The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending that the General Assembly accept new members to the United Nations, and approving any changes to its charter. Its powers include the establishment of peacekeeping operations and international sanctions as well as the authorization of military actions through resolutions – it is the only body of the United Nations with the authority to issue binding resolutions to member states. The council held its first session on 17 January 1946.

The United Nations General Assembly is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), the only one in which all member nations have equal representation, and the main deliberative, policy-making, and representative organ of the UN. Its powers are to oversee the budget of the UN, appoint the non-permanent members to the Security Council, appoint the Secretary-General of the United Nations, receive reports from other parts of the UN, and make recommendations in the form of General Assembly Resolutions. It has also established numerous subsidiary organs.

The United Nations member states are the 193 sovereign states that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the UN General Assembly. The UN is the world's largest intergovernmental organization.

The United Nations Secretariat is one of the six major organs of the United Nations, with the others being (a) the General Assembly; (b) the Security Council; (c) the Economic and Social Council; (d) the defunct Trusteeship Council; and (e) the International Court of Justice. The Secretariat is the United Nations' executive arm. The Secretariat has an important role in setting the agenda for the UN's deliberative and decision making bodies of the UN, and the implementation of the decision of these bodies. The Secretary-General, who is appointed by the General Assembly, is the head of the secretariat.
A United Nations General Assembly Resolution is voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.
The United Nations General Assembly may grant observer status to an international organization, entity or non-member state, which entitles the entity to participate in the work of the United Nations General Assembly, though with limitations. The General Assembly may determine what privileges it grants with the observer status, beyond those laid down in a 1986 Conference on treaties between States and International Organizations. Exceptionally, the EU was granted in 2011 the right to speak in debates, to submit proposals and amendments, the right of reply, to raise points of order and to circulate documents, etc. As of May 2011, the EU was the only international organisation to hold these enhanced rights, which has been likened to the rights of full membership, short of the right to vote.
Amendments to the United Nations Charter can be made by a procedure set out in Chapter XVIII of the UN Charter. The UN Charter has been amended five times since 1945.
Peacebuilding is an activity that aims to resolve injustice in nonviolent ways and to transform the cultural & structural conditions that generate deadly or destructive conflict. It revolves around developing constructive personal, group, and political relationships across ethnic, religious, class, national, and racial boundaries. This process includes violence prevention; conflict management, resolution, or transformation; and post-conflict reconciliation or trauma healing, i.e., before, during, and after any given case of violence.

The United Nations Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) is a United Nations Intergovernmental advisory body of both the United Nations General Assembly and the United Nations Security Council that supports peace efforts in conflict affected countries, and is a key addition to the capacity of the international community in the broad peace agenda. It was established in 2005 with the passage of both A/RES/60/180 and S/RES/1645
The Holy See is not a member of the United Nations but was granted permanent observer state status on 6 April 1964. In that capacity, it has the right to attend all sessions of the United Nations General Assembly, the United Nations Security Council, and the United Nations Economic and Social Council to observe their work. Accordingly, the Holy See has established permanent observer missions in New York and in Geneva and has been able to influence the decisions and recommendations of the United Nations.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1938, adopted unanimously on September 15, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Liberia, including resolutions 1509 (2003), 1626 (2005), 1836 (2005) and 1885 (2009), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Liberia (UNMIL) for a further twelve months until September 30, 2011 and required it to provide electoral assistance.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1947, adopted unanimously on October 29, 2010, after recalling Resolution 1645 (2005), the Council reaffirmed the role of the United Nations Peacebuilding Commission within the organisation.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1631, adopted unanimously on 17 October 2005, after recalling Chapter VIII of the United Nations Charter, the Council addressed co-operation between the United Nations and regional organisations in the maintenance of international peace and security.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1645, adopted unanimously on 20 December 2005, acting concurrently with the United Nations General Assembly, the Council established the United Nations Peacebuilding Commission to advise on post-conflict situations, in accordance with the declaration of the 2005 World Summit.
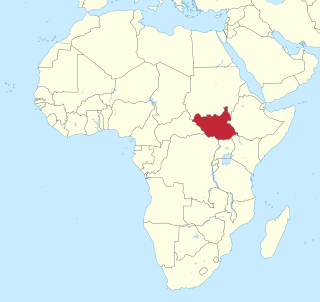
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1996, adopted unanimously on July 8, 2011, after welcoming the independence of South Sudan from Sudan, the Council established the United Nations Mission in the Republic of South Sudan (UNMISS) for an initial period of one year.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1998, adopted unanimously on July 12, 2011, after reaffirming resolutions 1261 (1999), 1314 (2000), 1379 (2001), 1460 (2003), 1539 (2004), 1612 (2005) and 1882 (2009) on the protection of children in armed conflict, the Council declared schools and hospitals off limits for both armed groups and military activities, asking the Secretary-General for such crimes to be placed on a list of those committing "grave violations" against children.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1734, adopted unanimously on December 22, 2006, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Sierra Leone, including resolutions 1620 (2005) and 1688 (2006), the Council renewed the mandate of the United Nations Integrated Office in Sierra Leone (UNIOSIL) until December 31, 2007.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2005 was unanimously adopted on 14 September 2011.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1829 was unanimously adopted on 4 August 2008.

The Republic of Korea and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea were simultaneously admitted to the United Nations (UN) in 1991. On 8 August 1991, the UN Security Council passed United Nations Security Council Resolution 702, recommending both states to the UN General Assembly for membership. On 17 September 1991, the General Assembly admitted both countries under Resolution 46/1.