or
- The population is no longer viable. There are no individuals able to reproduce, or the small population of breeding individuals will not be able to sustain itself due to inbreeding depression and genetic drift, which leads to a loss of fitness.

China's vast and diverse landscape is home to a profound variety and abundance of wildlife. As of one of 17 megadiverse countries in the world, China has, according to one measure, 7,516 species of vertebrates including 4,936 fish, 1,269 bird, 562 mammal, 403 reptile and 346 amphibian species. In terms of the number of species, China ranks third in the world in mammals, eighth in birds, seventh in reptiles and seventh in amphibians.
China Biosphere Reserve Network (CBRN) is a network established by the Chinese National Committee for UNESCO Man and the Biosphere Programme in 1993. Membership in the CBRN serves as a prerequisite for joining the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR). At present there are 191 members in the CBRN, including 34 UNESCO Biosphere Reserves.

The baiji is a possibly extinct species of freshwater dolphin native to the Yangtze river system in China. It is thought to be the first dolphin species driven to extinction due to the impact of humans. This dolphin is listed as “critically endangered: possibly extinct” by the IUCN, has not been seen in 40 years, and several surveys of the Yangtze have failed to find it. In China, the species is also called the Chinese river dolphin, Han river dolphin, Yangtze dolphin and whitefin dolphin. Nicknamed the "Goddess of the Yangtze", it was regarded as the goddess of protection by local fishermen and boatmen. It is not to be confused with the Chinese white dolphin or the finless porpoise. This is the only species in the genus Lipotes.
Yi'an District, formerly Tongling County, is a district of the city of Tongling, in the south of Anhui province, lying on the southern and eastern (right) bank of the Yangtze River. The total area is 1,113 km2 (430 sq mi). The population is 716,300.

Jiuduansha is a collection of four intertidal wetland shoals at the mouth of China's Yangtze River. They are administered as an island region of the municipality of Shanghai's Pudong New Area.

The East Asian finless porpoise is a species of porpoise native to the East China Sea, Yellow Sea, and the seas around Japan. The Yangtze finless porpoise was formerly considered a subspecies, but is now thought to be a distinct species.

The Yangtze finless porpoise is a species of toothed whale in the family Phocoenidae. It is endemic to the Yangtze River in China, making it the country's only known freshwater cetacean following the possible extinction of the baiji. The Yangtze finless porpoise is considered critically endangered and it is estimated that only about 1,000 remain. This small toothed whale faces many of the same threats that caused the baiji dolphin to possibly become extinct. The Yangtze River has a high traffic rate of human activity causing population declines due to illegal fishing, pollution, vessel traffic, and dam construction. Due to the rapidly declining population of the species, the Chinese Government and conservation charities are working to help save it from extinction.
References
- ↑ "Scientists Join Hands to Seek the Last Yangtze River Dolphin". WWF China. Archived from the original on November 12, 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ↑ Samuel Turvey, Witness to Extinction. Retrieved 2011-08-12.