
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of Lentivirus that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, the average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype.
A co-receptor is a cell surface receptor that binds a signalling molecule in addition to a primary receptor in order to facilitate ligand recognition and initiate biological processes, such as entry of a pathogen into a host cell.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) co-infection is a multi-faceted, chronic condition that significantly impacts public health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 2 to 15% of those infected with HIV are also affected by HCV, increasing their risk of morbidity and mortality due to accelerated liver disease. The burden of co-infection is especially high in certain high-risk groups, such as intravenous drug users and men who have sex with men. These individuals who are HIV-positive are commonly co-infected with HCV due to shared routes of transmission including, but not limited to, exposure to HIV-positive blood, sexual intercourse, and passage of the Hepatitis C virus from mother to infant during childbirth.
Integrin, alpha L , also known as ITGAL, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGAL gene. CD11a functions in the immune system. It is involved in cellular adhesion and costimulatory signaling. It is the target of the drug efalizumab.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 or CDK9 is a cyclin-dependent kinase associated with P-TEFb.

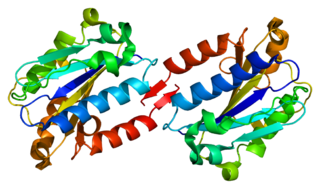
CD81 molecule, also known as CD81, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CD81 gene. It is also known as 26 kDa cell surface protein, TAPA-1, and Tetraspanin-28 (Tspan-28).

Programmed cell death protein 1(PD-1),. PD-1 is a protein encoded in humans by the PDCD1 gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor on T cells and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's response to the cells of the human body by down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T cell inflammatory activity. This prevents autoimmune diseases, but it can also prevent the immune system from killing cancer cells.

CD226, PTA1 or DNAM-1 is a ~65 kDa immunoglobulin-like transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on the surface of natural killer cells, NK T cell, B cells, dendritic cells, hematopoietic precursor cells, platelets, monocytes and T cells.
Phillip T. and Susan M. Ragon Institute is a medical institute founded in 2009 at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) by the funding from founder and CEO of InterSystems Phillip Ragon and his wife Susan Ragon to find vaccines for diseases of the immune system, particularly HIV/AIDS. The institute includes scientists from Harvard University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and the MGH, a level I trauma center which is the largest teaching hospital affiliated with Harvard Medical School.
Stuart C. Ray is an American physician. He is Vice Chair of Medicine for Data Integrity and Analytics, Associate Director of the Infectious Diseases Fellowship Training Program at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and a Professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases. Ray also holds appointments in Viral Oncology and the Division of Health Sciences Informatics. He is affiliated with the Institute for Computational Medicine at Johns Hopkins and is licensed to practice medicine in Maryland.
Thumbi Ndung’u is a Kenyan-born HIV/AIDS researcher. He is the deputy director (Science) and a Max Planck Research Group Leader at the Africa Health Research Institute (AHRI) in Durban, South Africa. He is Professor of Infectious Diseases in the Division of Immunity and Infection, University College London. He is Professor and Victor Daitz Chair in HIV/TB Research and Scientific Director of the HIV Pathogenesis Programme (HPP) at the Nelson R. Mandela School of Medicine, University of KwaZulu-Natal. He holds the South African Research Chair in Systems Biology of HIV/AIDS. He is an Adjunct Professor of Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. He is the Programme Director of the Sub-Saharan African Network for TB/HIV Research Excellence (SANTHE), a research and capacity building initiative funded by the African Academy of Sciences and the Wellcome Trust.

Bruce D. Walker is an American physician and scientist whose infectious disease research has produced many findings regarding HIV/AIDS. He became interested in studying HIV/AIDS after practicing on the front lines of the epidemic in the early 1980s, prior to the identification of HIV as the etiologic agent and prior to the availability of viable treatment options.

CD28 family receptors are a group of regulatory cell surface receptors expressed on immune cells. The CD28 family in turn is a subgroup of the immunoglobulin superfamily.

Hendrik Streeck is a German researcher of human immunodeficiency virus, epidemiologist and clinical trialist. He is professor of virology and the director of the Institute of Virology and HIV Research at the University Bonn.
Dan Hung Barouch is an American physician, immunologist, and virologist. He is known for his work on the pathogenesis and immunology of viral infections and the development of vaccine strategies for global infectious diseases.
Marylyn Martina Addo is a German infectiologist who is a Professor and the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) Head of Infectious Disease at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf. Addo has developed and tested vaccinations that protect people from Ebola virus disease and the MERS coronavirus EMC/2012. She is currently developing a viral vector based COVID-19 vaccine.

Alex K. Shalek is a biomedical engineer, and a core faculty member of the Institute for Medical Engineering and Science (IMES), an Associate Professor of Chemistry, and an Extramural Member of the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Additionally, he is a Member of the Ragon Institute and an Institute Member of the Broad Institute, an Assistant in Immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, and an Instructor in Health Sciences and Technology at Harvard Medical School. The multi-disciplinary research of the Shalek Lab aims to create and implement broadly-applicable methods to study and engineer cellular responses in tissues, to drive biological discovery and improve prognostics, diagnostics, and therapeutics for autoimmune, infectious, and cancerous diseases. Shalek and his lab are best known for their work in single-cell genomics and for studying a number of devastating, but difficult to study, human diseases with partners around the world.
Galit Alter is an immunologist and virologist, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, and group leader at the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard. She is known for her work on the expansion of particular natural killer cell subtypes in response to HIV-1 infection. She has also contributed to the understanding of how SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers correlate with sustained humoral protection, including identifying coordinated immune cell-antibody signatures that may predict COVID-19 infection outcome.

Riccardo Cortese was an Italian scientist, entrepreneur, and innovator in the field of gene expression, drug discovery and genetic vaccines. His work led to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for the prevention and cure of viral infections, including HIV, HCV, Ebola and RSV. He pioneered a novel platform technology based on simian adenoviral vectors for prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines, and authored more than 300 publications in peer-reviewed journals in the field of gene expression, transcriptional control, molecular virology and immunology.
Jayaraj Rajagopal is an Indian-American physician-scientist. He is the Bernard and Mildred Kayden MGH Research Institute Chair and Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. He founded and serves as the Chief of the Stanbury Physician-Scientist Pathway at the Massachusetts General Hospital Department of Medicine. His laboratory focuses on epithelial biology, lung stem cell biology, regenerative biology, and lung diseases.











