A business incubator is an organization that helps startup companies and individual entrepreneurs to develop their businesses by providing a fullscale range of services starting with management training and office space and ending with venture capital financing. The National Business Incubation Association (NBIA) defines business incubators as a catalyst tool for either regional or national economic development. NBIA categorizes its members' incubators by the following five incubator types: academic institutions; non-profit development corporations; for-profit property development ventures; venture capital firms, and a combination of the above.

Downtown San Jose is the central business district of San Jose, California. Downtown is one of the largest tech clusters in Silicon Valley, as well as the cultural and political center of San Jose.

Yaba is a suburb located on Lagos Mainland, Lagos in Lagos State, Nigeria. There are several federal government institutions in the area, which include Queen's College, the Nigerian Institute of Medical Research, the Yaba College of Technology, Igbobi College, the University of Lagos, the Federal Science and Technical College, and the Federal College of Education (Technical) Akoka.

ITESO, Universidad Jesuita de Guadalajara — distinct from the University of Guadalajara — also known as Instituto Tecnológico y de Estudios Superiores de Occidente, ITESO, is a Jesuit university in the Western Mexican state of Jalisco, located in the municipality of Tlaquepaque in the Guadalajara Metropolitan Area.

UF Innovate | Accelerate @ Sid Martin Biotech is located in Alachua, Florida, in Progress Park. The program's mission is to foster the growth of bioscience startup companies that have some relationship to the university. The Incubator works with companies in all product areas relating to the life sciences, biomedical research, medicine, and chemical sciences.

The Vale do Sinos Regional Development Association, VALETEC, was established in 1998 as a non-profit private civil partnership at the Sinos River Valley in southern Brazil. Its goal is to promote technological development in the Vale do Sinos region by stimulating regional integration, providing incentives for entrepreneurship, while creating, attracting, hosting, and developing companies. In order to achieve this goal, VALETEC develops and manages environments for technological innovation, such as incubators, entrepreneurial condominiums, technology parks and complexes, as well as other initiatives aligned with this focus. VALETEC's main commitment is to contribute for the improvement of the Vale do Sinos quality of life, while forging links between educational and research institutions and the society, governments, and companies. This contributes to generate jobs and wealth, boosting the sustainable development of the Vale do Sinos technopolitan project.
Techstars is a pre-seed investor that provides access to capital, mentorship, and other support for early-stage entrepreneurs. It was founded in 2006 in Boulder, Colorado. As of May 2022, the company had accepted over 2,900 companies into its accelerator programs with a combined market capitalization of $71bn USD. Techstars operates accelerator programs in North America, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa.
The Utah Science Technology and Research Initiative (USTAR) is a technology-based economic development agency funded by the state of Utah. The organization works to develop ideas and research into marketable products and successful companies through its competitive grant and entrepreneur support programs. USTAR facilitates the diversification of the state’s tech economy, increases private follow-on investment, and supports the creation of technology-based start-up firms, higher-paying jobs and additional business activity leading to a statewide expansion of Utah’s tax base.

The University City Science Center (UCSC) was established as the first and largest urban research park in the United States. It was established in 1963, within the demolished Black Bottom neighborhood of Philadelphia, now known as University City. Today it offers startup support services, allocates capital, gathers the innovation community, and builds inclusive STEM pathways for Philadelphia youth and adults.
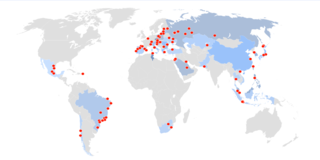
Microsoft Innovation Centers (MICs) are local government organizations, universities, industry organizations, or software or hardware vendors who partner with Microsoft with a common goal to foster the growth of local software economies. These are state of the art technology facilities which are open to students, developers, IT professionals, entrepreneurs, startups and academic researchers. While each Center tunes its programs to local needs, they all provide similar content and services designed to accelerate technology advances and stimulate local software economies through skills and professional training, industry partnerships and innovation. As of 10 September 2010, there are 115 Microsoft Innovation Centers worldwide, most of which are open to the public. Recently it was reported that Microsoft had proposed to build about 100 innovation centers in India, and several in China. Some innovation centers have also started to develop in Pakistan.
The Louisiana Business & Technology Center (LBTC) at Louisiana State University plays an important role to the state's flagship university, Louisiana State University as a part of LSU's Office of Research and Economic Development. LBTC's primary goal is to increase the economic growth of Louisiana by enhancing the development of small businesses and assisting in the development of new businesses. The center is ranked among the top ten entrepreneur programs in the nation. In 1988 it was jointly funded through LSU and the Greater Baton Rouge Chamber of Commerce to foster economic growth in Louisiana by providing businesses with applications and tools necessary for growth and survival in the real world. It comprises the Louisiana Technology Transfer Office (LTTO), the LBTC Business Incubator, and the LSU Student Incubator.
Universiteti Metropolitan Tirana (UMT), also known as the University Metropolitan Tirana is a private university located in Tirana, Albania. It was founded in 2010, by a group of architects and engineers as an university focused on information technology, engineering and architecture.
The San Jose BioCenter is a business incubator formed as a university foundation in 2004 and focused on the initiation and development of technology companies, with an emphasis on the life sciences industry. The BioCenter emerged from San Jose State University in an effort to revitalize an industrial area of San Jose, California. As of 2012, the BioCenter had thirty-five member (assisted) companies and twelve affiliate (supporting) companies. In addition to office space, the BioCenter provides wet laboratory facilities to member companies.
The Alchemist Accelerator is a venture-backed accelerator focused on accelerating the development of seed-stage ventures that monetize from enterprises. CB Insights rated Alchemist the top accelerator in 2016 based on median funding rates of its grads. The accelerator’s primary screening criteria are based on teams, with primacy placed on having distinctive technical co-founders. The organization provides seed investment into companies it admits, and provides founders a structured path to traction, fundraising, mentorship, and community over the course of a six month program. Alchemist's backers include many of the top corporate and VC funds in the Valley—including Khosla Ventures, DFJ, Cisco, Siemens, GE, and Salesforce, among others. The accelerator seeds around 75 enterprise-monetizing ventures per year.

Kerala Startup Mission is the central agency of the Government of Kerala for entrepreneurship development and incubation activities in Kerala, India. KSUM was primarily founded to undertake the planning, establishment, and management of the technology business incubator (TBI), a startup accelerator in Kerala, to promote technology-based entrepreneurship activities, and to create the infrastructure and environment required to support high-technology-based businesses.
The NanKang Biotech Incubation Center (NBIC) (Chinese: 南港生技育成中心) is a biotech incubator formed by the SME Foundation of the Ministry of Economic Affairs, ROC and managed by the Development Center for Biotechnology. The incubator focuses on the initiation and development of biotech startups with an emphasis of the biotech industry including pharmaceuticals, medical devices and applied biotech. NBIC is a model incubator in biotech industry, different from the university affiliated incubator, supported by the SME Foundation. As of 2015, the incubator has 21 Class I client companies, 1 Class II, and 20 Class III. Beside office space, the incubator provides wet laboratory with instruments and facilities.
Technology Hub is a bi-national startup accelerator and business incubator in the El Paso–Juárez area on the border of Mexico and the United States. It was founded in 2015 and is a Mexico National Institute for Entrepreneurship-certified incubator that has developed and housed 100 high-growth technology companies.

CIIE.CO is an Indian startup accelerator and incubator that supports early-stage startups located at IIM Ahmedabad in Ahmedabad, India. It was founded in 2002 to promote innovation and entrepreneurship in India. It is a Center of excellence set up at Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad with support from the Government of India's Department of Science and Technology and the Government of Gujarat.
The San Jose Redevelopment Agency was a redevelopment agency in the government of San Jose, California. It was created in 1956 and grew into the second-largest tax increment financing agency in the state.








