Linear predictive coding (LPC) is a method used mostly in audio signal processing and speech processing for representing the spectral envelope of a digital signal of speech in compressed form, using the information of a linear predictive model.

Congestion pricing or congestion charges is a system of surcharging users of public goods that are subject to congestion through excess demand, such as through higher peak charges for use of bus services, electricity, metros, railways, telephones, and road pricing to reduce traffic congestion; airlines and shipping companies may be charged higher fees for slots at airports and through canals at busy times. Advocates claim this pricing strategy regulates demand, making it possible to manage congestion without increasing supply.
Power management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers, computer CPUs, computer GPUs and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power state when inactive. In computing this is known as PC power management and is built around a standard called ACPI which superseded APM. All recent computers have ACPI support.
Prediction markets, also known as betting markets, information markets, decision markets, idea futures or event derivatives, are open markets that enable the prediction of specific outcomes using financial incentives. They are exchange-traded markets established for trading bets in the outcome of various events. The market prices can indicate what the crowd thinks the probability of the event is. A typical prediction market contract is set up to trade between 0 and 100%. The most common form of a prediction market is a binary option market, which will expire at the price of 0 or 100%. Prediction markets can be thought of as belonging to the more general concept of crowdsourcing which is specially designed to aggregate information on particular topics of interest. The main purposes of prediction markets are eliciting aggregating beliefs over an unknown future outcome. Traders with different beliefs trade on contracts whose payoffs are related to the unknown future outcome and the market prices of the contracts are considered as the aggregated belief.
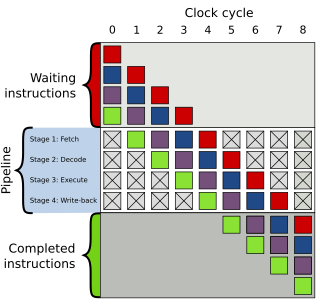
In computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch will go before this is known definitively. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow in the instruction pipeline. Branch predictors play a critical role in achieving high performance in many modern pipelined microprocessor architectures.

The Electronic Road Pricing (ERP) system is an electronic toll collection scheme adopted in Singapore to manage traffic by way of road pricing, and as a usage-based taxation mechanism to complement the purchase-based Certificate of Entitlement system. There are a total of 93 ERP gantries being built and located throughout the country, along expressways and roads leading towards the Central Area. As of July 2024, only 19 ERP gantries are in operation and are all in expressways where congestion continues to be severe.

LS-DYNA is an advanced general-purpose multiphysics simulation software package developed by the former Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC), which was acquired by Ansys in 2019. While the package continues to contain more and more possibilities for the calculation of many complex, real world problems, its origins and core-competency lie in highly nonlinear transient dynamic finite element analysis (FEA) using explicit time integration. LS-DYNA is used by the automobile, aerospace, construction and civil engineering, military, manufacturing, and bioengineering industries.
Prognostics is an engineering discipline focused on predicting the time at which a system or a component will no longer perform its intended function. This lack of performance is most often a failure beyond which the system can no longer be used to meet desired performance. The predicted time then becomes the remaining useful life (RUL), which is an important concept in decision making for contingency mitigation. Prognostics predicts the future performance of a component by assessing the extent of deviation or degradation of a system from its expected normal operating conditions. The science of prognostics is based on the analysis of failure modes, detection of early signs of wear and aging, and fault conditions. An effective prognostics solution is implemented when there is sound knowledge of the failure mechanisms that are likely to cause the degradations leading to eventual failures in the system. It is therefore necessary to have initial information on the possible failures in a product. Such knowledge is important to identify the system parameters that are to be monitored. Potential uses for prognostics is in condition-based maintenance. The discipline that links studies of failure mechanisms to system lifecycle management is often referred to as prognostics and health management (PHM), sometimes also system health management (SHM) or—in transportation applications—vehicle health management (VHM) or engine health management (EHM). Technical approaches to building models in prognostics can be categorized broadly into data-driven approaches, model-based approaches, and hybrid approaches.

The DynaTAC is a series of cellular telephones manufactured by Motorola from 1983 to 1994. The Motorola DynaTAC 8000X received approval from the U.S. FCC on September 21, 1983. A full charge took roughly 10 hours, and it offered 30 minutes of talk time. It also offered an LED display for dialing or recall of one of 30 phone numbers. It was priced at $3,995 in 1984, its commercial release year, equivalent to $11,716 in 2023. DynaTAC was an abbreviation of "Dynamic Adaptive Total Area Coverage".
Deep Thunder is a research project by IBM that aims to improve short-term local weather forecasting through the use of high-performance computing. It is part of IBM's Deep Computing initiative that also produced the Deep Blue chess computer.

A tropical cyclone forecast model is a computer program that uses meteorological data to forecast aspects of the future state of tropical cyclones. There are three types of models: statistical, dynamical, or combined statistical-dynamic. Dynamical models utilize powerful supercomputers with sophisticated mathematical modeling software and meteorological data to calculate future weather conditions. Statistical models forecast the evolution of a tropical cyclone in a simpler manner, by extrapolating from historical datasets, and thus can be run quickly on platforms such as personal computers. Statistical-dynamical models use aspects of both types of forecasting. Four primary types of forecasts exist for tropical cyclones: track, intensity, storm surge, and rainfall. Dynamical models were not developed until the 1970s and the 1980s, with earlier efforts focused on the storm surge problem.
Femap is an engineering analysis program sold by Siemens Digital Industries Software that is used to build finite element models of complex engineering problems ("pre-processing") and view solution results ("post-processing"). It runs on Microsoft Windows and provides CAD import, modeling and meshing tools to create a finite element model, as well as postprocessing functionality that allows mechanical engineers to interpret analysis results. The finite element method allows engineers to virtually model components, assemblies, or systems to determine behavior under a given set of boundary conditions, and is typically used in the design process to reduce costly prototyping and testing, evaluate differing designs and materials, and for structural optimization to reduce weight.
TransModeler is the name of a based traffic simulation platform for doing wide-area traffic planning, traffic management, and emergency evacuation studies that is developed by Caliper Corporation. It can animate the behavior of multi-modal traffic systems to show the flow of vehicles, the operation of traffic signals, and the overall performance of the transportation network.
Beat the Traffic was a provider of vehicle traffic reporting solutions for broadcast media and consumers. With a focus on daily commuters, Beat the Traffic was founded in 2001 by former CEO Andre Gueziec. On September 10, 2012, Pelmorex announced it had acquired Beat the Traffic.
Process simulation is used for the design, development, analysis, and optimization of technical process of simulation of processes such as: chemical plant s, chemical processes, environmental systems, power stations, complex manufacturing operations, biological processes, and similar technical functions.

Aimsun Live is a traffic forecasting solution based on simulation, developed and marketed by Aimsun.
Paramics is traffic microsimulation software, originally developed by Quadstone Ltd. There is a related pedestrian microsimulation product called the Urban Analytics Framework.

IBM Cognos Analytics with Watson is a web-based integrated business intelligence suite by IBM. It provides a toolset for reporting, analytics, scorecarding, and monitoring of events and metrics. The software consists of several components designed to meet the different information requirements in a company. IBM Cognos Analytics has components such as IBM Cognos Framework Manager, IBM Cognos Cube Designer, IBM Cognos Transformer.
Noise-Predictive Maximum-Likelihood (NPML) is a class of digital signal-processing methods suitable for magnetic data storage systems that operate at high linear recording densities. It is used for retrieval of data recorded on magnetic media.

Michel Bierlaire is a Belgian-Swiss applied mathematician specialized in transportation modeling and optimization. He is a professor at EPFL and the head of the Transport and Mobility Laboratory.










