Antisense therapy is a form of treatment that uses antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) to target messenger RNA (mRNA). ASOs are capable of altering mRNA expression through a variety of mechanisms, including ribonuclease H mediated decay of the pre-mRNA, direct steric blockage, and exon content modulation through splicing site binding on pre-mRNA. Several ASOs have been approved in the United States, the European Union, and elsewhere.

Omigapil is a drug that was developed by Novartis and tested in clinical trials for its ability to help treat Parkinson's disease (PD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The development for PD and ALS have been terminated due to lack of benefit, but Santhera Pharmaceuticals bought the compound for development for the treatment of congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD).

Naphthylaminopropane (PAL-287) is an experimental drug under investigation as of 2007 for the treatment of alcohol and stimulant addiction.

Lenabasum (also known as ajulemic acid, 1',1'-dimethylheptyl-delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol-11-oic acid, DMH-D8-THC-11-OIC, AB-III-56, HU-239, IP-751, CPL 7075, CT-3, JBT-101, Anabasum, and Resunab) is a synthetic cannabinoid that shows anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects in pre-clinical studies without causing a subjective "high". Although its design was inspired by a metabolite of delta-9-THC known as delta-9-THC-11-oic acid, lenabasum is an analog of the delta-8-THC metabolite delta-8-THC-11-oic acid. It is being developed for the treatment of inflammatory and fibrotic conditions such as systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis and cystic fibrosis. It does not share the anti-emetic effects of some other cannabinoids, but may be useful for treating chronic inflammatory conditions where inflammation fails to resolve. Side effects include dry mouth, tiredness, and dizziness. The mechanism of action is through activation of the CB2 receptor leading to production of specialized proresolving eicosanoids such as lipoxin A4 and prostaglandin J2. Studies in animals at doses up to 40 mg/kg show minimal psychoactivity of lenabasum, compared to that produced by tetrahydrocannabinol. Lenabasum is being developed by Corbus Pharmaceuticals (formerly JB Therapeutics) for the treatment of orphan chronic life-threatening inflammatory diseases. Development since been discontinued.

Translocator protein (TSPO) is an 18 kDa protein mainly found on the outer mitochondrial membrane. It was first described as peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR), a secondary binding site for diazepam, but subsequent research has found the receptor to be expressed throughout the body and brain. In humans, the translocator protein is encoded by the TSPO gene. It belongs to a family of tryptophan-rich sensory proteins. Regarding intramitochondrial cholesterol transport, TSPO has been proposed to interact with StAR to transport cholesterol into mitochondria, though evidence is mixed.
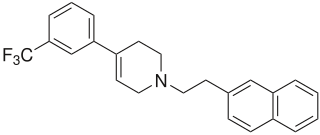
Xaliproden is a drug which acts as a 5HT1A agonist. It has neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects in vitro, and has been proposed for use in the treatment of several neurodegenerative conditions including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer's disease.

Bicifadine (DOV-220,075) is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) discovered at American Cyanamid as an analgesic drug candidate, and licensed to DOV Pharmaceutical in 1998 after American Cyanamid was acquired by Wyeth.

Solute carrier family 22 member 8, or organic anion transporter 3 (OAT3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC22A8 gene.

LY-503430 is an AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator developed by Eli Lilly.
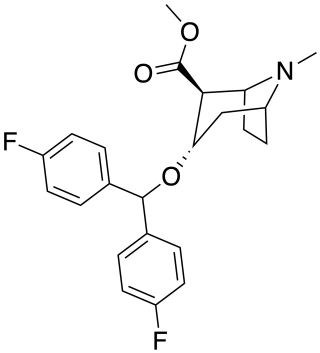
Difluoropine (O-620) is a stimulant drug synthesised from tropinone, which acts as a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Difluoropine is unique among the tropane-derived dopamine reuptake inhibitors in that the active stereoisomer is the (S) enantiomer rather than the (R) enantiomer, the opposite way round compared to natural cocaine. It is structurally related to benztropine and has similar anticholinergic and antihistamine effects in addition to its dopamine reuptake inhibitory action.
GSK-189,254 is a potent and selective H3 histamine receptor inverse agonist developed by GlaxoSmithKline. It has subnanomolar affinity for the H3 receptor (Ki = 0.2nM) and selectivity of over 10,000x for H3 over other histamine receptor subtypes. Animal studies have shown it to possess not only stimulant and nootropic effects, but also analgesic action suggesting a role for H3 receptors in pain processing in the spinal cord. GSK-189,254 and several other related drugs are currently being investigated as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, as well as possible use in the treatment of conditions such as narcolepsy, or neuropathic pain which do not respond well to conventional analgesic drugs.

SB-612,111 is an opioid receptor ligand which is a potent and selective antagonist for the nociceptin receptor (ORL-1), several times more potent than the older drug J-113,397. It does not have analgesic effects in its own right, but prevents the development of hyperalgesia, and also shows antidepressant effects in animal studies.

4-Methylamphetamine is a stimulant and anorectic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes.
The alpha-3 beta-4 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α3β4 receptor and the ganglion-type nicotinic receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of α3 and β4 subunits. It is located in the autonomic ganglia and adrenal medulla, where activation yields post- and/or presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Na+ and K+ permeability.
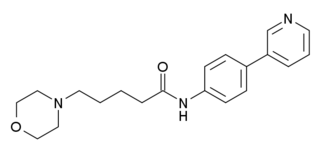
WAY-317538 (SEN-12333) is a drug that acts as a potent and selective full agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It was not the most potent compound in the series, but was selected for further development on the basis of its high selectivity over related receptors, ease of synthesis, and good in vivo properties including high oral bioavailability and good brain penetration. It has nootropic and neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and is being investigated as a potential treatment for neurodegenerative and neurocognitive conditions including Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia.

Olesoxime (TRO19622) is an experimental drug formerly under development by the now-defunct French company Trophos as a treatment for a range of neuromuscular disorders. It has a cholesterol-like structure and belongs to the cholesterol-oxime family of mitochondrial pore modulators.

Ro5-4864 (4'-chlorodiazepam) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative of diazepam. However unlike most benzodiazepine derivatives, Ro5-4864 lacks affinity for GABAA receptors and lacks typical benzodiazepine effects, instead being sedative yet also convulsant and anxiogenic in effects. Ro5-4864 was found to be a potent ligand for the "peripheral benzodiazepine receptor", later renamed to mitochondrial translocator protein 18kDa (TSPO). Despite its convulsant effects, at lower doses Ro5-4864 has proved to be neuroprotective and has become widely used for research into the role of the TSPO protein in neurotoxicity. In vitro studies and rodent models also suggest the possibility of analgesic, antidepressant, cardioprotective, and anti-cancer effects.

3,4-Dichloroamphetamine (DCA), is an amphetamine derived drug invented by Eli Lilly in the 1960s, which has a number of pharmacological actions. It acts as a highly potent and selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and binds to the serotonin transporter with high affinity, but also acts as a selective serotonergic neurotoxin in a similar manner to the related para-chloroamphetamine, though with slightly lower potency. It is also a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), as well as a very potent inhibitor of the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase which normally functions to transform noradrenaline into adrenaline in the body.

Acetothiolutamide is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) derived from the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide that was described in 2002 and was one of the first SARMs to be discovered and developed. It is a high-affinity, selective ligand of the androgen receptor (AR), where it acts as a full agonist in vitro, and has in vitro potency comparable to that of testosterone. However, in vivo, acetothiolutamide displayed overall negligible androgenic effects, though significant anabolic effects were observed at high doses. In addition, notable antiandrogen effects were observed in castrated male rats treated with testosterone propionate. The discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo actions of acetothiolutamide was determined to be related to rapid plasma clearance and extensive hepatic metabolism into a variety of metabolites with differing pharmacological activity, including AR partial agonism and antagonism. In accordance with its poor metabolic stability, acetothiolutamide is not orally bioavailable, and shows activity only via injected routes such as subcutaneous and intravenous.
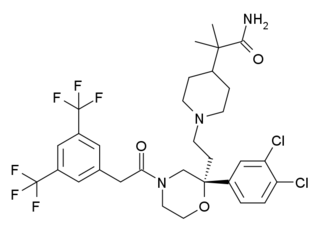
Burapitant (SSR-240,600) is a drug developed by Sanofi-Aventis which was one of the first compounds developed that acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor. While burapitant itself did not proceed beyond early clinical trials and was never developed for clinical use in humans, promising animal results from this and related compounds have led to a number of novel drugs from this class that have now been introduced into medical use.
















