
Ian Richard Kyle Paisley, Baron Bannside, was a loyalist politician and Protestant religious leader from Northern Ireland who served as leader of the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) from 1971 to 2008 and First Minister of Northern Ireland from 2007 to 2008.

Northern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It was created as a separate legal entity on 3 May 1921, under the Government of Ireland Act 1920. The new autonomous Northern Ireland was formed from six of the nine counties of Ulster: four counties with unionist majorities – Antrim, Armagh, Down, and Derry/Londonderry – and two counties with slight Irish nationalist majorities – Fermanagh and Tyrone – in the 1918 General Election. The remaining three Ulster counties with larger nationalist majorities were not included. In large part unionists, at least in the north-east, supported its creation while nationalists were opposed.

The Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) is a unionist, loyalist, British nationalist and national conservative political party in Northern Ireland. It was founded in 1971 during the Troubles by Ian Paisley, who led the party for the next 37 years. It is currently led by Gavin Robinson, who is stepping in as an interim after the resignation of Jeffrey Donaldson. It is the second largest party in the Northern Ireland Assembly, and is the fifth-largest party in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. The party has been described as centre-right to right-wing and socially conservative, being anti-abortion and opposing same-sex marriage. The DUP sees itself as defending Britishness and Ulster Protestant culture against Irish nationalism and republicanism. It is also Eurosceptic and supported Brexit.
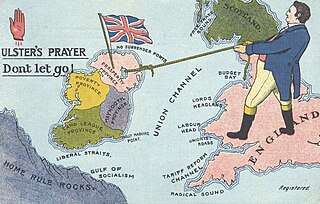
Unionism in Ireland is a political tradition that professes loyalty to the crown of the United Kingdom and to the union it represents with England, Scotland and Wales. The overwhelming sentiment of Ireland's Protestant minority, unionism mobilised in the decades following Catholic Emancipation in 1829 to oppose restoration of a separate Irish parliament. Since Partition in 1921, as Ulster unionism its goal has been to retain Northern Ireland as a devolved region within the United Kingdom and to resist the prospect of an all-Ireland republic. Within the framework of the 1998 Belfast Agreement, which concluded three decades of political violence, unionists have shared office with Irish nationalists in a reformed Northern Ireland Assembly. As of February 2024, they no longer do so as the larger faction: they serve in an executive with an Irish republican First Minister.

The 1998 Northern Ireland Assembly election took place on Thursday, 25 June 1998. This was the first election to the new devolved Northern Ireland Assembly. Six members from each of Northern Ireland's eighteen Westminster Parliamentary constituencies were elected by single transferable vote, giving a total of 108 Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs).

James Henry Molyneaux, Baron Molyneaux of Killead, KBE, PC, often known as Jim Molyneaux, was a unionist politician from Northern Ireland who served as leader of the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) from 1979 to 1995, and as the Member of Parliament (MP) for South Antrim from 1970 to 1983, and later Lagan Valley from 1983 to 1997. An Orangeman, he was also Sovereign Grand Master of the Royal Black Institution from 1971 to 1995, and a leading member of the Conservative Monday Club.
The Sunningdale Agreement was an attempt to establish a power-sharing Northern Ireland Executive and a cross-border Council of Ireland. The agreement was signed by the British and Irish governments at Northcote House in Sunningdale Park, located in Sunningdale, Berkshire, on 9 December 1973. Unionist opposition, violence and a general strike caused the collapse of the agreement in May 1974.

The Anglo-Irish Agreement was a 1985 treaty between the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland which aimed to help bring an end to the Troubles in Northern Ireland. The treaty gave the Irish government an advisory role in Northern Ireland's government while confirming that there would be no change in the constitutional position of Northern Ireland unless a majority of its citizens agreed to join the Republic. It also set out conditions for the establishment of a devolved consensus government in the region.

Robert Thomas William McCrea, Baron McCrea of Magherafelt and Cookstown is a Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) politician, Christian singer and retired Free Presbyterian minister from Northern Ireland. As a politician, he represented South Antrim and Mid Ulster as their Member of Parliament (MP), representing Mid Ulster from 1983 to 1997; then South Antrim between 2000 and 2001, and then again from 2005 to 2015.
The Northern Ireland peace process includes the events leading up to the 1994 Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) ceasefire, the end of most of the violence of the Troubles, the Good Friday Agreement of 1998, and subsequent political developments.

James Hugh Allister is a British Unionist politician and barrister in Northern Ireland. He founded the Traditional Unionist Voice (TUV) political party in 2007, leading the party since its formation. Allister has served as a Member of the Northern Ireland Assembly (MLA) for North Antrim since 2011, and is the TUV’s only representative in the Assembly.

United Ireland, also referred to as Irish reunification or a New Ireland, is the proposition that all of the island of Ireland should be a single sovereign state. At present, the island is divided politically: the sovereign state of Ireland has jurisdiction over the majority of Ireland, while Northern Ireland, which lies entirely within the Irish province of Ulster, is part of the United Kingdom. Achieving a united Ireland is a central tenet of Irish nationalism and Republicanism, particularly of both mainstream and dissident republican political and paramilitary organisations. Unionists support Northern Ireland remaining part of the United Kingdom and oppose Irish unification.

Henry William West was a Northern Irish unionist politician who served as leader of the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) from 1974 until 1979.

Ulster loyalism is a strand of Ulster unionism associated with working class Ulster Protestants in Northern Ireland. Like other unionists, loyalists support the continued existence of Northern Ireland within the United Kingdom, and oppose a united Ireland independent of the UK. Unlike other strands of unionism, loyalism has been described as an ethnic nationalism of Ulster Protestants and "a variation of British nationalism". Loyalists are often said to have a conditional loyalty to the British state so long as it defends their interests. They see themselves as loyal primarily to the Protestant British monarchy rather than to British governments and institutions, while Garret FitzGerald argued they are loyal to 'Ulster' over 'the Union'. A small minority of loyalists have called for an independent Ulster Protestant state, believing they cannot rely on British governments to support them. The term 'loyalism' is usually associated with paramilitarism.
The Ulster Clubs was the name given to a network of Unionist organisations founded in Northern Ireland in November 1985. Emerging from an earlier group based in Portadown, the Ulster Clubs briefly mobilised wide support across Northern Ireland and sought to coordinate opposition to the development of closer relations between the governments of the United Kingdom and Ireland. The group's motto was "hope for the best and prepare for the worst".

Ulster Resistance (UR), or the Ulster Resistance Movement (URM), is an Ulster loyalist paramilitary movement established by the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) in Northern Ireland in November 1986 in opposition to the Anglo-Irish Agreement.

The Northern Ireland Assembly established in 1982 represented an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to restore the devolution to Northern Ireland which had been suspended 10 years previously. The Assembly was dissolved in 1986.
William John Beattie is Northern Irish former minister of religion and unionist politician who was deputy leader of the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) from its foundation in 1971 until 1980.

The 1986 Northern Ireland by-elections were fifteen by-elections held on 23 January 1986, to fill vacancies in the Parliament of the United Kingdom caused by the resignation in December 1985 of all sitting Unionist Members of Parliament (MPs). The MPs, from the Ulster Unionist Party, Democratic Unionist Party and Ulster Popular Unionist Party, did this to highlight their opposition to the Anglo-Irish Agreement, signed the month before.
The Clontibret invasion was an incursion by Ulster loyalists into the small Monaghan village of Clontibret, in the Republic of Ireland, on 7 August 1986. After crossing the border the loyalists proceeded to vandalise many buildings in the village and attacked two police officers before being dispersed by the Garda Síochána. The incident occurred in the context of unionist opposition to the recently signed Anglo-Irish Agreement.















