Related Research Articles

Ivory Coast is a sub-Saharan nation in southern West Africa located at 8° N, 5° W. The country is approximately square in shape.

Guinea is a country on the coast of West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.
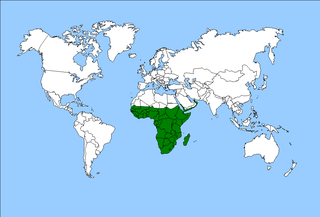
The Afrotropical realm is one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Sub-Saharan Africa, the southern Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region.

Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the coast of West Africa which lies along the Gulf of Guinea. It is a naturally moist tropical forest or savanna that stretches along the coast and borders the Sahel belt in the north.

Guinée forestière is a forested mountainous region in southeastern Guinea, extending into northeastern Sierra Leone. It is one of four natural regions into which Guinea is divided and covers 23% of the country. It includes all of the Nzérékoré administrative region, and shares a border with Sierra Leone and Liberia. Its rocky topology contains several mountain ranges and has an average elevation of 460m. Forested Guinea contains important areas of biological diversity such as the UNESCO World Heritage site Mount Nimba Strict Nature Reserve and biosphere reserve Ziama Massif. The Guéckédou prefectures also recorded the initial case of the 2014 Ebola outbreak in Meliandou, a rural village. The virus subsequently spread to urban areas and neighbouring countries Sierra Leone and Liberia.
In West Africa, the forest zone refers to the southern part of the region once covered by tropical rainforest. Sometimes this region is referred to as Guinea to distinguish it from the grassland-covered Sudan, drier Sahel and per-arid Sahara. It is made-up of vegetation having mainly trees and consist of the following local biotic communities: -mangrove swamp forest -tropical rain forest.

The individual member states of the African Union (AU) coordinate foreign policy through this agency, in addition to conducting their own international relations on a state-by-state basis. The AU represents the interests of African peoples at large in intergovernmental organizations (IGO's); for instance, it is a permanent observer at the United Nations' General Assembly.

The Western Guinean lowland forests ecoregion is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa. It is centered on Liberia, with portions in surrounding countries. It is the westernmost tropical rainforest in Africa, and has high levels of species endemism, with over 200 species of endemic plants.

The Guinean forests of West Africa is a biodiversity hotspot designated by Conservation International, which includes the belt of tropical moist broadleaf forests along the coast of West Africa, running from Sierra Leone and Guinea in the west to the Sanaga River of Cameroon in the east. The Dahomey Gap, a region of savanna and dry forest in Togo and Benin, divides the Guinean forests into the Upper Guinean forests and Lower Guinean forests.

The Upper Guinean forests is a tropical seasonal forest region of West Africa. The Upper Guinean forests extend from Guinea and Sierra Leone in the west through Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana to Togo in the east, and a few hundred kilometers inland from the Atlantic coast. A few enclaves of montane forest lie further inland in the mountains of central Guinea and central Togo and Benin.

The Guinean forest-savanna, also known as the Guinean forest-savanna transition, is a distinctive ecological region located in West Africa. It stretches across several countries including Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, and Cameroon. This region is characterized by a unique blend of forested areas and savannas, creating a diverse and dynamic landscape.

Rivières du Sud was a French colonial division in West Africa, roughly corresponding to modern coastal sections of Guinea. While the designation was used from the 18th to 20th century, the administrative division only existed from 1882-1891.

The Guinea Highlands is a densely forested mountainous plateau extending from central Guinea through northern Sierra Leone and Liberia to western Ivory Coast. The highlands include a number of mountains, ranges and plateaus, including the Fouta Djallon highlands in central Guinea, the Loma Mountains in Sierra Leone, the Simandou and Kourandou massifs in southeastern Guinea, the Nimba Range at the border of Guinea, Liberia, and Ivory Coast, and the Monts du Toura in western Ivory Coast.
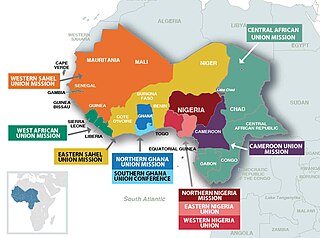
The West-Central Africa Division (WAD) of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which coordinates the Church's operations in 22 African countries, which include Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo. Its headquarters is in Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire. Founded in 2003, the division membership as of June 30, 2021 was 889,196.

The Guinean montane forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa.

The Nimba Range forms part of the southern extent of the Guinea Highlands, adjacent to the Toura Mountains. The highest peak is Mount Nimba on the border of Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire and Guinea, at 1,752 m (5,748 ft), and at the intersection of the Nimba and Toura Mountains. "Mount Nimba" may refer either to Mount Richard-Molard or to the entire range. Other peaks include Grand Rochers at 1,694 m (5,558 ft), Mont Sempéré at 1,682 m (5,518 ft), Mont Piérré Richaud at 1,670 m (5,480 ft), Mont Tô at 1,675 m (5,495 ft), and Mont LeClerc 1,577 m (5,174 ft), all of them are located in Guinea. Mount Nimba Strict Nature Reserve of Guinea and Côte d'Ivoire covers significant portions of the Nimba Range.
Maritime Guinea, also known as Lower Guinea, is one of the four natural regions of Guinea. It is located in the west of the country, between the Atlantic Ocean and the Fouta Djallon plateau. Conakry, Guinea's capital and largest city, is located in the region.
The Guineo-Congolian region is a biogeographical region in Africa straddling the Equator and stretching from the Atlantic Ocean through the Congo Basin to the Congo / Nile divide in Rwanda and Burundi. Formerly, this region was largely covered in rain forest, on both well-drained sites and in swamp forests, but little undisturbed primary forest now remains, having been replaced in many areas by savanna and secondary-growth forest.
References
- ↑ "Guinean Forests of West Africa." Conservation International. Accessed November 12, 2012.
- ↑ "Upper Guinea rivers and streams" WWF. Accessed November 12, 2012
- ↑ "Upper Guinea forests" Birdlife International. Accessed November 12, 2012.