
Gregory Wayne Abbott is an American politician, attorney, and jurist serving as the 48th governor of Texas since 2015. A member of the Republican Party, he served as the 50th attorney general of Texas from 2002 to 2015 and as a justice of the Texas Supreme Court from 1996 to 2001.
A sanctuary city is a municipality that limits or denies its cooperation with the national government in enforcing immigration law.
Earl Leroy Yeakel III, also known as Lee Yeakel, is a former United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Western District of Texas.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Texas have some protections in state law but may face legal and social challenges not faced by others. Same-sex sexual activity was decriminalized in Texas in 2003 by the Lawrence v. Texas ruling. On June 26, 2015, the Supreme Court of the United States ruled bans on same-sex marriage to be unconstitutional in Obergefell v. Hodges.
In the United States, the term constitutional carry, also called permitless carry, unrestricted carry, or Vermont carry, refers to the legal public carrying of a handgun, either openly or concealed, without a license or permit. The phrase does not typically refer to the unrestricted carrying of a long gun, a knife, or other weapons. The scope and applicability of constitutional carry may vary by state.
A six-week abortion ban, also called a "fetal heartbeat bill" by proponents, is a law in the United States which makes abortion illegal as early as six weeks gestational age, which is when proponents claim that a "fetal heartbeat" can be detected. Medical and reproductive health experts, including the American Medical Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, say that the reference to a fetal heartbeat is medically inaccurate and misleading because a conceptus is not called a fetus until eight weeks after fertilization, as well as that at four weeks after fertilization, the embryo has no heart, only a group of cells which will become a heart. Medical professionals advise that a true fetal heartbeat cannot be detected until around 17 to 20 weeks of gestation when the chambers of the heart have become sufficiently developed.

Steve Hixson Toth is an American businessman and politician serving as a member of the Texas House of Representatives from District 15, The Woodlands area.
Abortion in Texas is illegal in most cases, except to save the mother's life, or prevent substantial impairment of major bodily function. This is due to a trigger law passed in July 2021 that came in effect on August 25, 2022, as a consequence of the U.S. Supreme Court's 2022 decision Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization overturning Roe v. Wade. The law makes no exception for pregnancies resulting from rape or incest.

James Chiun-Yue Ho is a Taiwanese-born American lawyer and jurist serving since 2018 as a U.S. circuit judge of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit. He was appointed by President Donald Trump. Ho formerly served as Solicitor General of Texas from 2008 to 2010.
Jonathan Franklin Mitchell is an American lawyer, academic, and legal theorist who served as the Solicitor General of Texas from 2010 to 2015. He has argued seven cases before the Supreme Court of the United States. Mitchell has served on the faculties of Stanford Law School, the University of Texas School of Law, the George Mason University School of Law, and the University of Chicago Law School. In 2018, he opened a private solo legal practice in Austin, Texas.

Texas Senate Bill 4 is a bill that effectively bans sanctuary cities in the state of Texas. It was filed on November 15, 2016, and discussed during the regular session of the eighty-fifth Texas Legislature. Texas Governor Greg Abbott signed the bill into law on May 7, 2017.
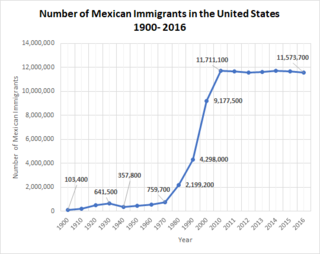
The state of Texas has a long history of immigration and immigration policy. The region that is now Texas was originally home to several Native American tribes. The first European immigrants arrived in the 1600s when the land was colonized by the French and the Spanish. Financial incentives created by the Mexican government brought many immigrants to Mexican Texas in the 1820s, mostly from slaveholding areas in the southern United States. This continued as significant illegal immigration to Mexico after 1830, when American migrants were banned.

Joe Biden's immigration policy is primarily based on reversing many of the immigration policies of the previous Trump administration. During his first day in office, Biden reversed many of Trump's policies on immigration, such as halting the construction of the Mexican border wall, ending Trump's travel ban restricting travel from 14 countries, and an executive order to reaffirm protections for DACA recipients. The Biden administration and Department of Homeland Security, under leadership of Alejandro Mayorkas, dramatically reined in deportation practices of Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), prioritizing national security and violent crime concerns over petty and nonviolent offenses. However, Biden has also faced criticism for extending Title 42, a Trump administration border restriction that arose due to the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as restarting the use of expediting families in Central America, which can cause families to be sent back in weeks, compared to years for an average immigration case. In the fiscal year 2021, the US Border Patrol confirmed more than 1.6 million encounters with migrants along the US-Mexico border, more than quadruple the number in the previous fiscal year and the largest annual total on record. In January 2023, Biden announced a program to strengthen the admission of immigrants from Cuba, Haiti, Nicaragua, and Venezuela, while at the same time his administration will crack down on those who fail to use the plan's legal pathway and strengthen border security. In May 2023, the Biden Administration approved sending 1,500 more troops to the U.S.-Mexico border following Title 42's expiration.
A Title 42 expulsion is the removal by the U.S. government of a person who had recently been in a country where a communicable disease was present. The extent of authority for contagion-related expulsions is set out by law in 42 U.S.C. § 265. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Trump administration used this provision to generally block land entry for many migrants. This practice was initially continued by the Biden administration before the program was ended with the end of the COVID-19 national emergency in the United States. Title 42 of the United States Code includes numerous sections dealing with public health, social welfare, and civil rights, but, in the context of immigration, the phrase "Title 42" came to be used to refer specifically to expulsions under section 265.

Operation Lone Star (OLS) is a joint operation between the Texas Department of Public Safety and the Texas Military Department along the United States–Mexico border in southern Texas. The operation started in 2021 and is ongoing. According to Texas Governor Greg Abbott, the operation is intended to counter a rise in illegal immigration, the illegal drug trade, and human smuggling. According to the governor's office, OLS has resulted in 503,800 migrant apprehensions, 40,400 criminal arrests, and 469 million doses of fentanyl seized. Between fiscal year 2020 and fiscal year 2021, migrant apprehensions had risen 278% along the US–Mexico border. As of April 2022, OLS was spending approximately $2.5 million per week and was expected to cost approximately $2 billion per year. Approximately 10,000 National Guard members were deployed in support of OLS at the height of the operation, with around 6,000 deployed as of November 2022. One year after the start of Operation Lone Star, Texas saw a 9% increase in migrant encounters along its border with Mexico, compared to a 62% increase in Arizona, California, and New Mexico along their respective borders with Mexico.
United States v. Texas may refer to the following cases:
The following is a list of events of the year 2024 in the United States, as well as predicted and scheduled events that have not yet occurred.
The following is a list of events of the year 2023 in Texas.
The following is a list of events of the year 2024 in Texas.
Texas Senate Bill 4 is a Texas state statute enacted by the Texas Legislature and signed into law by governor Greg Abbott on December 18, 2023. The bill allows state officials to arrest and deport migrants who enter the state illegally.








