
The Director of National Intelligence (DNI) is a senior cabinet-level United States government official, required by the Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 to serve as executive head of the United States Intelligence Community (IC) and to direct and oversee the National Intelligence Program (NIP). All IC agencies report directly to the DNI. The DNI also serves, upon invitation, as an advisor to the president of the United States, the National Security Council and the Homeland Security Council on all intelligence matters. The DNI, supported by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), produces the President's Daily Brief (PDB), a classified document including intelligence from all IC agencies, handed each morning to the president of the United States.

The United States Naval Criminal Investigative Service (NCIS) is the primary investigative law enforcement agency of the U.S. Department of the Navy. Its primary function is to investigate major criminal activities involving the Navy and Marine Corps, though its broad mandate includes national security, counterintelligence, counterterrorism, cyberwarfare, and the protection of U.S. naval assets worldwide. NCIS is the successor organization to the former Naval Investigative Service (NIS), which was established by the Office of Naval Intelligence after the Second World War.

The Defense Counterintelligence and Security Agency (DCSA) is a federal security and defense agency of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that reports to the Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence. DCSA is the largest counterintelligence and security agency in the federal government and is responsible for providing personnel vetting, critical technology protection, counterintelligence, training, education and certification. DCSA services over 100 federal entities, oversees 10,000 cleared companies, and conducts approximately 2 million background investigations each year.

The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is a headquarters-level staff of the United States Department of Defense. It is the principal civilian staff element of the U.S. Secretary of Defense, and it assists the Secretary in carrying out authority, direction and control of the Department of Defense in the exercise of policy development, planning, resource management, fiscal, and program evaluation responsibilities. OSD is the Secretary of Defense's support staff for managing the Department of Defense, and it corresponds to what the Executive Office of the President of the U.S. is to the U.S. president for managing the whole of the Executive branch of the federal government.

The United States under secretary of defense for policy (USDP) is a high level civilian official in the United States Department of Defense. The under secretary of defense for policy is the principal staff assistant and adviser to both the secretary of defense and the deputy secretary of defense for all matters concerning the formation of national security and defense policy.
The National Intelligence Board (NIB), formerly the National Foreign Intelligence Board and before that the United States Intelligence Board is a body of senior U.S. Intelligence Community leaders currently led by the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The Board is tasked with reviewing and approving National Intelligence Estimates (NIEs).

The Marine Corps Intelligence is the intelligence arm of the United States Marine Corps (USMC) and an element of the United States Intelligence Community. The Director of Intelligence supervises the Intelligence Department of HQMC and is responsible for policy, plans, programming, budgets, and staff supervision of Intelligence and supporting activities within the U.S. Marine Corps as well as supervising the Marine Corps Intelligence Activity (MCIA). The department supports the Commandant of the Marine Corps (CMC) in his role as a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), represents the service in Joint and Intelligence Community matters, and exercises supervision over the MCIA.

The under secretary of defense for personnel and readiness, or USD (P&R) is a high-ranking civilian position in the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) within the United States Department of Defense responsible for advising the secretary and deputy secretary of defense on recruitment, career development, pay and benefits, and oversight of the state of military readiness. The under secretary is appointed from civilian life by the president and confirmed by the Senate to serve at the pleasure of the President.

The Office of Intelligence and Counterintelligence (OICI), also abbreviated IN, DOE-IN, DOE/IN, I&CI, or OIC, was established in 2006 by the merger of pre-existing Energy Department intelligence and security organizations. It is an office of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) responsible for all intelligence and counterintelligence activities throughout the DOE complex; due to this central role, OICI is designated DOE's Headquarters Intelligence. As a component of the United States Intelligence Community in addition to the Department of Energy, OICI reports to both the Director of National Intelligence and Secretary of Energy.

The Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment, or USD (A&S), is the Principal Staff Assistant (PSA) and advisor to the Secretary of Defense for all matters relating to acquisition and sustainment in the Department of Defense. This includes the DoD Acquisition System; system design and development; production; logistics and distribution; installation maintenance, management, and resilience; military construction; procurement of goods and services; material readiness; maintenance; environment and energy resilience ; utilities; business management modernization; International Armaments Cooperation, Cooperative Acquisition and International Agreements, Promoting exportability of military components to allies and partners; nuclear, chemical and biological defense programs; and nuclear command, control, and communications.

The Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)/Chief Financial Officer, abbreviated USD(C)/CFO, is a high level civilian official in the United States Department of Defense. The Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller) is the principal staff assistant and adviser to both the Secretary of Defense and the Deputy Secretary of Defense for all budgetary and fiscal matters, including the development and execution of the Defense Department's annual budget.
National intelligence programs, and, by extension, the overall defenses of nations, are vulnerable to attack. It is the role of intelligence cycle security to protect the process embodied in the intelligence cycle, and that which it defends. A number of disciplines go into protecting the intelligence cycle. One of the challenges is there are a wide range of potential threats, so threat assessment, if complete, is a complex task. Governments try to protect three things:
National governments deal in both intelligence and military special operations functions that either should be completely secret, or simply cannot be linked to the sponsor. It is a continuing and unsolved question for governments whether clandestine intelligence collection and covert action should be under the same agency. The arguments for doing so include having centralized functions for monitoring covert action and clandestine HUMINT and making sure they do not conflict, as well as avoiding duplication in common services such as cover identity support, counterespionage, and secret communications. The arguments against doing so suggest that the management of the two activities takes a quite different mindset and skills, in part because clandestine collection almost always is on a slower timeline than covert action.
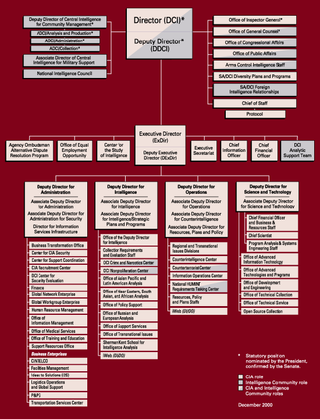
The CIA publishes organizational charts of its agency. Here are a few examples.

The Assistant Secretary of Defense for Indo-Pacific Security Affairs, or ASD (IPSA), is the principal advisor to the Under Secretary of Defense for Policy (USD(P)) and the Secretary of Defense on international security strategy and policy on issues of DoD interest that relate to the governments and defense establishments of the nations and international organizations within the Indo-Pacific region. It primarily includes the entire region from India to Japan, and the region where ASEAN is located. The position was originally titled Assistant Secretary of Defense for Asian and Pacific Security Affairs but was renamed by the Trump Administration alongside the renaming of the United States Indo-Pacific Command.
The Assistant Secretary of Defense for Special Operations/Low-Intensity Conflict or ASD(SO/LIC), is the principal civilian advisor to the U.S. Secretary of Defense on special operations and low-intensity conflict matters. Located within the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Policy, the ASD(SO/LIC) is responsible primarily for the overall supervision of special operations and low-intensity conflict activities. These activities, according to USSOCOM's 2007 Posture Statement, include counterterrorism; unconventional warfare; direct action; special reconnaissance; foreign internal defense; civil affairs, information operations, psychological operations, and counterproliferation of WMD.

The Assistant Secretary of Defense for Sustainment (ASD(Sustainment)), formerly known as the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Logistics and Materiel Readiness (ASD(L&MR)), is one of three assistant secretaries reporting to the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment. Formerly the position was an adviser to the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology and Logistics, Deputy Secretary of Defense, and Secretary of Defense on logistics and materiel readiness issues within the Department of Defense (DoD), including programs related to logistics, materiel readiness, maintenance, strategic mobility, and sustainment support. As the principal logistics official within the senior management of the DoD, the ASD(Sustainment) exercises authority, direction and control over the director of the Defense Logistics Agency. Like all other Assistant Secretaries of Defense, the ASD(Sustainment) is considered a part of the Office of the Secretary of Defense.

The Assistant Secretary of Defense for Energy, Installations, and Environment, concurrently the Chief Sustainability Officer, and formerly known as the Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Installations and Environment, provides management and oversight of military installations worldwide and manages environmental, safety, and occupational health programs for the Department of Defense (DoD). DoD's installations cover some 29,000,000 acres (120,000 km2), with 539,000 buildings and structures valued at more than $700 billion. The responsibilities of the ASD(EI&E) include the development of installation capabilities, programs, and budgets; installation-energy programs and policy; base realignment and closure; privatization of military housing and utilities; and integration of environmental needs into the weapons acquisition process. The ASD(EI&E) is also responsible for environmental management, safety and occupational health; environmental restoration at active and closing bases; conservation of natural and cultural resources; pollution prevention; environmental research and technology; fire protection; and explosives safety. The ASD(EI&E) reports to the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment, and is a part of the Office of the Secretary of Defense.

Assistant Secretary of Defense is a title used for many high-level executive positions in the Office of the Secretary of Defense within the U.S. Department of Defense. The Assistant Secretary of Defense title is junior to Under Secretary of Defense. Reorganization Plan No. 6 of 30 June 1953 increased the number of assistant secretaries. The list of Assistant Secretaries of Defense includes:

The Assistant Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, or ASD (A), is one of three assistant secretaries reporting to the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment. The position is the principal advisor to the Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment, the Deputy Secretary of Defense, and the Secretary of Defense on matters relating to acquisition program management; the Department of Defense Acquisition System; and the development of strategic, space, intelligence, tactical warfare, command and control, and business systems.



























