Related Research Articles

The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, and these are known as the Gulf States.

Texas is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,660 km2), and with more than 30 million residents in 2023, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both area and population. Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast.

The Western United States is the region comprising the westernmost U.S. states. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term the West changed. Before around 1800, the crest of the Appalachian Mountains was seen as the western frontier. The frontier moved westward and eventually the lands west of the Mississippi River were considered the West.

The Mexican Cession is the region in the modern-day southwestern United States that Mexico originally controlled, then ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. This region had not been part of the areas east of the Rio Grande that had been claimed by the Republic of Texas, though the Texas annexation resolution two years earlier had not specified the southern and western boundary of the new state of Texas. At roughly 529,000 square miles (1,370,000 km2), the Mexican Cession was the third-largest acquisition of territory in U.S. history, surpassed only by the 827,000-square-mile (2,140,000 km2) Louisiana Purchase and the 586,000-square-mile (1,520,000 km2) Alaska Purchase.

Quercus virginiana, also known as the southern live oak, is an evergreen oak tree endemic to the Southeastern United States. Though many other species are loosely called live oak, the southern live oak is particularly iconic of the Old South. Many very large and old specimens of live oak can be found today in the Deep South region of the United States.

Live oak or evergreen oak is any of a number of oaks in several different sections of the genus Quercus that share the characteristic of evergreen foliage. These oaks are generally not more closely related to each other than they are to other oaks.

Southeast Texas is a cultural and geographic region in the U.S. state of Texas, bordering Southwest Louisiana and its greater Acadiana region to the east. Being a part of East Texas, the region is geographically centered on the Greater Houston and Beaumont–Port Arthur metropolitan statistical areas with a combined population of 7,662,325 according to the 2020 U.S. census.

David Anthony Williams is a professional poker player and popular Magic: The Gathering player who also competed on Season 7 of the popular FOX cooking show MasterChef, where he finished as co-runner-up.

The Atakapa or Atacapa were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, who spoke the Atakapa language and historically lived along the Gulf of Mexico in what is now Texas and Louisiana.

Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1519 until 1821. Spain claimed ownership of the region in 1519. Slave raids by Spaniards into what became Texas began in the 16th century and created an atmosphere of antagonism with Native Americans (Indians) which would cause endless difficulties for the Spanish in the future. Spain did not attempt to establish a permanent presence until after France established the colony of Fort Saint Louis in 1685. In 1688, the French colony failed due to internal dissention and attacks by the Karankawa Indians. In 1690, responding to fear of French encroachment, Spanish explorer Alonso de León escorted several Catholic missionaries to east Texas, where they established the first mission in Texas. That attempt to establish a Spanish colony failed due to the hostility of the Caddo Indians.

The Western Gulf coastal grasslands are a subtropical grassland ecoregion of the southern United States and northeastern Mexico. It is known in Louisiana as the "Cajun Prairie", Texas as "Coastal Prairie," and as the Tamaulipan pastizal in Mexico.

Aransas Bay is a bay on the Texas Gulf Coast, approximately 30 miles (48 km) northeast of Corpus Christi, and 173 miles (278 km) south of San Antonio. It is separated from the Gulf of Mexico by San José Island. Aransas Pass is the most direct navigable outlet into the Gulf of Mexico from the bay. The cities of Aransas Pass and Port Aransas are located at the southern end, and Rockport is found on the central western shore. The bay is oriented laterally northeast–southwest, and is extended by Redfish Bay to the southwest, Copano Bay to the west, Saint Charles Bay to the north, and Mesquite Bay to the northeast. Aransas Bay is part of the Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve.
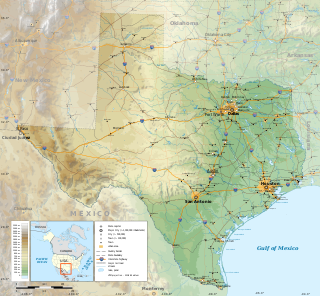
The geography of Texas is diverse and large. Occupying about 7% of the total water and land area of the U.S., it is the second largest state after Alaska, and is the southernmost part of the Great Plains, which end in the south against the folded Sierra Madre Oriental of Mexico. Texas is in the South Central United States of America, and is considered to form part of the U.S. South and also part of the U.S. Southwest.

George Holmes "Buddy" Tate was an American jazz saxophonist and clarinetist.

Texas' weather varies widely, from arid in the west to humid in the east. The huge expanse of Texas encompasses several regions with distinctly different climates: Northern Plains, Trans-Pecos Region, Texas Hill Country, Piney Woods, and South Texas. Generally speaking, the part of Texas that lies to the east of Interstate 35 is subtropical, while the portion that lies to the west of Interstate 35 is arid desert.

East Matagorda Bay is a bay off Matagorda County on the Texas Gulf Coast, enclosed by the Matagorda Peninsula and the tidal flats at the mouth of the Colorado River. It is a minor estuary, one of a series of estuaries along the Gulf Coast of Texas, but it has no significant river sources, receiving only the runoff from the adjacent coastal watershed. Its only true opening to the Gulf of Mexico is through Brown Cedar Cut, near the north end of the peninsula. East Matagorda Bay was devastated by the 1942 Matagorda Hurricane, the most devastating hurricane of the 1942 Atlantic hurricane season.

The Gulf Coast Conference (GCC) was a short-lived NCAA college athletic conference composed of universities in the U.S. state of Texas from 1949 until 1957. The charter members of the conference were University of Houston, Midwestern University, North Texas State College, and Trinity University. The Gulf Coast Conference spawned from then members of the Lone Star Conference, and its president was D.L. Ligon. In 1956, when the NCAA created divisions, all members of the conference at the time were classified as part of the NCAA's College Division, which was later subdivided into Division II and Division III in 1973. Charter member Houston had already left for the Missouri Valley Conference by the end of 1950, and was classified as a University Division school, which later became known as Division I.

The Laguna Madre is a long, shallow, hypersaline lagoon along the western coast of the Gulf of Mexico in Nueces, Kenedy, Kleberg, Willacy and Cameron Counties in Texas, United States. It is one of seven major estuaries along the Gulf Coast of Texas. The roughly 20-mile (32 km) long Saltillo Flats land bridge divides it into Upper and Lower lagoons joined by the Intracoastal Waterway, which has been dredged through the lagoon. Cumulatively, Laguna Madre is approximately 130 miles (210 km) long, the length of Padre Island in the US. The main extensions include Baffin Bay in Upper Laguna Madre, Red Fish Bay just below the Saltillo Flats, and South Bay near the Mexican border. As a natural ecological unit, the Laguna Madre of the United States is the northern half of the ecosystem as a whole, which extends into Tamaulipas, Mexico approximately 144 miles (232 km) south of the US border, to the vicinity of the Rio Soto La Marina and the town of La Pesca, extending approximately 275 miles (443 km) through USA and Mexico in total.

Andrew Vincent Dismukes is an American comedian, actor, and writer. Dismukes was hired as a writer for the NBC sketch comedy series Saturday Night Live in 2017, ahead of its 43rd season. He was then hired to join the cast as a featured player in 2020 for its 46th season, and became a repertory player during its 48th season in 2022.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Campbell, Thomas N. "Unpuncliegut Indians". Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved 22 July 2023.