Abydos is one of the oldest cities of ancient Egypt, and also of the eighth nome in Upper Egypt. It is located about 11 kilometres west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of El Araba El Madfuna and El Balyana. In the ancient Egyptian language, the city was called Abdju. The English name Abydos comes from the Greek Ἄβυδος, a name borrowed by Greek geographers from the unrelated city of Abydos on the Hellespont.

Khasekhemwy was the last Pharaoh of the Second Dynasty of Egypt. Little is known about him, other than that he led several significant military campaigns and built the mudbrick fort known as Shunet El Zebib.

Qa'a was the last king of the First Dynasty of Egypt. He reigned for 33 years at the end of the 30th century BC.

Hor-Aha is considered the second pharaoh of the First Dynasty of Egypt by some Egyptologists, while others consider him the first one and corresponding to Menes. He lived around the 31st century BC and is thought to have had a long reign.

Umm El Qaʻāb is a necropolis of the Early Dynastic Period kings at Abydos, Egypt. Its modern name means "Mother of Pots" as the whole area is littered with the broken pot shards of offerings made in earlier times. The cultic ancient name of the area was (w-)pkr or (rꜣ-)pkr "District of the pkr[-tree]" or "Opening of the pkr[-tree]", belonging to tꜣ-dsr "the secluded/cleared land" (necropolis) or crk-hh "Binding of Eternity".

Merneith was a consort and a regent of Ancient Egypt during the First Dynasty. She may have been a ruler of Egypt in her own right, based on several official records. If this was the case and the earlier royal wife Neithhotep never ruled as an independent regent, Merneith may have been the first female pharaoh and the earliest queen regnant in recorded history. Her rule occurred around 2950 BC for an undetermined period. Merneith’s name means "Beloved by Neith" and her stele contains symbols of that ancient Egyptian deity. She may have been Djer's daughter and was probably Djet's senior royal wife. The former meant that she would have been the great-granddaughter of unified Egypt's first pharaoh, Narmer. She was also the mother of Den, her successor.

Iry-Hor was a predynastic pharaoh of Upper Egypt during the 32nd century BC. Excavations at Abydos in the 1980s and 1990s and the discovery in 2012 of an inscription of Iry-Hor in the Sinai confirmed his existence. Iry-Hor is the earliest ruler of Egypt known by name and is sometimes cited as the earliest-living historical person known by name.

Seth-Peribsen is the serekh name of an early Egyptian monarch (pharaoh), who ruled during the Second Dynasty of Egypt. His chronological position within this dynasty is unknown and it is disputed who ruled both before and after him. The duration of his reign is also unknown.

Anedjib, more correctly Adjib and also known as Hor-Anedjib, Hor-Adjib and Enezib, is the Horus name of an early Egyptian king who ruled during the 1st Dynasty. The Egyptian historian Manetho named him "Miebîdós" and credited him with a reign of 26 years, whilst the Royal Canon of Turin credited him with an implausible reign of 74 years. Egyptologists and historians now consider both records to be exaggerations and generally credit Adjib with a reign of 8–10 years.

Semerkhet is the Horus name of an early Egyptian king who ruled during the First Dynasty. This ruler became known through a tragic legend handed down by the historian Manetho, who reported that a calamity of some sort occurred during Semerkhet's reign. The archaeological records seem to support the view that Semerkhet had a difficult time as king and some early archaeologists questioned the legitimacy of Semerkhet's succession to the Egyptian throne.

Hawara is an archaeological site of Ancient Egypt, south of the site of Crocodilopolis at the entrance to the depression of the Fayyum oasis. It is the site of a pyramid built by the Pharaoh Amenemhat III in the 19th century BC.

Ka, also (alternatively) Sekhen, was a Predynastic pharaoh of Upper Egypt belonging to Dynasty 0. He probably reigned during the first half of the 32nd century BC. The length of his reign is unknown.

Tarkhan is an ancient Egyptian necropolis, located around 50 km south of Cairo on the west bank of the Nile. The cemetery was excavated in two seasons by Flinders Petrie. Tombs of almost all periods were found, but most importantly many belonging to the time of Egyptian state formation, the Early Dynastic period around 3100 BC. Petrie found more than 2,000 tombs, most of them simple holes in the ground belonging to common people. However, there were also several mastabas of the First Dynasty, decorated with a palace facade.

The Abydos boats are the remnants of a group of ancient royal Egyptian ceremonial boats found at an archaeological site in Abydos, Egypt. Discovered in 1991, excavation of the Abydos boats began in 2000 at which time fourteen boats were identified. They are located alongside the massive mudbrick structure known as Shunet El Zebib, attributed to the 2nd Dynasty Pharaoh Khasekhemwy. Shunet El Zebib is one of several such "enclosure wall" constructions at this site dating back to the 1st Dynasty, and is located nearly one mile from the early dynastic royal cemetery of Umm El Qa'ab.
Betrest was a queen of Ancient Egypt. She lived during the First Dynasty.

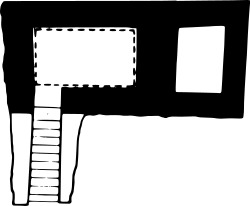
S 10 is the modern name given to a monumental ancient Egyptian tomb complex at Abydos in Egypt. The tomb is most likely royal and dates to the mid-13th Dynasty. Finds from nearby tombs indicate that S10 suffered extensive state-sanctioned stone and grave robbing during the Second Intermediate Period, only a few decades after its construction, as well as during the later Roman and Coptic periods. These finds also show that S10 was used for an actual burial and belonged to a king "Sobekhotep", now believed to be pharaoh Sobekhotep IV. According to the Egyptologist Josef W. Wegner who excavated S10, the tomb might originally have been capped by a pyramid, although Aidan Dodson states that it is still unclear whether S10 was a pyramid or a mastaba.
Mastaba S3504 is a large mastaba tomb located in the Saqqara necropolis in Lower Egypt. It was built during the reign of the ancient Egyptian Pharaoh Djet, in the First Dynasty, shortly after 3000 BC. It is one of the largest mastabas from this dynasty. The building was excavated in 1953 by Walter Bryan Emery.

Mastaba S3503 is a large mastaba tomb at the Saqqara necropolis in Lower Egypt. The burial was constructed around 3000 BC during the 1st Dynasty of Ancient Egypt.
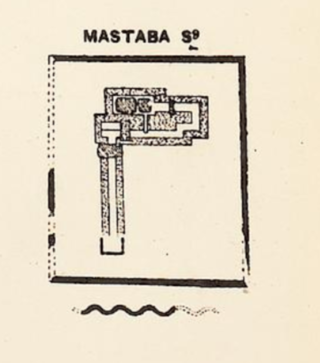
S 9 is the modern name given to a monumental ancient Egyptian tomb complex at Abydos in Egypt. The tomb is most likely royal and dates to the mid-13th Dynasty, during the late Middle Kingdom. Finds from the area of the tomb indicate that S9 suffered extensive, state-sanctioned stone and grave robbing during the Second Intermediate Period, only a few decades after its construction, as well as during the later Roman and Coptic periods. Although no direct evidence was found to determine the tomb owner, strong indirect evidence suggest that the neighbouring and slightly smaller tomb S10 belongs to pharaoh Sobekhotep IV. Consequently, S9 has been tentatively attributed by the Egyptologist Josef W. Wegner to Sobekhotep IV's predecessor and brother, Neferhotep I . According to Wegner, the tomb might originally have been capped by a pyramid.

Nyibunesu, Ni-Ibunesut or Ne-Ibunesu was an ancient Egyptian priest of Hathor and local chief who lived during the Third or Fourth Dynasty in the region of Dendera. What is known from his life comes from his mastaba burial tomb in the Dendera Necropolis, a few hundred metres south of the Temple to Hathor. This tomb was explored during 1897 and 1898 by a team led by the British archaeologist Flinders Petrie.