
The spider family Liphistiidae, recognized by Tamerlan Thorell in 1869, comprises 8 genera and about 100 species of medium-sized spiders from Southeast Asia, China, and Japan. They are among the most basal living spiders, belonging to the suborder Mesothelae. In Japan, the Kimura spider is well known.

The anatomy of spiders includes many characteristics shared with other arachnids. These characteristics include bodies divided into two tagmata, eight jointed legs, no wings or antennae, the presence of chelicerae and pedipalps, simple eyes, and an exoskeleton, which is periodically shed.

Zygoballus sexpunctatus is a species of jumping spider which occurs in the southeastern United States where it can be found in a variety of grassy habitats. Adult spiders measure between 3 and 4.5 mm in length. The cephalothorax and abdomen are bronze to black in color, with reddish brown or yellowish legs. The male has distinctive enlarged chelicerae and front femora. Like many jumping spiders, Z. sexpunctatus males exhibit ritualized courtship and agonistic behavior.

Argiope pulchella is a species of the orb-weaver spider family, Araneidae. It ranges from India to China and can be found on Java. It is a synanthropic species, often living in habitats associated with humans.
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids.
Stenoterommata tenuistyla is a species of mygalomorph spiders of Argentina, named after the thin, slender embolus in males of this species, which distinguish it from males of the sympatric S. crassistyla. Females are distinguished from other three-clawed Stenoterommata by their spermathecae, which have a short basal portion and a single receptaculum arising from near the tip of the base. Males are diagnosed by one of the species autapomorphies: the presence of numerous short spines on the ventral metatarsus I.
Acanthogonatus huaquen is a mygalomorph spider of Chile, its name referring to its type locality: Huaquén, Chile. Males are recognized from other two-clawed Acanthogonatus by the bulb with a lateral keel delimiting a concave area; females by the spermathecae with an almost conical basal mound and its duct arising from its tip.
Acanthogonatus quilocura is a mygalomorph spider of Chile, its name referring to the seemingly unending number of species within this genus. Males are similar to those of A. tacuariensis, from which are distinguished by a curved metatarsus I; female spermathecae are characteristic in having a strongly bent duct arising from the base of a blunt basal dome.
Acanthogonatus juncal is a mygalomorph spider of Argentina and Chile, named after its type locality: Juncal, Los.
Acanthogonatus centralis is a mygalomorph spider of Argentina, its name referring to its distribution, being one of the most common mygalomorphs in central Argentina. Females are most similar to those of A. parana, are distinguished by the widened fundus of the spermathecae. Males, on the other hand, are recognized by the smooth, keelless bulb, in combination with a well-developed tibial apophysis.
Acanthogonatus peniasco is a mygalomorph spider of Chile, its name arising from its type locality: El Peñasco, Linares, VII Region, Chile. Females differ from those of A. franki and A. recinto in the shorter, wider, and more sclerotized spermathecal ducts, and from those of other species in the genus by having 1-1-1 P spines in the patella IV.
Lycinus caldera is a mygalomorph spider of Chile, named after its type locality: Caldera, Copiapó, Region III. Males are distinguished from L. gajardoi by the larger cymbium, the thinner and more numerous modified cymbial setae and the shorter embolus, and from those of all other species in the tribe by having cymbial setae directed backwards. Females are distinguished from other Chilean species of Lycinus by the spermathecae with two or three receptacula on each side.
Lycinus frayjorge is a mygalomorph spider of Chile, named after its type locality: Parque Nacional Fray Jorge, Limarí, Region IV (Coquimbo). The female spermathecae are most similar to those of L. gajardoi, which differs by the less numerous maxillary cuspules, the lighter scopula IV, and the presence of pseudopreening combs.
Chaco tucumana is a species of mygalomorph spiders of Argentina, named after its type locality: Tucumán. This species differs from C. obscura in the shorter male embolus and the shorter female spermathecal ducts. From other species of the genus it differs in its dark uniform color, the flexible anterior female tarsi, the denser scopulae on the posterior tarsi, and the female spermathecae without a basal protuberance. As in C. obscura, smaller specimens are much lighter in color, and it has darker spots that are evident on the sides of its cephalic region, the apex of femora, base of the patellae and lateral tibiae and dorsal abdomen. Larger specimens are much darker, almost black, with no visible pattern.
Ummidia aedificatoria is a species of trap-door spider found in Portugal, Spain and Morocco. It builds a shallow silk-lined trapdoor burrow, similar to those of U. algeriana and U. picea. Only three female specimens have been positively identified, all ranging from 18 to 29 millimeters in length.
Anelosimus jabaquara is a species of spider found in subtropical, humid, lowland forests in Brazil. Anelosimus jabaquara was first described by Herbert W. Levi in 1956. These spiders cooperate to spin and repair the colonial web, capture prey, and care for the brood. Colony size is small, and the sex ratio is biased towards females.

Eucteniza is a genus of trapdoor spiders in the family Euctenizidae containing at least 14 species occurring in Mexico and the southern United States. Species are distinguished by a softened rear portion of the carapace, and males possess large spines on the first two pairs of walking legs that are used to hold females during mating. Like other trapdoor spiders they create burrows with a hinged lid, from which they await passing insects and other arthropods to prey upon. Many species are known from only one or two localities, or from only male specimens. More species are expected to be discovered. Eucteniza is closely related to spiders of the genera Entychides and Neoapachella.
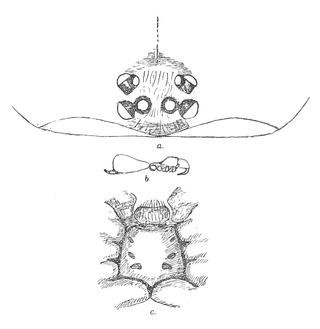
Cantuaria dendyi is a species of trapdoor spider in the family Idiopidae. It can be found in the South Island of New Zealand and is limited to the Christchurch and Banks Peninsula area.

Typhochlaena costae is a species of tarantula in the family Theraphosidae, subfamily Aviculariinae. It is native to Palmas, Tocantins state, Brazil. The species shows an arboreal trapdoor lifestyle.

Halonoproctidae is a family of mygalomorph spiders, split off from the family Ctenizidae in 2018. Species in the family are widely distributed in North and Central America, Australasia, Asia, southern Europe and North Africa. One species is recorded from Venezuela in South America. They are relatively large, sombrely coloured spiders, that live in burrows with some kind of trapdoor.







