
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted and typically has six or twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A guitar pick may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant hollow chamber on the guitar, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.
In music performance and notation, legato indicates that musical notes are played or sung smoothly and connected. That is, the player makes a transition from note to note with no intervening silence. Legato technique is required for slurred performance, but unlike slurring, legato does not forbid re-articulation.

An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental is the lowest pitch. While the fundamental is usually heard most prominently, overtones are actually present in any pitch except a true sine wave. The relative volume or amplitude of various overtone partials is one of the key identifying features of timbre, or the individual characteristic of a sound.

In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners.
Vibrato is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. Vibrato is typically characterized in terms of two factors: the amount of pitch variation and the speed with which the pitch is varied.
Falsetto is the vocal register occupying the frequency range just above the modal voice register and overlapping with it by approximately one octave.
A pull-off is a stringed instrument playing and articulation technique performed by plucking or "pulling" the finger that is grasping the sounding part of a string off the fingerboard of either a fretted or unfretted instrument. This intermediate- to advanced playing technique is done using the tip of a finger or fingernail on the fretting hand. Pull-offs are done to facilitate the playing of embellishments and ornaments such as grace notes. Pull-offs may be notated in sheet music or improvised by the performer, depending on the musical style and context.

Peter Hamilton Rowan is an American bluegrass musician and composer. He plays guitar and mandolin, yodels and sings. He is a seven-time Grammy Award nominee.
Chorus is an audio effect that occurs when individual sounds with approximately the same time, and very similar pitches, converge. While similar sounds coming from multiple sources can occur naturally, as in the case of a choir or string orchestra, it can also be simulated using an electronic effects unit or signal processing device.
A nut, on a stringed musical instrument, is a small piece of hard material that supports the strings at the end closest to the headstock or scroll. The nut marks one end of the vibrating length of each open string, sets the spacing of the strings across the neck, and usually holds the strings at the proper height from the fingerboard. Along with the bridge, the nut defines the scale lengths of the open strings.
Americana is an amalgam of American music formed by the confluence of the shared and varied traditions that make up the musical ethos of the United States of America, with particular emphasis on music historically developed in the American South.
An acoustic guitar is a musical instrument in the string family. When a string is plucked, its vibration is transmitted from the bridge, resonating throughout the top of the guitar. It is also transmitted to the side and back of the instrument, resonating through the air in the body, and producing sound from the sound hole. While the original, general term for this stringed instrument is guitar, the retronym 'acoustic guitar' – often used to indicate the steel stringed model – distinguishes it from an electric guitar, which relies on electronic amplification. Typically, a guitar's body is a sound box, of which the top side serves as a sound board that enhances the vibration sounds of the strings. In standard tuning the guitar's six strings are tuned (low to high) E2 A2 D3 G3 B3 E4.
In music, the undertone series or subharmonic series is a sequence of notes that results from inverting the intervals of the overtone series. While overtones naturally occur with the physical production of music on instruments, undertones must be produced in unusual ways. While the overtone series is based upon arithmetic multiplication of frequencies, resulting in a harmonic series, the undertone series is based on arithmetic division.
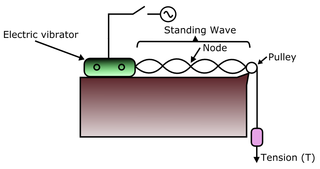
Melde's experiment is a scientific experiment carried out in 1859 by the German physicist Franz Melde on the standing waves produced in a tense cable originally set oscillating by a tuning fork, later improved with connection to an electric vibrator. This experiment, "a lecture-room standby", attempted to demonstrate that mechanical waves undergo interference phenomena. In the experiment, mechanical waves traveled in opposite directions form immobile points, called nodes. These waves were called standing waves by Melde since the position of the nodes and loops stayed static.
Sympathetic resonance or sympathetic vibration is a harmonic phenomenon wherein a passive string or vibratory body responds to external vibrations to which it has a harmonic likeness. The classic example is demonstrated with two similarly-tuned tuning forks. When one fork is struck and held near the other, vibrations are induced in the unstruck fork, even though there is no physical contact between them. In similar fashion, strings will respond to the vibrations of a tuning fork when sufficient harmonic relations exist between them. The effect is most noticeable when the two bodies are tuned in unison or an octave apart, as there is the greatest similarity in vibrational frequency. Sympathetic resonance is an example of injection locking occurring between coupled oscillators, in this case coupled through vibrating air. In musical instruments, sympathetic resonance can produce both desirable and undesirable effects.

The 3rd bridge is an extended playing technique used on the electric guitar and other string instruments that allows a musician to produce distinctive timbres and overtones that are unavailable on a conventional string instrument with two bridges. The timbre created with this technique is close to that of gamelan instruments like the bonang and similar Indonesian types of pitched gongs.
A third bridge can be devised by inserting a rigid preparation object between the strings and the body or neck of the instrument, effectively dividing the string into distinct vibrating segments.

A bridge is a device that supports the strings on a stringed musical instrument and transmits the vibration of those strings to another structural component of the instrument—typically a soundboard, such as the top of a guitar or violin—which transfers the sound to the surrounding air. Depending on the instrument, the bridge may be made of carved wood, metal or other materials. The bridge supports the strings and holds them over the body of the instrument under tension.

Twang is the twenty-sixth studio album by American country music artist George Strait. It was released on August 11, 2009, via MCA Nashville, the same label to which Strait has been signed since 1981. It is produced by Tony Brown. The lead-off single "Living for the Night", which Strait wrote with his son Bubba and songwriter Dean Dillon, was released in May 2009. As of the chart dated January 8, 2011, the album has sold 662,023 copies in the US. "Twang" was nominated for Best Country Album at the 2010 Grammy Awards.
Falsettone is a term used in modern Italian musicology to describe a vocal technique used by male opera singers in the past, in which the fluty sounds typical of falsetto singing are amplified by using the same singing technique used in the modal voice register. The result is a bright, powerful tone, often very high-pitched, although the sound is still different from and more feminine than what is produced by the modal voice. The term falsettone is also used for the mixed vocal register that can be achieved using this technique.

A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who plays a musical instrument is known as an instrumentalist. The history of musical instruments dates to the beginnings of human culture. Early musical instruments may have been used for rituals, such as a horn to signal success on the hunt, or a drum in a religious ceremony. Cultures eventually developed composition and performance of melodies for entertainment. Musical instruments evolved in step with changing applications and technologies.








