
Unemployment, according to the OECD, is people above a specified age not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period.
Full employment is a situation in which there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. Full employment does not entail the disappearance of all unemployment, as other kinds of unemployment, namely structural and frictional, may remain. For instance, workers who are "between jobs" for short periods of time as they search for better employment are not counted against full employment, as such unemployment is frictional rather than cyclical. An economy with full employment might also have unemployment or underemployment where part-time workers cannot find jobs appropriate to their skill level, as such unemployment is considered structural rather than cyclical. Full employment marks the point past which expansionary fiscal and/or monetary policy cannot reduce unemployment any further without causing inflation.

The economy of the Netherlands is a highly developed market economy focused on Trade and Logistics, Manufacturing, Services, Innovation and Technology and Sustainable and Renewable Energy. It is the world's 18th largest economy by nominal GDP and the 28th largest by purchasing power parity (PPP) and is the fifth largest economy in European Union by nominal GDP. It has the world's 11th highest per capita GDP (nominal) and the 13th highest per capita GDP (PPP) as of 2023 making it one of the highest earning nations in the world. Many of the world's largest tech companies are based in its capital Amsterdam or have established their European headquarters in the city, such as IBM, Microsoft, Google, Oracle, Cisco, Uber, Netflix and Tesla. Its second largest city Rotterdam is a major trade, logistics and economic center of the world and is Europe's largest seaport. Netherlands is ranked fifth on global innovation index and fourth on the Global Competitiveness Report.
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a compulsory governmental insurance system, not taxes on individual citizens. Depending on the jurisdiction and the status of the person, those sums may be small, covering only basic needs, or may compensate the lost time proportionally to the previous earned salary.
A layoff or downsizing is the temporary suspension or permanent termination of employment of an employee or, more commonly, a group of employees for business reasons, such as personnel management or downsizing an organization. Originally, layoff referred exclusively to a temporary interruption in work, or employment but this has evolved to a permanent elimination of a position in both British and US English, requiring the addition of "temporary" to specify the original meaning of the word. A layoff is not to be confused with wrongful termination. Laid off workers or displaced workers are workers who have lost or left their jobs because their employer has closed or moved, there was insufficient work for them to do, or their position or shift was abolished. Downsizing in a company is defined to involve the reduction of employees in a workforce. Downsizing in companies became a popular practice in the 1980s and early 1990s as it was seen as a way to deliver better shareholder value as it helps to reduce the costs of employers. Research on downsizing in the US, UK, and Japan suggests that downsizing is being regarded by management as one of the preferred routes to help declining organizations, cutting unnecessary costs, and improve organizational performance. Usually a layoff occurs as a cost-cutting measure. A study of 391 downsizing announcements of the S&P 100 firms for the period 1990-2006 found, that layoff announcements resulted in substantial increase in the companies’ stock prices, and that the gain was larger, when the company had prior layoffs. The authors suggested, that the stock price manipulation alone creates a sufficient motivation for publicly-traded corporations to adopt the practice of regular layoffs.
A severance package is pay and benefits that employees may be entitled to receive when they leave employment at a company unwillfully. In addition to their remaining regular pay, it may include some of the following:

Social welfare has long been an important part of New Zealand society and a significant political issue. It is concerned with the provision by the state of benefits and services. Together with fiscal welfare and occupational welfare, it makes up the social policy of New Zealand. Social welfare is mostly funded through general taxation. Since the 1980s welfare has been provided on the basis of need; the exception is universal superannuation.

The United States federal budget is divided into three categories: mandatory spending, discretionary spending, and interest on debt. Also known as entitlement spending, in US fiscal policy, mandatory spending is government spending on certain programs that are required by law. Congress established mandatory programs under authorization laws. Congress legislates spending for mandatory programs outside of the annual appropriations bill process. Congress can only reduce the funding for programs by changing the authorization law itself. This normally requires a 60-vote majority in the Senate to pass. Discretionary spending on the other hand will not occur unless Congress acts each year to provide the funding through an appropriations bill.

Unemployment was the dominant issue of British society during the interwar years. Unemployment levels rarely dipped below 1,000,000 and reached a peak of more than 3,000,000 in 1933, a figure which represented more than 20% of the working population. The unemployment rate was even higher in areas including South Wales and Liverpool. The Government extended unemployment insurance schemes in 1920 to alleviate the effects of unemployment.
In April and July 1981, there were riots in several cities and towns in England. The riots mainly involved black English youth clashing with police. They were caused by tension between black people and the police, especially perceived racist discrimination against black people through increased use of stop-and-search, and were also fuelled by inner-city deprivation. The most serious riots were the April Brixton riots in London, followed in July by the Toxteth riots in Liverpool, the Handsworth riots in Birmingham, the Chapeltown riots in Leeds, and the Moss Side riots in Manchester. There were also a series of less serious riots in other towns and cities. As a result of the riots, the government commissioned the Scarman Report.

The United States spends approximately $2.3 trillion on federal and state social programs include cash assistance, health insurance, food assistance, housing subsidies, energy and utilities subsidies, and education and childcare assistance. Similar benefits are sometimes provided by the private sector either through policy mandates or on a voluntary basis. Employer-sponsored health insurance is an example of this.
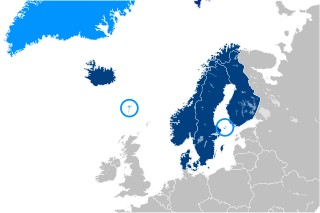
Social security or welfare in Finland is very comprehensive compared to what almost all other countries provide. In the late 1980s, Finland had one of the world's most advanced welfare systems, which guaranteed decent living conditions to all Finns. Created almost entirely during the first three decades after World War II, the social security system was an outgrowth of the traditional Nordic belief that the state is not inherently hostile to the well-being of its citizens and can intervene benevolently on their behalf. According to some social historians, the basis of this belief was a relatively benign history that had allowed the gradual emergence of a free and independent peasantry in the Nordic countries and had curtailed the dominance of the nobility and the subsequent formation of a powerful right wing. Finland's history was harsher than the histories of the other Nordic countries but didn't prevent the country from following their path of social development.
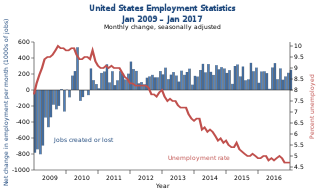
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage levels.
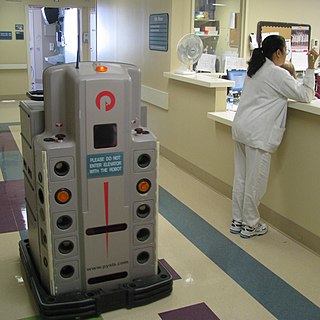
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment. Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficient "mechanical-mind" processes (automation), and humans' role in these processes are minimized. Just as horses were gradually made obsolete as transport by the automobile and as labourer by the tractor, humans' jobs have also been affected throughout modern history. Historical examples include artisan weavers reduced to poverty after the introduction of mechanized looms. During World War II, Alan Turing's bombe machine compressed and decoded thousands of man-years worth of encrypted data in a matter of hours. A contemporary example of technological unemployment is the displacement of retail cashiers by self-service tills and cashierless stores.

Unemployment in the United Kingdom is measured by the Office for National Statistics.
The Middle Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012, also known as the "payroll tax cut", was an Act of the United States Congress. The bill was passed by the U.S. House of Representatives on February 17, 2012 by a vote of 293‑132, and by the Senate by a vote of 60‑36 on the same day. The bill was signed into law by President Barack Obama on February 22, 2012.
National Assistance was the main means-tested benefit in the United Kingdom from 1948 to 1966.

Unemployment insurance in the United States, colloquially referred to as unemployment benefits, refers to social insurance programs which replace a portion of wages for individuals during unemployment. The first unemployment insurance program in the U.S. was created in Wisconsin in 1932, and the federal Social Security Act of 1935 created programs nationwide that are administered by state governments. The constitutionality of the program was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1937.
South Africa has one of the most extensive social welfare systems among developing countries in the world. In 2019, an estimated 18 million people received some form of social grant provided by the government.

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, also known as the CARES Act, is a $2.2 trillion economic stimulus bill passed by the 116th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump on March 27, 2020, in response to the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The spending primarily includes $300 billion in one-time cash payments to individual people who submit a tax return in America, $260 billion in increased unemployment benefits, the creation of the Paycheck Protection Program that provides forgivable loans to small businesses with an initial $350 billion in funding, $500 billion in loans for corporations, and $339.8 billion to state and local governments.












