
The International Maritime Organization is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating maritime transport. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time on 17 March 1958. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, the IMO, in 2024, has 176 Member States and three Associate Members.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 425, adopted on 19 March 1978, five days after the Israeli invasion of Lebanon in the context of Palestinian insurgency in South Lebanon and the Lebanese Civil War, called on Israel to withdraw immediately its forces from Lebanon and established the United Nations Interim Force In Lebanon (UNIFIL). It was adopted by 12 votes to none; Czechoslovakia and the Soviet Union abstained, and China did not participate.

The United Nations Confidence Restoration Operation in Croatia, commonly abbreviated UNCRO, was a United Nations (UN) peacekeeping mission in Croatia. It was established under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter and approved by the UN Security Council (UNSC) Resolution 981 on 31 March 1995. UNCRO inherited personnel and infrastructure from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR). Its command was located in Zagreb; the peacekeeping troops were deployed in four sectors named North, South, East, and West. Twenty different countries contributed troops to the mission.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1695, adopted unanimously on July 15, 2006, banned the selling of material that would further the ability of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea to bolster its ballistic missiles programme. Resolution 1695 was adopted after recalling resolutions 825 (1993) and 1540 (2004) concerning North Korea and the non-proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, respectively.
The ISIL (Da'esh) and Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee is a committee of the United Nations Security Council tasked with implementing international sanctions against the Islamic State and al-Qaeda. It was established as the Al-Qaida and Taliban Sanctions Committee on 15 October 1999, pursuant to Security Council Resolution 1267, which designated al-Qaeda and the Taliban as terrorist organizations. Following the creation of a separate Taliban Sanctions Committee on 17 June 2011, it was renamed the Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee. The scope of the sanctions regime was expanded to include the Islamic State on 17 December 2015 pursuant to Resolution 2253.

The African Union-United Nations Hybrid Operation in Darfur was a joint African Union (AU) and United Nations (UN) peacekeeping mission formally approved by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1769 on 31 July 2007, to bring stability to the war-torn Darfur region of Sudan while peace talks on a final settlement continue.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 163, adopted on June 9, 1961, after General Assembly Resolution 1603 declaring Angola a Non-Self-Governing Territory the Council reaffirmed that resolution calling on Portugal to act in accordance with the terms. The Council called upon the Portuguese to desist from repressive measures and to extend every facility to the Sub-Committee on the Situation in Angola, appointed under the terms of the GA resolution, as well as expressing its hope that a peaceful solution will be found and requested that the Sub-Committee report to the Council and GA as soon as possible.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 276, adopted on January 30, 1970, after reaffirming previous resolutions and statements, the Council condemned South Africa's continued occupation of Namibia as illegal and decided to establish an ad hoc sub-committee to study the ways and means by which the Council's resolutions could be implemented. The Council requested all states and organizations give the sub-committee all the information and other assistance it may require and further requested the Secretary-General to give every assistance to the sub-committee.

United Nations Security Council resolution 789, adopted unanimously on 25 November 1992, after reaffirming resolutions on Cyprus including 365 (1974), 367 (1975), 541 (1983), 550 (1984) and 774 (1992) and noting a report by the Secretary-General, the Council urged all concerned to implement a set of confidence-building measures.
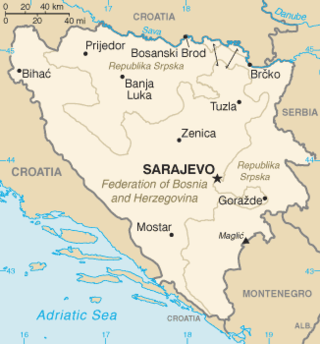
United Nations Security Council resolution 820, adopted on 17 April 1993, after reaffirming all previous resolutions on the topic for a lasting peace settlement in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the region, the council discussed the peace plan for Bosnia and Herzegovina and comprehensive steps to ensure its implementation.

United Nations Security Council resolution 994, adopted unanimously on 17 May 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, particularly resolutions 981 (1995), 982 (1995) and 990 (1995), the Council discussed the withdrawal of Croatian Army from the zone of separation taken in Operation Flash on May 1st and the full deployment of the United Nations Confidence Restoration Operation in Croatia (UNCRO).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1059, adopted unanimously on 31 May 1996, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in Liberia, particularly Resolution 1041 (1996), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Liberia (UNOMIL) until 31 August 1996 and discussed the security situation in the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1178, adopted unanimously on 29 June 1998, after reaffirming all past resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 31 December 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1217, adopted unanimously on 22 December 1998, after reaffirming all past resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 30 June 1999.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1303, adopted unanimously on 14 June 2000, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, including resolutions 1251 (1999) and 1283 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 15 December 2000. The resolution also noted that the Government of Cyprus had agreed that, given the prevailing conditions on the island, it was necessary for UNFICYP to remain beyond 15 June 2000.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1412, adopted unanimously on 17 May 2002, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 864 (1993) and all subsequent resolutions on Angola, particularly Resolution 1127 (1997), the council suspended travel restrictions against UNITA officials the country after the signing of a memorandum of understanding between it and the Angolan government.
The following lists events that happened during 1950 in the Democratic People's Republic of Korea.
The following lists events that happened during 1959 in Laos.













