
The Malpighiales comprise one of the largest orders of flowering plants. The order is very diverse, with well-known members including willows, violets, aspens and poplars, poinsettia, corpse flower, coca plant, cassava, flaxseed, castor bean, Saint John's wort, passionfruit, mangosteen, and manchineel tree.

Saxifragales is an order of angiosperms, or flowering plants, containing 15 botanical families and around 100 genera, with nearly 2,500 species. Of the 15 families, many are small, with eight of them being monotypic. The largest family is the Crassulaceae (stonecrops), a diverse group of mostly succulent plants, with about 35 genera. Saxifragales are found worldwide, primarily in temperate to subtropical zones, rarely being encountered growing wild in the tropics; however, many species are now cultivated throughout the world as knowledge of plant husbandry has improved. They can be found in a wide variety of environments, from deserts to fully aquatic habitats, with species adapted to alpine, forested or fully-aquatic habitats. Many are epiphytic or lithophytic, growing on exposed cliff faces, on trees or on rocks, and not requiring a highly organic or nutrient-dense substrate to thrive.

Rhododendron is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants and in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are native to eastern Asia and the Himalayan region, but smaller numbers occur elsewhere in Asia, and in North America, Europe and Australia.

The Crassulaceae, also known as the stonecrop family or the orpine family, are a diverse family of dicotyledon flowering plants characterized by succulent leaves and a form of photosynthesis, known as Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM). Flowers generally have five floral parts. Crassulaceae are usually herbaceous but there are some subshrubs, and relatively few treelike or aquatic plants. Crassulaceae are a medium-sized monophyletic family in the core eudicots, among the order Saxifragales, whose diversity has made infrafamilial classification very difficult. The family includes approximately 1,400 species and 34–35 genera, depending on the circumscription of the genus Sedum, and distributed over three subfamilies. Members of the Crassulaceae are found worldwide, but mostly in the Northern Hemisphere and southern Africa, typically in dry and/or cold areas where water may be scarce, although a few are aquatic.

The Clusiaceae or GuttiferaeJuss. (1789) are a family of plants including 13 genera and ca 750 species. Several former members of Clusiacae are now placed in Calophyllaceae and Hypericaceae. They are mostly trees and shrubs, with milky sap and fruits or capsules for seeds. The family is primarily tropical. More so than many plant families, it shows large variation in plant morphology. According to the APG III, this family belongs to the order Malpighiales.

Gesneriaceae, the gesneriad family, is a family of flowering plants consisting of about 152 genera and ca. 3,540 species in the tropics and subtropics of the Old World and the New World, with a very small number extending to temperate areas. Many species have colorful and showy flowers and are cultivated as ornamental plants.

Sedum is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Crassulaceae, members of which are commonly known as stonecrops. The genus has been described as containing up to 600 species, subsequently reduced to 400–500. They are leaf succulents found primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, but extending into the southern hemisphere in Africa and South America. The plants vary from annual and creeping herbs to shrubs. The plants have water-storing leaves. The flowers usually have five petals, seldom four or six. There are typically twice as many stamens as petals. Various species formerly classified as Sedum are now in the segregate genera Hylotelephium and Rhodiola.

Saxifragaceae is a family of herbaceous perennial flowering plants, within the core eudicot order Saxifragales. The taxonomy of the family has been greatly revised and the scope much reduced in the era of molecular phylogenetic analysis. The family is divided into ten clades, with about 640 known species in about 35 accepted genera. About half of these consist of a single species, but about 400 of the species are in the type genus Saxifraga. The family is predominantly distributed in the northern hemisphere, but also in the Andes in South America.

The Monimiaceae is a family of flowering plants in the magnoliid order Laurales. It is closely related to the families Hernandiaceae and Lauraceae. It consists of shrubs, small trees, and a few lianas of the tropics and subtropics, mostly in the southern hemisphere. The largest center of diversity is New Guinea, with about 75 species. Lesser centres of diversity are Madagascar, Australia, and the neotropics. Africa has one species, Xymalos monospora, as does Southern Chile. Several species are distributed through Malesia and the southwest Pacific.

Ochnaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Malpighiales. In the APG III system of classification of flowering plants, Ochnaceae is defined broadly, to include about 550 species, and encompasses what some taxonomists have treated as the separate families Medusagynaceae and Quiinaceae. In a phylogenetic study that was published in 2014, Ochnaceae was recognized in the broad sense, but two works published after APG III have accepted the small families Medusagynaceae and Quiinaceae. These have not been accepted by APG IV (2016).

Podostemaceae, a family in the order Malpighiales, comprise about 50 genera and c. 300 species of more or less thalloid aquatic herbs.

Clusia is the type genus of the plant family Clusiaceae. Comprising 300-400 species, it is native to the Neotropics. The genus is named by Carl Linnaeus in honor of the botanist Carolus Clusius.

Coccothrinax is a genus of palms in the family Arecaceae. There are more than 50 species described in the genus, plus many synonyms and subspecies. A new species was described as recently as 2017. Many Coccothrinax produce thatch. In Spanish-speaking countries, guano is a common name applied to Coccothrinax palms. The species are native throughout the Caribbean, the Bahamas, extreme southern Florida and southeastern Mexico, but most of the species are known only from Cuba.

Haloragaceae is a eudicot flowering plant family in the order Saxifragales, based on the phylogenetic APG system. In the Cronquist system, it was included in the order Haloragales.

Rhodiola is a genus of perennial plants in the family Crassulaceae that resemble Sedum and other members of the family. Like sedums, Rhodiola species are often called stonecrops. Some authors merge Rhodiola into Sedum.

Hylotelephium is a genus of flowering plants in the stonecrop family Crassulaceae. It includes about 33 species distributed in Asia, Europe, and North America.
Maringma-tepui, also written Mount Maringma and historically known as Mount Marima, is a small tepui of the Pacaraima Mountains in Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Guyana. It is known as Malaima-tepui in the local Akawaio language. Most published sources place it just inside Guyanese territory, very close to the border with Brazil, and around 17 kilometres (11 mi) east of Roraima-tepui. However, the mountain remains the subject of considerable toponymic confusion and its name has been applied to at least one other nearby peak.[nb a]

Orostachys is a genus of the succulent family Crassulaceae that contains about 15 species. It is a biennial herb growing in China, Japan, Kazakhstan, Korea, Mongolia, Russia. Eight species occur in China.
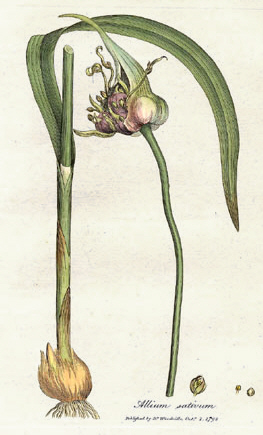
Allium is a large genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants with around 1000 accepted species, making Allium the largest genus in the family Amaryllidaceae and amongst the largest plant genera in the world. Many of the species are edible, and some have a long history of cultivation and human consumption as a vegetable including the onion, garlic, scallions, shallots, leeks, and chives, with onions being the second most grown vegetable globally after tomatoes as of 2023.

Adenotrias is a section of flowering plants in the family Hypericaceae. It is made up of Hypericum aciferum, H. aegypticum, and H. russeggeri. When it was first described, it was considered its own independent genus, but was later placed under Hypericum and demoted to a section. Its Latin name Adenotrias is made of the Greek prefix adeno- and the Latin word trias. Species in the section are shrubs up to 2 metres (6.6 ft) tall with smooth leaves and bark, and are the only species in Hypericum with heterostylous flowers. They are found around the Mediterranean coast, with H. aciferum restricted to the island of Crete and H. russeggeri present only in parts of Turkey and Syria. Plants of the section have a habitat among limestone and other calcareous rocks. While H. aegypticum has a wide and generally secure distribution, H. aciferum was evaluated as endangered several times since the 1980s, although it is now considered only vulnerable because it is protected in part by a plant micro-reserve near Agia Roumeli.



















