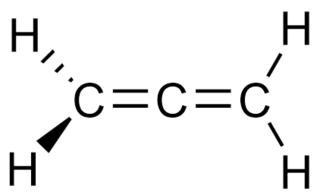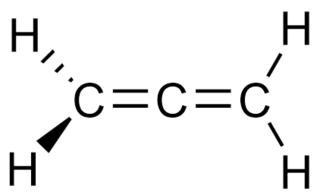
Allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon centres. Allenes are classified as cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene, which is itself also called allene. Compounds with an allene-type structure but with more than three carbon atoms are members of a larger class of compounds called cumulenes with X=C=Y bonding.

An ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid in which at least one –OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an –O– alkyl (alkoxy) group, as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils.

An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which an enol or an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone, followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone.
A sigmatropic reaction in organic chemistry is a pericyclic reaction wherein the net result is one σ-bond is changed to another σ-bond in an uncatalyzed intramolecular reaction. The name sigmatropic is the result of a compounding of the long-established sigma designation from single carbon–carbon bonds and the Greek word tropos, meaning turn. In this type of rearrangement reaction, a substituent moves from one part of a π-bonded system to another part in an intramolecular reaction with simultaneous rearrangement of the π system. True sigmatropic reactions are usually uncatalyzed, although Lewis acid catalysis is possible. Sigmatropic reactions often have transition-metal catalysts that form intermediates in analogous reactions. The most well-known of the sigmatropic rearrangements are the [3,3] Cope rearrangement, Claisen rearrangement, Carroll rearrangement, and the Fischer indole synthesis.
The Cope rearrangement is an extensively studied organic reaction involving the [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of 1,5-dienes. It was developed by Arthur C. Cope and Elizabeth Hardy. For example, 3-methyl-hexa-1,5-diene heated to 300 °C yields hepta-1,5-diene.

The Bamford–Stevens reaction is a chemical reaction whereby treatment of tosylhydrazones with strong base gives alkenes. It is named for the British chemist William Randall Bamford and the Scottish chemist Thomas Stevens Stevens (1900–2000). The usage of aprotic solvents gives predominantly Z-alkenes, while protic solvent gives a mixture of E- and Z-alkenes. As an alkene-generating transformation, the Bamford–Stevens reaction has broad utility in synthetic methodology and complex molecule synthesis.
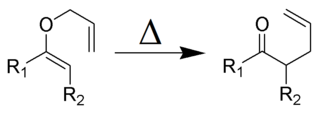
The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl.

Rainer Ludwig Claisen was a German chemist best known for his work with condensations of carbonyls and sigmatropic rearrangements. He was born in Cologne as the son of a jurist and studied chemistry at the university of Bonn (1869), where he became a member of K.St.V. Arminia. He served in the army as a nurse in 1870–1871 and continued his studies at Göttingen University. He returned to the University of Bonn in 1872 and started his academic career at the same university in 1874. He died in 1930 in Godesberg am Rhein.
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen, who first published his work on the reaction in 1887.
The Overman rearrangement is a chemical reaction that can be described as a Claisen rearrangement of allylic alcohols to give allylic trichloroacetamides through an imidate intermediate. The Overman rearrangement was discovered in 1974 by Larry Overman.

In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is R2C=CR-OR where R = H, alkyl or aryl. A common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers, with the formula ROCH=CH2. Important enol ethers include the reagent 3,4-dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether.

Elemicin is a phenylpropene, a natural organic compound, and is a constituent of several plant species' essential oils.
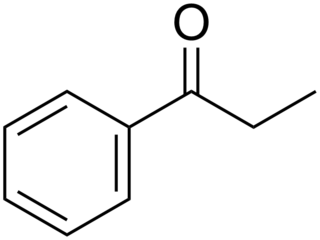
Propiophenone is an aryl ketone. It is a colorless, sweet-smelling liquid that is insoluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. It is used in the preparation of other compounds.

In organic chemistry, an ortho ester is a functional group containing three alkoxy groups attached to one carbon atom, i.e. with the general formula RC(OR′)3. Orthoesters may be considered as products of exhaustive alkylation of unstable orthocarboxylic acids and it is from these that the name 'ortho ester' is derived. An example is ethyl orthoacetate, CH3C(OCH2CH3)3, more correctly known as 1,1,1-triethoxyethane.

Triethyl orthoformate is an organic compound with the formula HC(OC2H5)3. This colorless volatile liquid, the orthoester of formic acid, is commercially available. The industrial synthesis is from hydrogen cyanide and ethanol.
The Ireland–Claisen rearrangement is a chemical reaction of an allylic ester with strong base to give an γ,δ-unsaturated carboxylic acid.

Larry E. Overman is Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at the University of California, Irvine. He was born in Chicago in 1943. Overman obtained a B.A. degree from Earlham College in 1965, and he completed his Ph.D. in chemistry from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1969, under Howard Whitlock Jr. Professor Overman is a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He was the recipient of the Arthur C. Cope Award in 2003, and he was awarded the Tetrahedron Prize for Creativity in Organic Chemistry for 2008.
The RXNO Ontology is a formal ontology of chemical named reactions. It was originally developed at the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) and is associated with the Open Biomedical Ontologies Foundry. The RXNO ontology unifies several previous attempts to systematize chemical reactions including the Merck Index and the hierarchy of Carey, Laffan, Thomson and Williams.

Ethyl propiolate is an organic compound with the formula HC2CO2C2H5. It is the ethyl ester of propiolic acid, the simplest acetylenic carboxylic acid. It is a colorless liquid that is miscible with organic solvents. The compound is a reagent and building block for the synthesis of other organic compounds, reactions that exploit the electrophilicity of the alkyne group.
The Cadogan-Sundberg indole synthesis, or simply Cadogan indole synthesis, is a name reaction in organic chemistry that allows for the generation of indoles from o-nitrostyrenes with the use of trialkyl phosphites, such as triethyl phosphite.