Related Research Articles

Hydropower, also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a water source to produce power. Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production.

Tidal power or tidal energy is harnessed by converting energy from tides into useful forms of power, mainly electricity using various methods.

Wave power is the capture of energy of wind waves to do useful work – for example, electricity generation, water desalination, or pumping water. A machine that exploits wave power is a wave energy converter (WEC).

Micro hydro is a type of hydroelectric power that typically produces from 5 kW to 100 kW of electricity using the natural flow of water. Installations below 5 kW are called pico hydro. These installations can provide power to an isolated home or small community, or are sometimes connected to electric power networks, particularly where net metering is offered. There are many of these installations around the world, particularly in developing nations as they can provide an economical source of energy without the purchase of fuel. Micro hydro systems complement solar PV power systems because in many areas water flow, and thus available hydro power, is highest in the winter when solar energy is at a minimum. Micro hydro is frequently accomplished with a pelton wheel for high head, low flow water supply. The installation is often just a small dammed pool, at the top of a waterfall, with several hundred feet of pipe leading to a small generator housing. In low head sites, generally water wheels and Archimedes screws are used.
Off-the-grid or off-grid is a characteristic of buildings and a lifestyle designed in an independent manner without reliance on one or more public utilities. The term "off-the-grid" traditionally refers to not being connected to the electrical grid, but can also include other utilities like water, gas, and sewer systems, and can scale from residential homes to small communities. Off-the-grid living allows for buildings and people to be self-sufficient, which is advantageous in isolated locations where normal utilities cannot reach and is attractive to those who want to reduce environmental impact and cost of living. Generally, an off-grid building must be able to supply energy and potable water for itself, as well as manage food, waste and wastewater.
Marine currents can carry large amounts of water, largely driven by the tides, which are a consequence of the gravitational effects of the planetary motion of the Earth, the Moon and the Sun. Augmented flow velocities can be found where the underwater topography in straits between islands and the mainland or in shallows around headlands plays a major role in enhancing the flow velocities, resulting in appreciable kinetic energy. The sun acts as the primary driving force, causing winds and temperature differences. Because there are only small fluctuations in current speed and stream location with minimal changes in direction, ocean currents may be suitable locations for deploying energy extraction devices such as turbines. Other effects such as regional differences in temperature and salinity and the Coriolis effect due to the rotation of the earth are also major influences. The kinetic energy of marine currents can be converted in much the same way that a wind turbine extracts energy from the wind, using various types of open-flow rotors.

The Gorlov helical turbine (GHT) is a water turbine evolved from the Darrieus turbine design by altering it to have helical blades/foils. It was patented in a series of patents from September 19, 1995 to July 3, 2001 and won 2001 ASME Thomas A. Edison. GHT was invented by Alexander M. Gorlov, professor of Northeastern University.

SeaGen was the world's first large scale commercial tidal stream generator. It was four times more powerful than any other tidal stream generator in the world at the time of installation. It was successfully decommissioned by SIMEC Atlantis Energy Limited in summer 2019, having exported 11.6GWh to the grid since 2008.
Marine Current Turbines Ltd (MCT), a Siemens business, is a United Kingdom-based company which is developing tidal stream generators.

A wind turbine is a device that converts the wind's kinetic energy into electrical energy.

New Zealand has large ocean energy resources but does not yet generate any power from them. TVNZ reported in 2007 that over 20 wave and tidal power projects are currently under development. However, not a lot of public information is available about these projects. The Aotearoa Wave and Tidal Energy Association was established in 2006 to "promote the uptake of marine energy in New Zealand". According to their 10 February 2008 newsletter, they have 59 members. However, the association doesn't list its members.
Low-head hydropower refers to the development of hydroelectric power where the head is typically less than 20 metres, although precise definitions vary. Head is the vertical height measured between the hydro intake water level and the water level at the point of discharge. Using only a low head drop in a river or tidal flows to create electricity may provide a renewable energy source that will have a minimal impact on the environment. Since the generated power is a function of the head these systems are typically classed as small-scale hydropower, which have an installed capacity of less than 5MW.

Marine energy or marine power refers to the energy carried by ocean waves, tides, salinity, and ocean temperature differences. The movement of water in the world's oceans creates a vast store of kinetic energy, or energy in motion. Some of this energy can be harnessed to generate electricity to power homes, transport and industries.
A tidal farm is a group of multiple tidal stream generators assembled in the same location used for production of electric power, similar to that of a wind farm. The low-voltage powerlines from the individual units are then connected to a substation, where the voltage is stepped up with the use of a transformer for distribution through a high voltage transmission system.

A tidal stream generator, often referred to as a tidal energy converter (TEC), is a machine that extracts energy from moving masses of water, in particular tides, although the term is often used in reference to machines designed to extract energy from run of river or tidal estuarine sites. Certain types of these machines function very much like underwater wind turbines, and are thus often referred to as tidal turbines. They were first conceived in the 1970s during the oil crisis.

A tidal barrage is a dam-like structure used to capture the energy from masses of water moving in and out of a bay or river due to tidal forces.

Alexander M. Gorlov was a Russian mechanical engineer who was Professor Emeritus and Director of Hydro-Pneumatic Power Laboratory at Northeastern University in Boston, Massachusetts.

Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or biomass, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power.

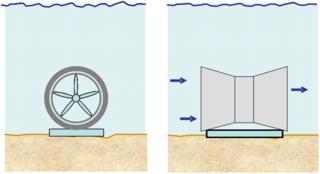
The water wall turbine is a water turbine designed to utilize hydrostatic pressure differences for low head hydropower generation. It supports bidirectional inflow operation using radial blades that rotate around a horizontal axis. The water wall turbine is suitable for energy extraction from tidal and freshwater currents. For tidal power installations, the turbine operates in both directions as the tide ebbs and flows.

Fotis Sotiropoulos is a Greek-born American engineering professor and university administrator known for his research contributions in computational fluid dynamics for river hydrodynamics, renewable energy, biomedical and biological applications. He currently serves as the Provost and Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs of Virginia Commonwealth University, a position he has held since August 1, 2021
References
- ↑ USpatent 4722665,Warren N. Tyson,published 1988-02-02
- ↑ Tuckey, A.M.; D.J. Pattereson; and J. Sewnson (November 1997). A Kinetic Energy Tidal Generator in the Northern Territory – Results. 23rd International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control and Instrumentation IECON 97. pp. 937–942.
- ↑ Khan, M.J.; G. Bhuyana; M.T. Iqbal; J.E. Quaicoe (2009). "Hydrokinetic energy conversion systems and assessment of horizontal and vertical axis turbines for river and tidal applications: A technology status review". Applied Energy. 86: 1823–1835. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.02.017.
- ↑ Anyi, Martin; Brian Kirke (2010). "Evaluation of small axial flow hydrokinetic turbines for remote communities". Energy for Sustainable Development . 14: 110–116. doi:10.1016/j.esd.2010.02.003.
