
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. Heating and cooling (HVAC), waste removal, and potable water delivery are among the most common uses for plumbing, but it is not limited to these applications. The word derives from the Latin for lead, plumbum, as the first effective pipes used in the Roman era were lead pipes.
Fiskars Oyj Abp is a Finnish consumer goods company founded in 1649 in Fiskars, a locality now in the town of Raseborg, Finland, about 100 kilometres (62 mi) west of Helsinki. Fiskars' global headquarters are located in the Arabianranta district of Helsinki.

Elisa Oyj is a Finnish telecommunications company founded in 1882. It was called HPY HTF until July 2000. The mobile operations of Elisa were previously known as Radiolinja.

Hydronics is the use of liquid water or gaseous water (steam) or a water solution as a heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and refrigerant systems.
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, insulation for high tension electrical cables, and baby play mats. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries. PEX is an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) or copper tubing for use as residential water pipes.
Designated as an American National Standard, the Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) is a model code developed by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) to govern the installation and inspection of plumbing systems as a means of promoting the public's health, safety and welfare.

Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods.

District cooling is the cooling equivalent of district heating. Working on broadly similar principles to district heating, district cooling delivers chilled water to buildings like offices and factories. In winter, the source for cooling can often be seawater, so it is a cheaper resource than electricity to run compressors for cooling. Alternatively, district cooling can be provided by a Heat Sharing Network which enables each building on the circuit to use a heat pump to reject heat to an ambient ground temperature circuit.

Building insulation is material used in a building to reduce the flow of thermal energy. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation. Often an insulation material will be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once.

A pipefitter or steamfitter is a tradesman who installs, assembles, fabricates, maintains, and repairs mechanical piping systems. Pipefitters usually begin as helpers or apprentices. Journeyman pipefitters deal with industrial/commercial/marine piping and heating/cooling systems. Typical industrial process pipe is under high pressure, which requires metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and many different alloy metals fused together through precise cutting, threading, grooving, bending, and welding. A plumber concentrates on lower pressure piping systems for sewage and potable tap water in the industrial, commercial, institutional, or residential atmosphere. Utility piping typically consists of copper, PVC, CPVC, polyethylene, and galvanized pipe, which is typically glued, soldered, or threaded. Other types of piping systems include steam, ventilation, hydraulics, chemicals, fuel, and oil.
Ahlstrom Oyj is a manufacturer of fiber-based products. Renewable fibers represent about 95% of Ahlstrom's total fiber use.
A chilled beam is a type of radiation/convection HVAC system designed to heat and cool large buildings through the use of water. This method removes most of the zone sensible local heat gains and allows the flow rate of pre-conditioned air from the air handling unit to be reduced, lowering by 60% to 80% the ducted design airflow rate and the equipment capacity requirements. There are two types of chilled beams, a Passive Chilled Beam (PCB) and an Active Chilled Beam (ACB). They both consist of pipes of water (fin-and-tube) that pass through a heat exchanger contained in a case suspended from, or recessed in, the ceiling. As the beam cools the air around it, the air becomes denser and falls to the floor. It is replaced by warmer air moving up from below, causing a constant passive air movement called convection, to cool the room. The active beam consists of air duct connections, induction nozzles, hydronic heat transfer coils, supply outlets and induced air inlets. It contains an integral air supply that passes through nozzles, and induces air from the room to the cooling coil. For this reason, it has a better cooling capacity than the passive beam. Instead, the passive beam provides space cooling without the use of a fan and it is mainly done by convection. Passive beams can be either exposed or recessed. The passive approach can provide higher thermal comfort levels, while the active approach uses the momentum of ventilation air that enters at relatively high velocity to induce the circulation of room air through the unit. A chilled beam is similar in appearance to a VRF unit.
Polybutylene (polybutene-1, poly(1-butene), PB-1) is a polyolefin or saturated polymer with the chemical formula (CH2CH(Et))n. Not be confused with polybutene, PB-1 is mainly used in piping.

YIT Oyj is the largest Finnish and a significant North European construction company. YIT is headquartered in Helsinki and its stock is listed on Nasdaq Helsinki Oy. YIT develops and builds apartments, business premises and entire areas. YIT is also specialised in demanding infrastructure construction and paving. YIT operates in 11 countries: Finland, Russia, Scandinavia, the Baltic States, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Poland.

Viega is a family owned international manufacturer of Plumbing and HVAC solutions. Viega sells PEX for Radiant heating and plumbing systems along with copper, stainless, and metal alloy pipe along with mechanical pressure fitting products.
Variable refrigerant flow (VRF), also known as variable refrigerant volume (VRV), is an HVAC technology invented by Daikin Industries, Ltd. in 1982. Similar to ductless mini-split systems, VRFs use refrigerant as the primary cooling and heating medium, and are usually less complex than conventional chiller-based systems. This refrigerant is conditioned by one or more condensing units, and is circulated within the building to multiple indoor units. VRF systems, unlike conventional chiller-based systems, allow for varying degrees of cooling in more specific areas, may supply hot water in a heat recovery configuration without affecting efficiency, and switch to heating mode during winter without additional equipment, all of which may allow for reduced energy consumption. Also, air handlers and large ducts are not used which can reduce the height above a dropped ceiling as well as structural impact as VRF uses smaller penetrations for refrigerant pipes instead of ducts.
The Uniform Mechanical Code (UMC) is a model code developed by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) to govern the installation, inspection and maintenance of HVAC and refrigeration systems. It is designated as an American National Standard.
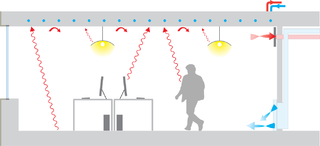
Radiant heating and cooling is a category of HVAC technologies that exchange heat by both convection and radiation with the environments they are designed to heat or cool. There are many subcategories of radiant heating and cooling, including: "radiant ceiling panels", "embedded surface systems", "thermally active building systems", and infrared heaters. According to some definitions, a technology is only included in this category if radiation comprises more than 50% of its heat exchange with the environment; therefore technologies such as radiators and chilled beams are usually not considered radiant heating or cooling. Within this category, it is practical to distinguish between high temperature radiant heating, and radiant heating or cooling with more moderate source temperatures. This article mainly addresses radiant heating and cooling with moderate source temperatures, used to heat or cool indoor environments. Moderate temperature radiant heating and cooling is usually composed of relatively large surfaces that are internally heated or cooled using hydronic or electrical sources. For high temperature indoor or outdoor radiant heating, see: Infrared heater. For snow melt applications see: Snowmelt system.
The Assemblin Caverion Group is a Nordic contracting concern in the building sector, headquartered in Stockholm-Hägersten. Its main activities are in building services and building automation, which comprise base systems, smart technologies and digital solutions. Assemblin Caverion delivers smart and sustainable solutions for the built environment, enabling efficient building performance and occupant well-being. The group focuses on the life-cycle of buildings, infrastructure and industrial compounds. Its services consist of technical installation, maintenance, plant management and engineering. The Assemblin Caverion Group operates in Northern and Central Europe.
Eagle Filters Group Oyj is a Finnish industrial company that manufactures gas turbine air intake filters for the energy and process industries, energy-saving and filtration efficiency-enhancing fibre solutions for industrial and building applications, and FFP2/FFP3 respirators for healthcare professionals and industry.











