
USS Bonefish (SS-223) was a Gato-class submarine, the first United States Navy ship to be named for the bonefish.

USS Tuna (SS-203) was a United States Navy Tambor-class submarine, serving in the Pacific during World War II and earning seven battle stars for her service. After the war, she participated in the Bikini Atoll atomic testing in 1946.
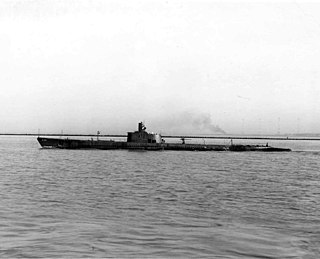
USS Silversides (SS/AGSS-236) is a Gato-class submarine, the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the silversides.

USS Billfish (SS-286), a Balao-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to bear the generic name for any fish, such as gar or marlin, with bill-shaped jaws. During World War II, Billfish made eight war patrols between 12 August 1943 and 27 August 1945. During these patrols she sank three Japanese cargo ships totaling 4,074 gross register tons and five smaller craft. She spent part of her seventh and eighth war patrols on lifeguard duty off Japan during Allied airstrikes.

USS Snapper (SS-185), a Salmon-class submarine, was the third ship of the United States Navy of the name and the second to be named for the snapper.

USS Sturgeon (SS-187), a Salmon-class submarine, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for the sturgeon. Her 1944 sinking of the Japanese troopship Toyama Maru, killing more than 5,000 Japanese, was one of the highest death tolls from the sinking of a single ship in history. Her 1942 sinking of the Montevideo Maru which, unknown to crew on the Sturgeon, was carrying over 1,000 POWs, was the worst maritime disaster in Australian history.

USS Bluegill (SS-242/SSK-242) was a Gato-class submarine in commission in the United States Navy from 1943 to 1946, from 1951 to 1952, and from 1953 to 1969. She was named for the bluegill, a sunfish of the Mississippi Valley.

USS Kingfish (SS-234), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the kingfish.

USS Gurnard (SS-254), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the gurnard.

USS Raton (SS/SSR/AGSS-270), a Gato-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named for the raton, a polynemoid fish inhabiting semitropical waters off the Pacific coast of the Americas.

USS Ray (SS/SSR-271), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the ray, a fish characterized by a flat body, large pectoral fins, and a whiplike tail.

USS Rock (SS/SSR/AGSS-274), a Gato-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named for the rockfish, a striped bass found in the Chesapeake Bay region and elsewhere along the United States East Coast.

USS Baya (SS/AGSS-318), a Balao-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named for the baya. During World War II, she completed five war patrols in the South China Sea, Gulf of Siam, Java Sea, and Philippine Sea between 23 August 1944 and 25 July 1945. She sank four Japanese vessels totaling 8855 gross register tons, and shared credit with the submarine USS Hawkbill (SS-366) for sinking a Japanese 8,407-gross register ton passenger-cargo ship. After World War II, she saw service as a research submarine during the Cold War and operated off Vietnam during the Vietnam War.

USS Becuna (SS/AGSS-319), a Balao-class submarine in commission from 1944 to 1969, was a submarine of the United States Navy named for the becuna, a pike-like fish of Europe. During World War II, she conducted five war patrols between August 23, 1944 and July 27, 1945, operating in the Philippine Islands, South China Sea, and Java Sea. She is credited with sinking two Japanese tankers totaling 3,888 gross register tons.

USS Besugo, a Balao-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy in commission from 1944 to 1958. She was named for the besugo.

USS Blenny (SS/AGSS-324), a Balao-class submarine in commission from 1944 to 1969, was a ship of the United States Navy named for the blenny, a fish found along the rocky shores of the Atlantic Ocean. During World War II, Blenny conducted four war patrols in the Java Sea and South China Sea between 10 November 1944 and 14 August 1945. She sank eight Japanese vessels totaling 18,262 tons. In addition, she is credited with destroying more than 62 miscellaneous Japanese small craft by gunfire.

USS Brill (SS-330), a Balao-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy in commission from 1944 to 1947. She was named for the brill, a European flatfish.

USS Bumper (SS-333), a Balao-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named for the bumper, a small fish of the North and South Atlantic Ocean.

USS Hammerhead (SS-364), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the hammerhead shark, a shark found in warm seas with a flattened anterior forward of the gill slits, presenting a hammer-like silhouette when viewed from above.

USS Piranha (SS-389/AGSS-389), a Balao-class submarine, was the only ship of the United States Navy to be named for the piranha. Piranha conducted six war patrols during World War II, receiving five battle stars. She was scrapped in 1970.





















