
Bajirao I, born as Visaji, was the 7th Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy. During his 20-year tenure as a Peshwa, he defeated Nizam-ul-Mulk at several battles like the Battle of palkhed and Battle of Bhopal. Bajirao contributed to Maratha supremacy in southern India and northern India. Thus, he was partly responsible for establishing Maratha power in Gujarat, Malwa, Rajputana and Bundelkhand and liberating Konkan from the Siddis of Janjira and Portuguese rule.

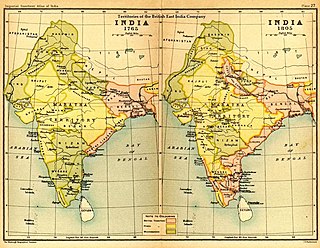
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that rose to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shivaji of the Bhonsle Dynasty as the Chhatrapati. Although Shivaji came from the Maratha caste, the Maratha empire also included warriors, administrators and other notables from Maratha and several other castes from Maharashtra.

The Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803–1805) was the second conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India.

The Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817–1819) was the final and decisive conflict between the English East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha territory by British East India Company troops, and although the British were outnumbered, the Maratha army was decimated. The troops were led by Governor General Hastings, supported by a force under General Thomas Hislop. Operations began against the Pindaris, a band of Muslim mercenaries and Marathas from central India.

Vasai, is a historical place and City near Mumbai (Bombay)'s western suburbs, located in Palghar district which was partitioned from the Thane district in 2014. It also forms a part of Vasai-Virar twin cities in the Konkan division of Maharashtra, India.

Shrimant Peshwa Baji Rao II was the 13th and the last Peshwa of the Maratha Empire. He governed from 1795 to 1818. He was installed as a puppet ruler by the Maratha nobles, whose growing power prompted him to flee his capital Poona and sign the Treaty of Bassein (1802) with the British. This resulted in the Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803–1805), in which the British emerged victorious and re-installed him as the titular Peshwa. In 1817, Baji Rao II joined the Third Anglo-Maratha War against the British, after they favoured the Gaekwad nobles in a revenue-sharing dispute. After suffering several battle defeats, the Peshwa surrendered to the British, and agreed to retire in return for an estate at Bithoor and an annual pension.
The Battle of Palkhed was fought on February 28, 1728 at the village of Palkhed, near the city of Nashik, Maharashtra, India between the Maratha Empire and the Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah I of Hyderabad wherein, the Marathas defeated the Nizam.

Arnala Fort is built on a small island off the port town of Arnala, located around 13 km north of Bassein, Maharashtra, India. Being an island fort, it is also called Jaldurg or Janjire-Arnala. The Portuguese, who built the present fort, called the island Ilha das Vacas.

Shrimant Daulat Rao Shinde was the Maharaja (ruler) of Gwalior state in central India from 1794 until his death in 1827. His reign coincided with struggles for supremacy within the Maratha Empire, and wars with the expanding East India Company. Daulatrao played a significant role in the Second and Third Anglo-Maratha wars.
Treaty of Bassein may refer to:
The Treaty of Purandar was a doctrine signed on 1 March 1776 by the peshwa of the Maratha Empire and the British East India Company's Supreme Council of Bengal in Calcutta. Based on the terms of the accord, the British were able to secure Salsette. Treaty was signed between the then Governor General Warren Hasting who sent Colonel Upton and Nana Phadnavis of Peshwa in which British accepted Sawai Madhav Rao as a new Peshwa and Maratha accepted not to recognise existence of French in India.
The Maratha Conquests were a series of conquests in the Indian subcontinent which led to the building of the Maratha Empire. These conquests were started by Shivaji in 1659, from the victory at the Battle of Pratapgad against Bijapur. The expansion of the empire was limited and interrupted by the Mughal conquests of south India by Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. Marathas were forced to defend their territories against the overwhelmingly strong Mughal army in the 27 years long Deccan wars. They were able to defend their territories and gain an upper hand over Mughals in the sustained conflict.
The Battle of Pune took place on 25 October 1802 near Pune between the rival factions of the Maratha empire. The forces of the Scindia (Shinde) and the Peshwa Bajirao II were attacked by the Holkars. While the British East India Company was not involved in the battle, its outcome and aftermath led to the Second Anglo-Maratha War.

Madhav Rao Bhat II was the 12th Peshwa of the Maratha Empire in India, from his infancy. He was known as Sawai Madhav Rao or Madhav Rao Narayan. He was the posthumous son of Narayanrao Peshwa, murdered in 1773 on the orders of Raghunathrao. Madhavrao II was considered the legal heir, and was installed as Peshwa by the Treaty of Salbai in 1782 after First Anglo-Maratha War.

Yashwant Rao Holkar also known as Jaswantrao Holkar belonging to the Holkar dynasty of the Maratha Empire was the Maharaja of the Maratha Empire. He was a gifted military leader and educated in accountancy as well as literate in Persian and Marathi and Urdu.
Baloji Kunjar / Kunjir (17??–1816) was Sardar and Minister of Affairs in service of Peshwa Baji Rao II. He was Peshwa Baji Rao II's favorite. After the death of Peshwa Sawai Madhavrao, there was debates for the position of Peshwa among the Maratha Empire. Balaji Kunjar performed a successful role to convey most friendly declaration and assurance between Baji Rao II and Nana Phadanvis, to appoint Baji Rao II as peshwa of Maratha Empire. Peshwa Baji Rao II and Nana Phadanvis awarded inam (Jagir) to him in 14 villages near Purandhar fort, for his role. He performed successful role in administration of maratha empire and as affairs minister or diplomat (vakil) for Peshwa Baji Rao II. He along with his son Pandoji Kunjar and Narayan, enjoyed the position as Sur-Patil (सर-पाटील) at Pune Punch Mahals during the era of Peshawa Baji Rao II. He along with his family has long enjoyed the privileges of sar-patil of 360 villages and towns in the Subha of Poona.
The Maratha conquest of Northwest India occurred between 1757 and 1759, when the Maratha Empire captured the northwestern parts of the Indian subcontinent from the Durrani Empire. It had long-lasting effects upon the future geopolitics of the Indian subcontinent.

Jhansi was an independent princely state ruled by the Maratha Newalkar dynasty under suzerainty of British India from 1804 till 1853, when the British authorities took over the state under the terms of the Doctrine of Lapse, and renamed it the Jhansi State. Before the takeover, it was under the Peshwas from 1728 to 1804. The fortified town of Jhansi served as its capital.
The Bhat Peshwa family earlier known as Bhat family is a prominent Indian Chitpavan Brahmin family who dominated India for around 100 years in the late 18th century and early 19th century. Most of the members in this family were the Peshwas in the Peshwa Era of the Maratha Empire, and Peshwa later became their family name. During their regime, most of the Indian subcontinent was under their control. The last Peshwa, Baji Rao II, was defeated by the British East India Company in the Third Anglo-Maratha War in 1818. The territory was annexed to the British East India Company's Bombay Presidency, and he was pensioned
Amrut Rao was a Maratha noble, and the adopted son of Peshwa Raghunath Rao. In 1803, Yashwant Rao Holkar invaded Pune and deposed his adoptive brother Peshwa Baji Rao II. Subsequently, Holkar set up an ad hoc council nominally headed by Amrut Rao, and ran the Peshwa's government in his name. Holkar also installed Amrut Rao's son Vinayak Rao as the Peshwa to strengthen the legal status of his government, because Vinayak had been adopted by the widow of the deceased Peshwa Madhav Rao II. However, Baji Rao sought assistance from the British East India Company, whose advance forced Amrut Rao and his son to flee Pune. Subsequently, Amrut Rao signed a treaty with the British, agreeing to give up all claims over the Peshwa's office in return for a pension and an estate in Bundelkhand.












