
The Bayeux Tapestry is an embroidered cloth nearly 70 metres long and 50 centimetres tall that depicts the events leading up to the Norman Conquest of England in 1066, led by William, Duke of Normandy challenging Harold II, King of England, and culminating in the Battle of Hastings. It is thought to date to the 11th century, within a few years of the battle. Now widely accepted to have been made in England perhaps as a gift for William, it tells the story from the point of view of the conquering Normans and for centuries has been preserved in Normandy.

The depiction of Jesus in pictorial form dates back to early Christian art and architecture, as aniconism in Christianity was rejected within the ante-Nicene period. It took several centuries to reach a conventional standardized form for his physical appearance, which has subsequently remained largely stable since that time. Most images of Jesus have in common a number of traits which are now almost universally associated with Jesus, although variants are seen.

A tetramorph is a symbolic arrangement of four differing elements, or the combination of four disparate elements in one unit. The term is derived from the Greek tetra, meaning four, and morph, shape.

The ichthys or ichthus, from the Greek ikhthū́s is a symbol consisting of two intersecting arcs, the ends of the right side extending beyond the meeting point so as to resemble the profile of a fish. It has been speculated that the symbol was adopted by early Christians as a secret symbol; a shibboleth to determine if another was indeed Christian. It is now known colloquially as the "Jesus fish".

The Adoration of the Magi or Adoration of the Kings or Visitation of the Wise Men is the name traditionally given to the subject in the Nativity of Jesus in art in which the three Magi, represented as kings, especially in the West, having found Jesus by following a star, lay before him gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh, and worship him. It is related in the Bible by Matthew 2:11: "On entering the house, they saw the child with Mary his mother; and they knelt down and paid him homage. Then, opening their treasure chests, they offered him gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh. And having been warned in a dream not to return to Herod, they left for their own country by another path".
In the Catholic Church, a titular church is a church in Rome that is assigned to a member of the clergy who is created a cardinal. These are Catholic churches in the city, within the jurisdiction of the Diocese of Rome, that serve as honorary designations symbolising the relationship of cardinals to the pope, the bishop of Rome. According to the 1983 Code of Canon Law, a cardinal may assist his titular church through counsel or through patronage, although "he has no power of governance over it, and he should not for any reason interfere in matters concerning the administration of its good, or its discipline, or the service of the church".

The St Augustine Gospels is an illuminated Gospel Book which dates from the 6th century and has been in the Parker Library in Corpus Christi College, Cambridge since 1575. It was made in Italy and has been in England since fairly soon after its creation; by the 16th century it had probably already been at Canterbury for almost a thousand years. It has 265 leaves measuring about 252 x 196 mm, and is not entirely complete, in particular missing pages with miniatures.

The Basilica of Santa Maria in Trastevere ; English: Our Lady in Trastevere) is a titular minor basilica in the Trastevere district of Rome, and one of the oldest churches of Rome. The basic floor plan and wall structure of the church date back to the 340s, and much of the structure to 1140–43. The first sanctuary was built in 221 and 227 by Pope Callixtus I and later completed by Pope Julius I. The church has large areas of important mosaics from the late 13th century by Pietro Cavallini.

Arma Christi, or the Instruments of the Passion, are the objects associated with the Passion of Jesus Christ in Christian symbolism and art. They are seen as arms in the sense of heraldry, and also as the weapons Christ used to achieve his conquest over Satan. There is a group, at a maximum of about 20 items, which are frequently used in Christian art, especially in the Late Middle Ages. Typically they surround either a cross or a figure of Christ of the Man of Sorrows type, either placed around the composition, or held by angels.
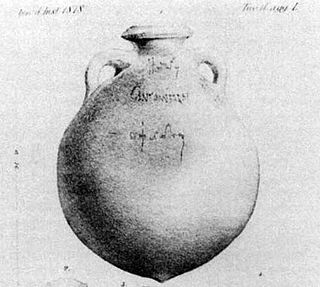
A titulus pictus is an ancient Roman commercial inscription made on the surface of certain artefacts, usually the neck of an amphora. Typically, these inscriptions were made in red or black paint. The inscription specifies information such as origin, destination, type of product, and owner. Tituli picti are frequent on ancient Roman pottery containers used for trade. They were not exclusively used for trade. They were also used to provide easily recognizable advertisements and may have served as insurance if a good was damaged in some way. There are around 2,500 tituli picti recorded in CIL IV.

The Titulus Crucis is a venerated piece of wood kept in the Church of Santa Croce in Gerusalemme in Rome which is claimed to be the titulus of the True Cross on which Jesus Christ was crucified. It is venerated by some Catholics as a relic associated with Jesus. Its authenticity is disputed, with some scholars confirming a plausible authenticity, while others ignore or consider it to be a medieval forgery. Radiocarbon dating tests on the artifact have shown that it dates between 980 and 1146 AD.

In art history, a speech scroll is an illustrative device denoting speech, song, or other types of sound.

The Nativity of Jesus has been a major subject of Christian art since the 4th century.

The Flagellation of Christ, in art sometimes known as Christ at the Column or the Scourging at the Pillar, is an episode from the Passion of Jesus as presented in the Gospels. As such, it is frequently shown in Christian art, in cycles of the Passion or the larger subject of the Life of Christ. Catholic tradition places the Flagellation at the beginning of Via Dolorosa in Jerusalem, and the modern alternate Stations of the Cross locate it at the fourth station; it represents a Sorrowful Mystery of the Rosary. The column to which Christ is normally shown to be tied, and the rope, scourge, whip or birch are elements in the Arma Christi. The Basilica di Santa Prassede in Rome is one of the churches claiming to possess the original column or parts of it.

The life of Christ as a narrative cycle in Christian art comprises a number of different subjects showing events from the life of Jesus on Earth. They are distinguished from the many other subjects in art showing the eternal life of Christ, such as Christ in Majesty, and also many types of portrait or devotional subjects without a narrative element.

The Hand of God, or Manus Dei in Latin, also known as Dextera domini/dei, is a motif in Jewish and Christian art, especially of the Late Antique and Early Medieval periods, when depiction of Yahweh or God the Father as a full human figure was considered unacceptable. The hand, sometimes including a portion of an arm, or ending about the wrist, is used to indicate the intervention in or approval of affairs on Earth by God, and sometimes as a subject in itself. It is an artistic metaphor that is generally not intended to indicate that a hand was physically present or seen at any subject depicted. The Hand is seen appearing from above in a fairly restricted number of narrative contexts, often in a blessing gesture, but sometimes performing an action. In later Christian works it tends to be replaced by a fully realized figure of God the Father, whose depiction had become acceptable in Western Christianity, although not in Eastern Orthodox or Jewish art. Though the hand of God has traditionally been understood as a symbol for God's intervention or approval of human affairs, it is also possible that the hand of God reflects the anthropomorphic conceptions of the deity that may have persisted in late antiquity.

Saint Joseph's dreams are four dreams described in the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament in which Joseph, the legal father of Jesus, is visited by an angel of the Lord and receives specific instructions and warnings of impending danger. All four dreams come from the period around the Nativity of Jesus and his early life, between the onset of Mary's pregnancy and the family's return from the Flight to Egypt. They are often distinguished by numbers as "Joseph's first dream" and so on. Especially in art history, the first may be referred to as the Annunciation to Joseph.

In the New Testament, Jesus is referred to as the King of the Jews, both at the beginning of his life and at the end. In the Koine Hellenic of the New Testament, e.g., in John 19:3, this is written as Basileus ton Ioudaion.

The Bayeux Tapestry tituli are Medieval Latin captions that are embroidered on the Bayeux Tapestry and describe scenes portrayed on the tapestry. These depict events leading up to the Norman conquest of England concerning William, Duke of Normandy, and Harold, Earl of Wessex, later King of England, and culminating in the Battle of Hastings.

Christ in the winepress or the mystical winepress is a motif in Christian iconography showing Christ standing in a winepress, where Christ himself becomes the grapes in the press. It derives from the interpretation by Augustine and other early theologians of a group of passages in the Bible and is found as a visual image in Christian art between about 1100 and the 18th century, as well as in religious literature of many kinds. The image in art underwent a number of changes of emphasis, while remaining fairly consistent in its basic visual content, and was one of the relatively few medieval metaphorical or allegorical devotional images to maintain a foothold in Protestant iconography after the Reformation.
























