The Tidewater Railway was formed in 1904 as an intrastate railroad in Virginia, in the United States, by William N. Page, a civil engineer and entrepreneur, and his silent partner, millionaire industrialist Henry Huttleston Rogers of Standard Oil fame. It was put together with the intention of creating an outlet to Hampton Roads, where coal mined along their older West Virginia short-line railroad, the Deepwater Railway, could be exported. [1]
In 1907, the Tidewater Railway was renamed the "Virginian Railway". A short time later, the Virginian Railway acquired its sister, the Deepwater Railway. Before the Tidewater division of the Virginian was linked to the Deepwater line, it played an important role, in conjunction with the regional Norfolk and Southern Railway, in transporting thousands of people to the Jamestown Exposition of 1907, an event marking the three-hundredth anniversary of the founding of the British colony at Jamestown. It took two years to complete, but in 1909, both portions (the Tidewater portion and the Deepwater portion) were finally completed, and coal exports, from a new coal pier at Sewell's Point, began.
In 1959, the Virginian Railway was merged with the Norfolk and Western Railway. This was the first major U.S. railroad merger of the last half of the twentieth century, an era of rampant mergers, acquisitions, and consolidations among the American railroads.

Brookneal is an incorporated town in Campbell County, Virginia, United States. The population was 1,112 as of the 2010 census. It is part of the Lynchburg Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Victoria is an incorporated town in Lunenburg County, Virginia, United States. The population was 1,725 at the 2010 census, which was down from the 1,821 reported in 2000.

Princeton, is a city in and the county seat of Mercer County, West Virginia, United States. The city is coined the "Heart of Mercer County" or the "Jewel of the South" in past decades. The population was 6,432 at the 2010 census with approximately 35,000 residents living in the greater Princeton area. It is part of the Bluefield, WV-VA micropolitan area which has a population of 107,342. The city hosts the Princeton WhistlePigs baseball club of the Appalachian League. A main tourist destination of the city is the Mercer Street Grassroots District located in Downtown Princeton. This area has been revitalized and is now home to cafes, restaurants, shops, and artistic venues.

The Jamestown Exposition was one of the many world's fairs and expositions that were popular in the United States in the early part of the 20th century. Commemorating the 300th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown in the Virginia Colony, it was held from April 26 to December 1, 1907, at Sewell's Point on Hampton Roads, in Norfolk, Virginia. It celebrated the first permanent English settlement in the present United States. In 1975, the 20 remaining exposition buildings were included on the National Register of Historic Places as a national historic district.

The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows 348 miles (560 km) to Chesapeake Bay. The river length extends to 444 miles (715 km) if one includes the Jackson River, the longer of its two source tributaries. It is the longest river in Virginia. Jamestown and Williamsburg, Virginia's first colonial capitals, and Richmond, Virginia's current capital, lie on the James River.

The Virginian Railway was a Class I railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The VGN was created to transport high quality "smokeless" bituminous coal from southern West Virginia to port at Hampton Roads.

The Norfolk and Western Railway, commonly called the N&W, was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its existence. Its motto was "Precision Transportation"; it had a variety of nicknames, including "King Coal" and "British Railway of America". In 1986, N&W merged with Southern Railway to form Today’s Norfolk Southern Railway.
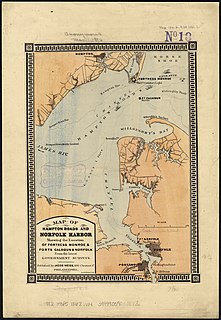
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to the north, Hampton Roads to the west, and the Lafayette River to the south. It is the site of Naval Station Norfolk.

William Nelson Page was an American civil engineer and industrialist. He was active in the Virginias following the U.S. Civil War. Page was widely known as a metallurgical expert by other industry leaders and investors as well as state and federal authorities.
The Deepwater Railway was an intrastate short line railroad located in West Virginia in the United States which operated from 1898 to 1907.

Lamberts Point is a point of land on the east shore of the Elizabeth River near the downtown area of the independent city of Norfolk in the South Hampton Roads region of eastern Virginia, United States. It includes a large coal exporting facility, a residential area, and a golf course. The area is south of Old Dominion University

The Norfolk and Petersburg Railroad was built between Norfolk and Petersburg, Virginia and was completed by 1858. The line was 85 miles (137 km) of 5 ft track gauge.
Page is a census-designated place (CDP) and coal town in Fayette County, West Virginia, United States. As of the 2010 census, its population was 224. It was named for William Nelson Page (1854-1932), a civil engineer and industrialist who lived in nearby Ansted, where he managed Gauley Mountain Coal Company and many iron, coal, and railroad enterprises.
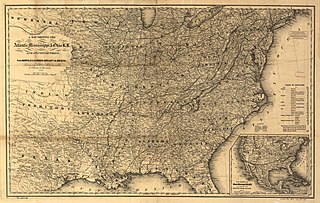
Atlantic, Mississippi and Ohio Railroad (AM&O) was formed in 1870 in Virginia from three east–west railroads which traversed across the southern portion of the state. Organized and led by former Confederate general William Mahone (1826-1895), the 428-mile (689 km) line linked Norfolk with Bristol, Virginia by way of Suffolk, Petersburg, Lynchburg, and Salem. The AM&O was promoted as a trade link to the west, and further expansion was envisioned with the goal of increasing Virginia's Ohio Valley and Mississippi Valley commerce. It was heavily backed by investors from England and Scotland.

Transportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established trails of the Native Americans.
The Seaboard and Roanoke Railroad was organized in 1833 to extend from the area of the rapids of the Roanoke River at its fall line near Weldon, North Carolina to Portsmouth, Virginia, across the Elizabeth River from Norfolk on the harbor of Hampton Roads.
The Kanawha and Pocahontas Railroad Company was incorporated in West Virginia in 1898 by either a son or the estate of Charles Pratt to reach new coal mining territory on land which was owned and/or leased by Gallego Coal & Land Company, Charles Pratt and Company, and other investors based in New York City.

The Western New York and Pennsylvania Railroad is a short-line railroad that operates freight trains in Western New York and Northwest Pennsylvania, United States. The company is controlled by the Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad, with which it does not connect. It started operations in 2001 on the Southern Tier Extension, a former Erie Railroad line between Hornell, NY and Corry, PA, owned by the public Chautauqua, Cattaraugus, Allegany and Steuben Southern Tier Extension Railroad Authority (STERA). Through acquisitions and leases, the line was extended from Corry to Meadville, PA in 2002 and to Oil City, PA in 2006. In 2007, the WNY&P leased and sub-leased portions of the north-south Buffalo Line, a former Pennsylvania Railroad line mostly built by a predecessor of the defunct Western New York and Pennsylvania Railway. The two lines cross at Olean, NY.

The Farmville and Powhatan Railroad went bankrupt in 1905 and became the Tidewater and Western Railroad. The line survived until 1917 when it was pulled up and sent to France for the World War I effort. The Tidewater and Western Railroad carried freight and passengers along a route from Farmville, Virginia to Bermuda Hundred. The Tidewater and Western Railroad continued to have Western Union Telegraphs run along the rails. These connected to telegraphs on the Atlantic Coast Line along the East Coast of the US and to Europe.
The Princeton–Deepwater District is a rail line in West Virginia that connects Deep Water, West Virginia on the Kanawha River southwards to Princeton, West Virginia and beyond to rail lines leading to Virginia. It is known for its rugged terrain and opportunities for rail photography.